Membrane Proteins Integral membrane proteins often contain
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
... Integral membrane proteins often contain helical segments of appropriate length to span the lipid bilayer. In a protein that has a single segment that spans the membrane, the helix usually only contains hydrophobic residues and is called a single-span membrane protein. In transmembrane proteins with ...
Plasmodium falciparum causes malaria in humans
... (Remember that ‘Ctrl-PrintScreen’ will capture the image on a screen to the computer’s clipboard which can then be pasted into an image editing program like Photoshop to be manipulated for use in your homework. Alternatively the alignments and trees can be printed out separately.) ...
... (Remember that ‘Ctrl-PrintScreen’ will capture the image on a screen to the computer’s clipboard which can then be pasted into an image editing program like Photoshop to be manipulated for use in your homework. Alternatively the alignments and trees can be printed out separately.) ...
Bioinformatics for biomedicine Protein domains and 3D structure
... • Good: 2.0 Å or less • Bad: 3 Å or higher ...
... • Good: 2.0 Å or less • Bad: 3 Å or higher ...
Capturing denaturing proteins * Small Heat Shock Protein substrate
... sHSP chaperone action and interaction with substrates, therefore, has wide-ranging implications for understanding cellular stress and disease processes. We are studying the mechanism of sHSP substrate recognition by identifying specific crosslinking sites between sHSPs and denaturing substrates. sHS ...
... sHSP chaperone action and interaction with substrates, therefore, has wide-ranging implications for understanding cellular stress and disease processes. We are studying the mechanism of sHSP substrate recognition by identifying specific crosslinking sites between sHSPs and denaturing substrates. sHS ...
secstruct
... The peptide bond is formed as the cacboxyl group of an aa bind to the amino group of the adjacent aa. The primary structure of a protein is simply the linear arrangement, or sequence, of the amino acid residues that compose it ...
... The peptide bond is formed as the cacboxyl group of an aa bind to the amino group of the adjacent aa. The primary structure of a protein is simply the linear arrangement, or sequence, of the amino acid residues that compose it ...
Computational protein design
... • Most atomistic protein design efforts require a fixed back• bone. The calculation is performed under the assumption • that the target backbone is precisely the backbone that • will be achieved by the computed sequence. Fortunately, • alterations in the backbone do not necessarily lead to • large c ...
... • Most atomistic protein design efforts require a fixed back• bone. The calculation is performed under the assumption • that the target backbone is precisely the backbone that • will be achieved by the computed sequence. Fortunately, • alterations in the backbone do not necessarily lead to • large c ...
Biological Databases - University of Alberta
... • Classification of proteins based on domain structures • Each protein chopped into individual domains and assigned into homologous superfamilies. • Hierarchial domain classification of PDB entries. ...
... • Classification of proteins based on domain structures • Each protein chopped into individual domains and assigned into homologous superfamilies. • Hierarchial domain classification of PDB entries. ...
Homework 3 - Haixu Tang`s Homepage
... ----------------------------------- Mini Group Project # 2 ---------------------------------------Mini group project # 2 is sequential to the HW Section 1. 30 points Membrane proteins compromise a large fraction of eukaryotic proteins, and carry out many important protein functions as ion transport ...
... ----------------------------------- Mini Group Project # 2 ---------------------------------------Mini group project # 2 is sequential to the HW Section 1. 30 points Membrane proteins compromise a large fraction of eukaryotic proteins, and carry out many important protein functions as ion transport ...
No Slide Title
... • Hidden Markov model is a statistical model and has been mostly developed for speech recognition. • The most popular use of HMM in molecular biology is as a ‘probabilistic profile’ of a protein family, which is called a profile HMM. • Apart from this, HMMs are also used for multiple sequence alignm ...
... • Hidden Markov model is a statistical model and has been mostly developed for speech recognition. • The most popular use of HMM in molecular biology is as a ‘probabilistic profile’ of a protein family, which is called a profile HMM. • Apart from this, HMMs are also used for multiple sequence alignm ...
Proteins - Kaikoura High School
... • Are polymers • (note: often confusion over peptides, proteins and polypeptides = all are amino acid chains, difference is length.) • Units are amino acids (made up from 64 nucleotide combinations) ...
