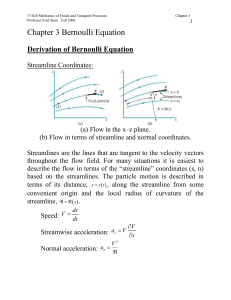
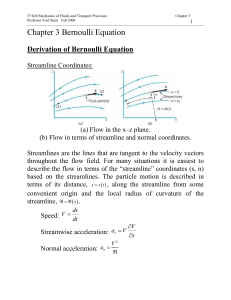
NOTES ON LESSON ENGINEERING PHYSICS
... Classical free electron theory. Quantum free electron theory Band theory Drawbacks of Classical Free Electron Theory: Contradiction occurs between classical and Quantum free electron theories on the energy absorption of free electrons. Wiedemann - Franz law (Lorentz Number) The ratio of thermal cond ...
... Classical free electron theory. Quantum free electron theory Band theory Drawbacks of Classical Free Electron Theory: Contradiction occurs between classical and Quantum free electron theories on the energy absorption of free electrons. Wiedemann - Franz law (Lorentz Number) The ratio of thermal cond ...
Friction and pressure
... • Friction acts on materials that are in contact with one another • Friction is caused by irregularities in the two surfaces • meter stick demo ...
... • Friction acts on materials that are in contact with one another • Friction is caused by irregularities in the two surfaces • meter stick demo ...
Physics 6B Hydrodynamics
... Example 3: A medical technician is trying to determine what percentage of a patient’s artery is blocked by plaque. To do this, she measures the blood pressure just before the region of blockage and finds that it is 12 kPa, while in the region of blockage it is 11.5 kPa. Furthermore, she knows that ...
... Example 3: A medical technician is trying to determine what percentage of a patient’s artery is blocked by plaque. To do this, she measures the blood pressure just before the region of blockage and finds that it is 12 kPa, while in the region of blockage it is 11.5 kPa. Furthermore, she knows that ...
11.2 Physics 6B Fluids - Hydrodynamics
... Example 3: A medical technician is trying to determine what percentage of a patient’s artery is blocked by plaque. To do this, she measures the blood pressure just before the region of blockage and finds that it is 12 kPa, while in the region of blockage it is 11.5 kPa. Furthermore, she knows that ...
... Example 3: A medical technician is trying to determine what percentage of a patient’s artery is blocked by plaque. To do this, she measures the blood pressure just before the region of blockage and finds that it is 12 kPa, while in the region of blockage it is 11.5 kPa. Furthermore, she knows that ...
Chapter 15 - College of Engineering WordPress
... Adapted from Fig. 15.3, Callister & Rethwisch 8e. (Fig. 15.3 is from T.S. Carswell and J.K. Nason, 'Effect of Environmental Conditions on the Mechanical Properties of Organic Plastics", Symposium on Plastics, ...
... Adapted from Fig. 15.3, Callister & Rethwisch 8e. (Fig. 15.3 is from T.S. Carswell and J.K. Nason, 'Effect of Environmental Conditions on the Mechanical Properties of Organic Plastics", Symposium on Plastics, ...
Chapter 5 Pressure Variation in Flowing Fluids
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
... For such devices the flowrate of liquid over the top of the weir plate is dependent on the weir height, Pw, the width of the channel, b, and the head, H, of the water above the top of the weir. Between points (1) and (2) the pressure and gravitational fields cause the fluid to accelerate from veloci ...
American Journal of Physics, Vol. 71, Nº 1, 46-48 (2003).
... Three different methods have been described to solve the profile of velocities of an incompressible fluid moving in a permanent laminar regime inside a hollow tube. In one approach we have made use of the Navier-Stokes equation to solve the velocity profile of the fluid inside the hollow tube. We ha ...
... Three different methods have been described to solve the profile of velocities of an incompressible fluid moving in a permanent laminar regime inside a hollow tube. In one approach we have made use of the Navier-Stokes equation to solve the velocity profile of the fluid inside the hollow tube. We ha ...
lecture 4 linear momentum principle and general equation of
... As before, we can change order of time differentiation and integration. Then, after insertion of the expressions for the forces, we get ...
... As before, we can change order of time differentiation and integration. Then, after insertion of the expressions for the forces, we get ...
SUMMARY
... following the reactions initiation. The initial concentration of analyte is then determined using the integral form of the reaction’s rate law. Alternatively, the time required to effect a given change in concentration may be measured. In a differential kinetic method the rate of the reaction is mea ...
... following the reactions initiation. The initial concentration of analyte is then determined using the integral form of the reaction’s rate law. Alternatively, the time required to effect a given change in concentration may be measured. In a differential kinetic method the rate of the reaction is mea ...
