Echocardiography studies
... view, with the sample volume positioned just below to the aortic valve. Myocardial Performance Index (MPI) is the ratio of total time spent in isovolumic activity (isovolumic contraction time and isovolumic relaxation time) to the ejection time (ET). These Doppler time intervals were measured from t ...
... view, with the sample volume positioned just below to the aortic valve. Myocardial Performance Index (MPI) is the ratio of total time spent in isovolumic activity (isovolumic contraction time and isovolumic relaxation time) to the ejection time (ET). These Doppler time intervals were measured from t ...
Packed Bed Reactors - EngineeringDuniya.com
... • Consists of a tube, usually vertical, packed with catalyst particles. • Medium can be fed either at the top or bottom of the column • Medium forms a continuous liquid phase between the particles. • Damage due to particle attrition is minimal • Used for production of aspartate and fumarate, convers ...
... • Consists of a tube, usually vertical, packed with catalyst particles. • Medium can be fed either at the top or bottom of the column • Medium forms a continuous liquid phase between the particles. • Damage due to particle attrition is minimal • Used for production of aspartate and fumarate, convers ...
BASICS OF DIELECTRIC MATERIALS
... There is a magnetic analog where ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
... There is a magnetic analog where ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
Introduction
... industry. Interest in recent years has focused on advanced ceramics that, with minor exception , have been developed with in that last 30 years or so. Advanced ceramics include ceramics for electrical, magnetic, electronic, Thermal and optical applications, and ceramics for structural applications a ...
... industry. Interest in recent years has focused on advanced ceramics that, with minor exception , have been developed with in that last 30 years or so. Advanced ceramics include ceramics for electrical, magnetic, electronic, Thermal and optical applications, and ceramics for structural applications a ...
AP PHYSICS 2 E01
... 3. TSW create and use free-body diagrams to analyze physical situations to solve problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively, and can explain forces based on internal structure. [LO 3.B.2.1, SP 1.1, SP 1.4, SP 2.2] 4. TSW predict the motion of an object subject to forces exerted by several ...
... 3. TSW create and use free-body diagrams to analyze physical situations to solve problems with motion qualitatively and quantitatively, and can explain forces based on internal structure. [LO 3.B.2.1, SP 1.1, SP 1.4, SP 2.2] 4. TSW predict the motion of an object subject to forces exerted by several ...
151-0902-00 Micro- and Nano-Particle (MNP) Technology FS09
... b) What would be the edge length of a cube of the same material falling in the same fluid at the same steady state settling velocity? ...
... b) What would be the edge length of a cube of the same material falling in the same fluid at the same steady state settling velocity? ...
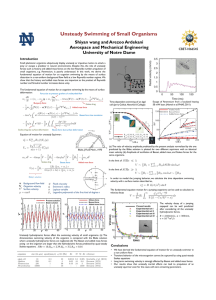
Unsteady Swimming of Small Organisms
... Small planktonic organisms ubiquitously display unsteady or impulsive motion to attack a prey or escape a predator in natural environments. Despite this, the role of unsteady forces such as history and added mass forces on the low Reynolds number propulsion of small organisms, e.g. Paramecium, is po ...
... Small planktonic organisms ubiquitously display unsteady or impulsive motion to attack a prey or escape a predator in natural environments. Despite this, the role of unsteady forces such as history and added mass forces on the low Reynolds number propulsion of small organisms, e.g. Paramecium, is po ...
THE EQUATIONS OF FLUID DYNAMICS—DRAFT
... DYNAMICS—DRAFT The equations of fluid mechanics are derived from first principles here, in order to point out clearly all the underlying assumptions. The equations can take various different forms and in numerical work we will find that it often makes a difference what form we use for a particular p ...
... DYNAMICS—DRAFT The equations of fluid mechanics are derived from first principles here, in order to point out clearly all the underlying assumptions. The equations can take various different forms and in numerical work we will find that it often makes a difference what form we use for a particular p ...
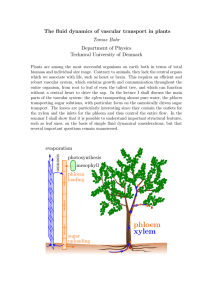
phloem xylem
... biomass and individual size range. Contrary to animals, they lack the central organs which we associate with life, such as heart or brain. This requires an efficient and robust vascular system, which sustains growth and communication throughout the entire organism, from root to leaf of even the tall ...
