ConcepTest Question
... c. Values of fluid velocity depend on the molecular concentration in that part of the fluid. ...
... c. Values of fluid velocity depend on the molecular concentration in that part of the fluid. ...
MAE 3130: Fluid Mechanics Lecture 4: Bernoulli Equation
... Possible Forces: Body Forces and Surface Forces Surface Forces: Pressure and Shear Stresses Body Forces: Gravity, Magnetic Fields, etc. Consider Inviscid Flow: If a flow is inviscid, it has zero viscosity, and likewise no thermal conductivity or heat transfer. In practice, there are no inviscid flui ...
... Possible Forces: Body Forces and Surface Forces Surface Forces: Pressure and Shear Stresses Body Forces: Gravity, Magnetic Fields, etc. Consider Inviscid Flow: If a flow is inviscid, it has zero viscosity, and likewise no thermal conductivity or heat transfer. In practice, there are no inviscid flui ...
printable worksheet - Technology Student
... in an electrical circuit. Resistors are found in almost every electronic circuit. They are used to protect sensitive components, such as transistors and LEDs (see diagram below). FIXED RESISTOR ...
... in an electrical circuit. Resistors are found in almost every electronic circuit. They are used to protect sensitive components, such as transistors and LEDs (see diagram below). FIXED RESISTOR ...
SATIR INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL
... need is to be protected, safe and respected. Physically this stance would be represented by a person pointing a finger with a stretched arm leaning forward on one front leg. Front leg is one and a half shoulders’ lengths apart and slightly bent. Back hand is on a waist. The feeling in this position ...
... need is to be protected, safe and respected. Physically this stance would be represented by a person pointing a finger with a stretched arm leaning forward on one front leg. Front leg is one and a half shoulders’ lengths apart and slightly bent. Back hand is on a waist. The feeling in this position ...
Chapter 12
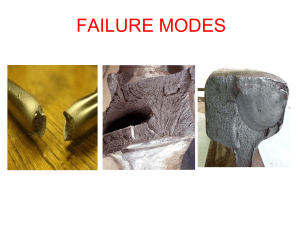
... The elastic limit is the maximum stress that can be applied to the substance before it becomes permanently deformed When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed ...
... The elastic limit is the maximum stress that can be applied to the substance before it becomes permanently deformed When the stress exceeds the elastic limit, the substance will be permanently deformed ...
Notes #11
... and a sink is associated with a drag. This formula works for both two and three dimension flows. ...
... and a sink is associated with a drag. This formula works for both two and three dimension flows. ...
MAGNETIC GARNETS, YxGd3-xFe5O12 TUNABLE MAGNETIC
... • Many useful materials, such as ceramics, are most often produced from high temperature reactions (500-3000°C) between solid reagents which often take many days due to the slow nature of solid-solid diffusion. • Rapid SS new method enables high quality refractory materials to be synthesized in seco ...
... • Many useful materials, such as ceramics, are most often produced from high temperature reactions (500-3000°C) between solid reagents which often take many days due to the slow nature of solid-solid diffusion. • Rapid SS new method enables high quality refractory materials to be synthesized in seco ...
Materials Science and Engineering
... "Nanomaterials," is an interdisciplinary introduction to processing, structure, and properties of materials at the nanometer length scale. The course will cover recent breakthroughs and assess the impact of this burgeoning field. Specific nanofabrication topics include epitaxy, beam lithographies, s ...
... "Nanomaterials," is an interdisciplinary introduction to processing, structure, and properties of materials at the nanometer length scale. The course will cover recent breakthroughs and assess the impact of this burgeoning field. Specific nanofabrication topics include epitaxy, beam lithographies, s ...
Lecture 15-16
... The conservation of energy still holds for a real fluid, but the energy flux must include ...
... The conservation of energy still holds for a real fluid, but the energy flux must include ...
Viscous normal stress on a slip surface
... section of the channel generated by the transverse electric field and that of a twodimensional cavity flow. A two-dimensional cavity flow is driven by the tangential movement of the top surface and/or the bottom surface. This is in essence a flow driven by prescribed “slip-velocities” of the boundi ...
... section of the channel generated by the transverse electric field and that of a twodimensional cavity flow. A two-dimensional cavity flow is driven by the tangential movement of the top surface and/or the bottom surface. This is in essence a flow driven by prescribed “slip-velocities” of the boundi ...
Chapter 9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... Water pressure increases with depth because the water at a given depth has to support the weight of the water above it. Imagine an object suspended in a fluid. There is an imaginary column that is the same cross-sectional area of the object. There is water trapped below pushing up on the object. The ...
... Water pressure increases with depth because the water at a given depth has to support the weight of the water above it. Imagine an object suspended in a fluid. There is an imaginary column that is the same cross-sectional area of the object. There is water trapped below pushing up on the object. The ...
Convection in the Mantle
... again and begins to rise. This flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called a convection current. The heating and cooling of the fluid, changes in the fluid’s density, and the force of gravity combine to set convection currents in motion. Convection currents continue as long as heat is added to ...
... again and begins to rise. This flow that transfers heat within a fluid is called a convection current. The heating and cooling of the fluid, changes in the fluid’s density, and the force of gravity combine to set convection currents in motion. Convection currents continue as long as heat is added to ...
Lect15
... filaments contained within the closed curve. This can be seen by re-writing the line integral into a surface integral using Stokes theorem... ...
... filaments contained within the closed curve. This can be seen by re-writing the line integral into a surface integral using Stokes theorem... ...
Ellen Cerreta Trustee-Elect (2015-2018)
... Abstract: Under conditions of static and dynamic loading to high pressures or stresses, it can be critical to quantify the strength of a material and it is well understood that material microstructure controls properties like strength. It is also expected that microstructures, particularly for many ...
... Abstract: Under conditions of static and dynamic loading to high pressures or stresses, it can be critical to quantify the strength of a material and it is well understood that material microstructure controls properties like strength. It is also expected that microstructures, particularly for many ...
Chapter 7 File
... Archimedes’ Principle is very useful in determining the volume of an object and therefore its density. Eg: crown of king – made of pure or not made of pure gold. Example: A queen’s gold crown has mass 1.30kg. However when it is weighed while it is completely immersed in water, its effective mass is ...
... Archimedes’ Principle is very useful in determining the volume of an object and therefore its density. Eg: crown of king – made of pure or not made of pure gold. Example: A queen’s gold crown has mass 1.30kg. However when it is weighed while it is completely immersed in water, its effective mass is ...