... • Are polymers • (note: often confusion over peptides, proteins and polypeptides = all are amino acid chains, difference is length.) • Units are amino acids (made up from 64 nucleotide combinations) ...
Protein structure - LSU School of Medicine
... Proteins fold into the local minimum free energy structure defined by their primary sequence. ...
... Proteins fold into the local minimum free energy structure defined by their primary sequence. ...
Atomistic modeling of the structural components of the
... Blood-brain barrier, which is a barrage system between the brain and blood vessels, plays a key role in the "isolation" of the brain of unnecessary information, and reduce the "noise" in the interneuron communication. It is known that the barrier function of the BBB strictly depends on the initial s ...
... Blood-brain barrier, which is a barrage system between the brain and blood vessels, plays a key role in the "isolation" of the brain of unnecessary information, and reduce the "noise" in the interneuron communication. It is known that the barrier function of the BBB strictly depends on the initial s ...
Through the Looking Glass a New World of Proteins Enabled
... Recent advances in synthetic methods enable the routine synthesis of protein enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image ...
... Recent advances in synthetic methods enable the routine synthesis of protein enantiomorphs, unnatural protein molecules made up entirely of D-amino acids. These D-proteins have a tertiary structure that is the mirror image of the backbone fold of their counterparts found in nature. Such mirror image ...
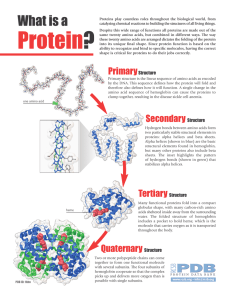
Protein?
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
... catalyzing chemical reactions to building the structures of all living things. Despite this wide range of functions all proteins are made out of the same twenty amino acids, but combined in different ways. The way these twenty amino acids are arranged dictates the folding of the protein into its uni ...
PowerPoint 0.8MB - The Biomolecular Modeling & Computational
... – low resolution (fold level) – should fit many sequences ...
... – low resolution (fold level) – should fit many sequences ...
1. Amino acids. Of all data abstractions in
... Here are five key assumptions, listed in decreasing importance, all of these examples would be full mark answers. 1. S. pombe TCTP and MSS4 are homologues, even if they don't have significant sequence similarity, since they have similar structures. Insignificant sequence similarity seems to be the c ...
... Here are five key assumptions, listed in decreasing importance, all of these examples would be full mark answers. 1. S. pombe TCTP and MSS4 are homologues, even if they don't have significant sequence similarity, since they have similar structures. Insignificant sequence similarity seems to be the c ...
NMR experiment-driven modeling of biological macromolecules
... Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) is one of the more versatile experimental techniques that allow determining three-dimensional (3D) structures of biomacromolecules at atomic resolution, whether these are proteins, RNA, DNA, and their complexes. Knowledge of the 3D structure is vital for ...
... Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) is one of the more versatile experimental techniques that allow determining three-dimensional (3D) structures of biomacromolecules at atomic resolution, whether these are proteins, RNA, DNA, and their complexes. Knowledge of the 3D structure is vital for ...
Hoku`s Slides
... Several coupled DNA and protein libraries are constructed, randomizing 3 base pairs and 5 contacting amino acids for each NNNGGAGGTTTCTCTGTAAA TGANNNGGTTTCTCTGTAAA ...
... Several coupled DNA and protein libraries are constructed, randomizing 3 base pairs and 5 contacting amino acids for each NNNGGAGGTTTCTCTGTAAA TGANNNGGTTTCTCTGTAAA ...
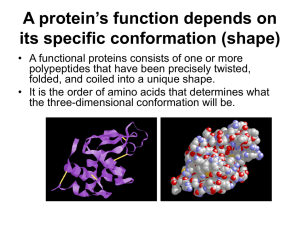
A protein’s function depends on its specific conformation
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
... bind to some other molecule. – For example, antibodies bind to particular foreign substances that fit their binding sites. – Enzyme recognize and bind to specific substrates, facilitating a chemical reaction. – Neurotransmitters pass signals from one cell to another by binding to receptor sites on p ...
Document
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
... Cryogenic protein storage and assessment of protein purity Flash freezing of protein for long term storage. Mass spectrometry and SDS-PAGE for determination of purity and molecular weight. Preparation of buffers for experiments in following weeks. ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.