... biomass and individual size range. Contrary to animals, they lack the central organs which we associate with life, such as heart or brain. This requires an efficient and robust vascular system, which sustains growth and communication throughout the entire organism, from root to leaf of even the tall ...
Glossary
... Elastic constant: The factors of proportionality that relate elastic displacement of a material to applied forces. See also modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, bulk modulus of elasticity, and Poisson´s ratio. Elastic deformation: A change in dimention directly proportional to and in phase with an ...
... Elastic constant: The factors of proportionality that relate elastic displacement of a material to applied forces. See also modulus of elasticity, shear modulus, bulk modulus of elasticity, and Poisson´s ratio. Elastic deformation: A change in dimention directly proportional to and in phase with an ...
Progress Review
... To test the air flow distribution across the surface of the core, the pressure distribution should be modelled. Using data from the spreadsheet will show the required cooling and heat transfer; the simulation will not show this as typical data can be given from the spreadsheet. The simulation will o ...
... To test the air flow distribution across the surface of the core, the pressure distribution should be modelled. Using data from the spreadsheet will show the required cooling and heat transfer; the simulation will not show this as typical data can be given from the spreadsheet. The simulation will o ...
Dimensional Analysis, hydraulic similitude and model
... It is known that when a steady wind blows past this type of bluff body, vortices may develop on the downwind side that are shed in a regular fashion at some definite frequency. Since these vortices can create harmful periodic forces acting on the structure, it is important to determine the shedding ...
... It is known that when a steady wind blows past this type of bluff body, vortices may develop on the downwind side that are shed in a regular fashion at some definite frequency. Since these vortices can create harmful periodic forces acting on the structure, it is important to determine the shedding ...
The Conversion of Fluid Flow into Laminar Flow Device
... enclosure with an inlet port, and out port, a discharge laminar flow device body having a discharge outlet passage there through, and a means for reducing turbulence within the enclosure by increasing the random and chaotic interaction of the fluid molecules to create a more uniform velocity profile ...
... enclosure with an inlet port, and out port, a discharge laminar flow device body having a discharge outlet passage there through, and a means for reducing turbulence within the enclosure by increasing the random and chaotic interaction of the fluid molecules to create a more uniform velocity profile ...
09_Solids and Fluids
... 9.3 Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle A body immersed wholly or partially in a fluid experiences a buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of the volume of fluid that is displaced: ...
... 9.3 Buoyancy and Archimedes’ Principle A body immersed wholly or partially in a fluid experiences a buoyant force equal in magnitude to the weight of the volume of fluid that is displaced: ...
Buoyancy
... during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As fluid particles of definite mass are selected, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fluid particles is quite dif ...
... during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As fluid particles of definite mass are selected, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fluid particles is quite dif ...
iii. simulation method
... (MD) simulation, based on the statistical mechanics of nonequilibrium liquids [1], is an effective way to describe the details of a flow at the nano scale. At the same time, MD simulations also calculate physical properties of nanofluids by solving the equations of molecular motion. The role of repl ...
... (MD) simulation, based on the statistical mechanics of nonequilibrium liquids [1], is an effective way to describe the details of a flow at the nano scale. At the same time, MD simulations also calculate physical properties of nanofluids by solving the equations of molecular motion. The role of repl ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-COMSOL2011.pdf
... magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) approach was validated by comparison with the existing solution for the Hartmann problem while the back step flow was validated by comparison with previously obtained solutions. The implementation of the magnetic and electric field has significant impact on the effective Re ...
... magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) approach was validated by comparison with the existing solution for the Hartmann problem while the back step flow was validated by comparison with previously obtained solutions. The implementation of the magnetic and electric field has significant impact on the effective Re ...
Xie-EGM-RPI-COMSOL2011.doc
... magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) approach was validated by comparison with the existing solution for the Hartmann problem while the back step flow was validated by comparison with previously obtained solutions. The implementation of the magnetic and electric field has significant impact on the effective Re ...
... magnetohydrodynamic (MHD) approach was validated by comparison with the existing solution for the Hartmann problem while the back step flow was validated by comparison with previously obtained solutions. The implementation of the magnetic and electric field has significant impact on the effective Re ...