Statistics --
... As we found out in Chapter 5, even though the Lagrangian framework is the most direct way to apply Newton’s laws, it is usually computationally cumbersome in most circumstances as a method of describing the overall flow field in a given domain. An alternative approach is to utilize the Eulerian fram ...
... As we found out in Chapter 5, even though the Lagrangian framework is the most direct way to apply Newton’s laws, it is usually computationally cumbersome in most circumstances as a method of describing the overall flow field in a given domain. An alternative approach is to utilize the Eulerian fram ...
CartesianTensors.pdf
... Although it is known that all matter at the microscopic scale is particulate and hence discontinuous, the size scale of the discontinuities is much smaller than the size scale at which much of the work in mechanics in engineering and science takes place. Continuum mechanics is a description of the m ...
... Although it is known that all matter at the microscopic scale is particulate and hence discontinuous, the size scale of the discontinuities is much smaller than the size scale at which much of the work in mechanics in engineering and science takes place. Continuum mechanics is a description of the m ...
Double-Chamber Plethysmographs Respiratory Systems Respiration
... with aerosol challenge possibility • Aerosol challenge • Applications: – Toxicology – Environmental studies – Long term drug effects This plethysmograph box has been specially developed for the investigation of bronchospas-molytically active substances on the conscious animal. The awake animal is pl ...
... with aerosol challenge possibility • Aerosol challenge • Applications: – Toxicology – Environmental studies – Long term drug effects This plethysmograph box has been specially developed for the investigation of bronchospas-molytically active substances on the conscious animal. The awake animal is pl ...
Fluid Motion (ppt)
... Examples 15.1 , 15.2 Calculating Pressure and Pascals Law Examples 15.3 , 15.4 Buoyancy Forces: Working Underwater + Tip of Iceberg Examples 15.5 Continuity Equation: Ausable Chasm Examples 15.6, 15.7 Bernoulli's Equation – Draining a Tank and Venturi Flow ...
... Examples 15.1 , 15.2 Calculating Pressure and Pascals Law Examples 15.3 , 15.4 Buoyancy Forces: Working Underwater + Tip of Iceberg Examples 15.5 Continuity Equation: Ausable Chasm Examples 15.6, 15.7 Bernoulli's Equation – Draining a Tank and Venturi Flow ...
Matter powerpoint
... matter. There are three familiar states of matter— solid, liquid, and gas. Plasma, the fourth state, occurs only at extremely high temperatures and is found in stars, lightning, and neon lights ...
... matter. There are three familiar states of matter— solid, liquid, and gas. Plasma, the fourth state, occurs only at extremely high temperatures and is found in stars, lightning, and neon lights ...
Strength of materials
... uniaxial strain in the range of stress in which Hooke's Law holds. In solid mechanics, the slope of the stress-strain curve at any point is called the tangent modulus. The tangent modulus of the initial, linear portion of a stress-strain curve is called Young's modulus, also known as the tensile mod ...
... uniaxial strain in the range of stress in which Hooke's Law holds. In solid mechanics, the slope of the stress-strain curve at any point is called the tangent modulus. The tangent modulus of the initial, linear portion of a stress-strain curve is called Young's modulus, also known as the tensile mod ...
Materials
... After setting, the concrete and the steel work together as if they are only one material. They react the temperature changes similarly (their thermal expansion coefficients are close to each other.) Otherwise, the use of reinforced concrete structures will be very limited. ...
... After setting, the concrete and the steel work together as if they are only one material. They react the temperature changes similarly (their thermal expansion coefficients are close to each other.) Otherwise, the use of reinforced concrete structures will be very limited. ...
Slide 1
... Because the shock wave lies close to the surface at high Mach numbers, there is an interaction between the shock wave and the boundary layer on the wedge surface. In order to illustrate this shock wave-boundary layer interaction, consider the flow of air over a wedge having a half angle of 5 degree ...
... Because the shock wave lies close to the surface at high Mach numbers, there is an interaction between the shock wave and the boundary layer on the wedge surface. In order to illustrate this shock wave-boundary layer interaction, consider the flow of air over a wedge having a half angle of 5 degree ...
Document
... Newton’s second law. • Each of these laws is expressed using a Lagrangian description of motion; they apply to a specified mass of the fluid. They are stated as follows: Mass: The mass of a system remains constant. Energy: The rate of heat transfer to a system minus the work rate done by a system eq ...
... Newton’s second law. • Each of these laws is expressed using a Lagrangian description of motion; they apply to a specified mass of the fluid. They are stated as follows: Mass: The mass of a system remains constant. Energy: The rate of heat transfer to a system minus the work rate done by a system eq ...
Tissue Fluid and Lymph
... acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen. • The fluid then returns to the blood in the capillaries taking any waste products from the cells with it e.g. CO2 and Urea ...
... acids, fatty acids, salts and oxygen. • The fluid then returns to the blood in the capillaries taking any waste products from the cells with it e.g. CO2 and Urea ...