drag
... average body density. Prediction equations then allow for estimation of %fat and %lean body mass. ...
... average body density. Prediction equations then allow for estimation of %fat and %lean body mass. ...
Tissue Fluid and Lymph
... acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen. • The fluid then returns to the blood in the capillaries taking any waste products from the cells with it e.g. CO2 and Urea ...
... acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen. • The fluid then returns to the blood in the capillaries taking any waste products from the cells with it e.g. CO2 and Urea ...
Resume - Deep Space Systems
... radiators, vehicle performance under failure conditions and vehicle ascent performance. - Responsible for coordinating Paragon’s contract with Lockheed Martin to provide thermal analysis under Lockheed Martin’s direction. Responsibilities included managing Paragon thermal analysis team, writing cont ...
... radiators, vehicle performance under failure conditions and vehicle ascent performance. - Responsible for coordinating Paragon’s contract with Lockheed Martin to provide thermal analysis under Lockheed Martin’s direction. Responsibilities included managing Paragon thermal analysis team, writing cont ...
How Airplanes Fly: Lift and Circulation
... K-J hypothesis works for θ less than 8 to 20 degrees depending on airfoil shape; at higher angles boundary layer separation on the upper surface causes a stall. [9] On December 17, 1903, the Wright brothers achieved the first successful powered flight. They did not use the lift theorem, but took an ...
... K-J hypothesis works for θ less than 8 to 20 degrees depending on airfoil shape; at higher angles boundary layer separation on the upper surface causes a stall. [9] On December 17, 1903, the Wright brothers achieved the first successful powered flight. They did not use the lift theorem, but took an ...
Small-size permanent magnet system for contactless
... Introduction Local velocity or even volumetric flow rate measurements of liquid metals is still an unsolved problem. The commercial classical measurement techniques (fly-wheel, Pitot tube, hot wire probes, etc.) require direct contact with the fluid and cannot be used for chemical aggressive and hig ...
... Introduction Local velocity or even volumetric flow rate measurements of liquid metals is still an unsolved problem. The commercial classical measurement techniques (fly-wheel, Pitot tube, hot wire probes, etc.) require direct contact with the fluid and cannot be used for chemical aggressive and hig ...
Wilson-Ch
... An object’s density will tell you whether it will sink or float in a particular fluid. ...
... An object’s density will tell you whether it will sink or float in a particular fluid. ...
Evidence of the influence of plasma jets on a helium flow into open air
... The Reynolds number of the flow at the exit plane of the dielectric tube is defined as Re = V∅int /ν, where V is the mean helium flow velocity, ν is the helium kinematic viscosity, and Øint is the inner diameter of the dielectric. From left to right, the Reynolds number increases from 150 (2 L/min f ...
... The Reynolds number of the flow at the exit plane of the dielectric tube is defined as Re = V∅int /ν, where V is the mean helium flow velocity, ν is the helium kinematic viscosity, and Øint is the inner diameter of the dielectric. From left to right, the Reynolds number increases from 150 (2 L/min f ...
10 - PSU MNE
... When in service, materials may be subjected to loads of various intensities, types and duration. The response of the material to these applied loads is termed the mechanical behavior of the material, and it is one of the most important factors to be considered for materials design. The most importan ...
... When in service, materials may be subjected to loads of various intensities, types and duration. The response of the material to these applied loads is termed the mechanical behavior of the material, and it is one of the most important factors to be considered for materials design. The most importan ...
chapter 8 ceramic/metal nanocomposites
... silicone nitride ceramic can enhance its fracture strength not only at Troom but also at high T up to 1500C. ...
... silicone nitride ceramic can enhance its fracture strength not only at Troom but also at high T up to 1500C. ...
Three Types of Heat Transfer
... spread apart. As a result, the particles of the heated fluid occupy more space. The fluid’s density decreases. When the fluid cools, the density increases because the particles slow down and move closer together. ...
... spread apart. As a result, the particles of the heated fluid occupy more space. The fluid’s density decreases. When the fluid cools, the density increases because the particles slow down and move closer together. ...
Problem Set 1: Stresses in the Earth
... your final solution, when appropriate. Include this page as the cover, show all of your work, and list all who helped with this set, including your instructor. An answer with incorrect or absent units will be considered wrong! ...
... your final solution, when appropriate. Include this page as the cover, show all of your work, and list all who helped with this set, including your instructor. An answer with incorrect or absent units will be considered wrong! ...
Ch 4 Electrical and optical properties
... radiowave and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The transmission and absorption of radiation by the polymer dielectric are determined by the quantities e, and e". Even higher frequencies bring us into the infrared and visible parts of the spectrum, that is, to optical phenomena. In ...
... radiowave and microwave regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. The transmission and absorption of radiation by the polymer dielectric are determined by the quantities e, and e". Even higher frequencies bring us into the infrared and visible parts of the spectrum, that is, to optical phenomena. In ...
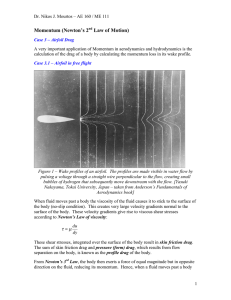
Momentum (Newton`s 2nd Law of Motion)
... Viscous effects along the wind tunnel walls are neglected What else is going on: One flow stream Non-uniform velocity profile downstream Flow speed changes from streamline to streamline Flow cross-sectional area remains constant: A1 = A2 Since the airfoil is inside a wind tunnel the top an ...
... Viscous effects along the wind tunnel walls are neglected What else is going on: One flow stream Non-uniform velocity profile downstream Flow speed changes from streamline to streamline Flow cross-sectional area remains constant: A1 = A2 Since the airfoil is inside a wind tunnel the top an ...
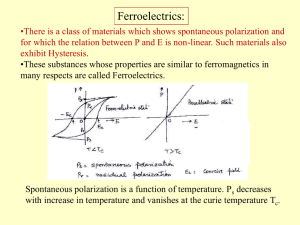
Dielectric loss
... There is a magnetic analog where ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
... There is a magnetic analog where ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
Huang2000.pdf
... with time, and we can not obtain the trajectory of a ball from this dynamical system. The curved flight path is caused by the complex interaction between the ball and the fluid. Another classic problem about interaction between an object and a fluid is the oscillation of a falling paper. As yet, the ...
... with time, and we can not obtain the trajectory of a ball from this dynamical system. The curved flight path is caused by the complex interaction between the ball and the fluid. Another classic problem about interaction between an object and a fluid is the oscillation of a falling paper. As yet, the ...
fluid transport mechanisms in microfluidic devices
... UV laser beam and tracked by fluorescence imaging, see Fig. 2, (Paul et al., 1998). In contrast to standard methods injecting dye, this visualization technique allows definition of narrow, fluorescent regions at virtually any location along the channel. Specifically, this allows for a precise defini ...
... UV laser beam and tracked by fluorescence imaging, see Fig. 2, (Paul et al., 1998). In contrast to standard methods injecting dye, this visualization technique allows definition of narrow, fluorescent regions at virtually any location along the channel. Specifically, this allows for a precise defini ...
Lesson 1.1 Mechanisms - Key Terms Term Definition
... A support that only prevents a beam from translating in one direction. ...
... A support that only prevents a beam from translating in one direction. ...