CFTR – gene cloning and initial bioinformatic analysis Riordan et 12
... • R domain is one exon 69/241 residues are polar alternating +ve and –ve charge regions • Also most of the phosphorylation kinase sites • All family members secrete something: – Chloride (CFTR) ...
... • R domain is one exon 69/241 residues are polar alternating +ve and –ve charge regions • Also most of the phosphorylation kinase sites • All family members secrete something: – Chloride (CFTR) ...
Flexible Multi-scale Fitting of Atomic Structures into Low
... Evaluate a set of mutants and try to predict the ΔΔG for a single amino acid mutation - contact potentials parameterized from experimental data (experimental error ~ kt) They show that contact potentials are neither accurate nor transferable and claim that it is impossible to develop a set of transf ...
... Evaluate a set of mutants and try to predict the ΔΔG for a single amino acid mutation - contact potentials parameterized from experimental data (experimental error ~ kt) They show that contact potentials are neither accurate nor transferable and claim that it is impossible to develop a set of transf ...
Document
... • Make predictions of peptides in the presence of substrates using physics-based force-fields such as GROMACS • Analyse for similarity of structures (local and global) as well as common contact patterns between atoms in amino acids – the structural similarities and patterns give us the structural pa ...
... • Make predictions of peptides in the presence of substrates using physics-based force-fields such as GROMACS • Analyse for similarity of structures (local and global) as well as common contact patterns between atoms in amino acids – the structural similarities and patterns give us the structural pa ...
Examination in Gene Technology, TFKE38 2011-10-18
... instead you use the socalled TA cloning technique.. How does the TA cloning work? What are the requirements for the DNA polymerase used in this technique, how is the vector treated? (6p) c) For the transformation, you use two different controls, transformation and ligation control. What are the purp ...
... instead you use the socalled TA cloning technique.. How does the TA cloning work? What are the requirements for the DNA polymerase used in this technique, how is the vector treated? (6p) c) For the transformation, you use two different controls, transformation and ligation control. What are the purp ...
here - BioGeometry
... the simulation of that motion right now is not good enough,” he said. For example, he said, in building a mathematical simulation of protein motion, researchers must now largely ignore the smaller vibrations of the thousands of individual atoms in the protein, although they can prove important to un ...
... the simulation of that motion right now is not good enough,” he said. For example, he said, in building a mathematical simulation of protein motion, researchers must now largely ignore the smaller vibrations of the thousands of individual atoms in the protein, although they can prove important to un ...
BIO520 Final Exam 5/07 Jim Lund You may use any books, notes
... and reliable list of proteins known to bind ESR1? To start with, an IntAct search indicates that human ESR1 interacts with 14 proteins. What would you do to expand or refine this list of proteins to arrive at your final list? ...
... and reliable list of proteins known to bind ESR1? To start with, an IntAct search indicates that human ESR1 interacts with 14 proteins. What would you do to expand or refine this list of proteins to arrive at your final list? ...
Recombinant human BRD9 protein (Active)
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
... The application notes include recommended starting dilutions; optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. ...
PROTEIN STRUCTURE SIMILARITY CALCULATION AND VISUALIZATION
... Calculate pairwise similarity between two proteins implemented in PARALLEL (moduleA) Structure of 1QLQ ...
... Calculate pairwise similarity between two proteins implemented in PARALLEL (moduleA) Structure of 1QLQ ...
AS Biology - Everything Protein
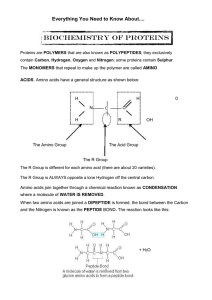
... The CONDENSATION reaction is said to be REVERSIBLE. The reverse reaction is known as HYDROLYSIS. Protein molecules have very complex and intricate structures that let them perform their specific roles. PRIMARY STRUCTURE is the AMINO ACID SEQUENCE; peptide bonds are present in this level of structur ...
... The CONDENSATION reaction is said to be REVERSIBLE. The reverse reaction is known as HYDROLYSIS. Protein molecules have very complex and intricate structures that let them perform their specific roles. PRIMARY STRUCTURE is the AMINO ACID SEQUENCE; peptide bonds are present in this level of structur ...
Research Interests
... Gram negative bacteria deploy various secretion systems for exporting proteins to eukaryotic hosts. We study the Type III secretion systems (T3SS) which are directly related to pathogenicity and essential mediators of the interactions between bacteria and eukaryotes . We have determined the first cr ...
... Gram negative bacteria deploy various secretion systems for exporting proteins to eukaryotic hosts. We study the Type III secretion systems (T3SS) which are directly related to pathogenicity and essential mediators of the interactions between bacteria and eukaryotes . We have determined the first cr ...
BB 450/500 Lecture 5 Highlights
... 1. Another type of fibrous protein is collagen, the most abundant protein in your body. It contains three intertwined helices comprised of abundant repeating units of glycine, proline, and hydroxylproline 2. Hydroxylation of proline is a post-translational modification (occurs after the protein is m ...
... 1. Another type of fibrous protein is collagen, the most abundant protein in your body. It contains three intertwined helices comprised of abundant repeating units of glycine, proline, and hydroxylproline 2. Hydroxylation of proline is a post-translational modification (occurs after the protein is m ...
Protein Structure
... classification of protein structures in the Brookhaven protein databank. Only NMR structures and crystal structures solved to resolution better than 3.0 angstroms are considered. • There are four major levels in this hierarchy: Class, Architecture, Topology (fold family) and Homologous superfamily. ...
... classification of protein structures in the Brookhaven protein databank. Only NMR structures and crystal structures solved to resolution better than 3.0 angstroms are considered. • There are four major levels in this hierarchy: Class, Architecture, Topology (fold family) and Homologous superfamily. ...
Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can
... Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can manufacture some amino acids (used as the building blocks of proteins) out of nitrogen. What name is given to this group of amino acids? ...
... Protein: How Cows and Carrots Become People 1. Your body can manufacture some amino acids (used as the building blocks of proteins) out of nitrogen. What name is given to this group of amino acids? ...
College 5
... 3. Non-covalent interactions. As a result of ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds, each type of protein has a particular three dimensional structure, which is determined by the order of the amino acids in the chain. ...
... 3. Non-covalent interactions. As a result of ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds, each type of protein has a particular three dimensional structure, which is determined by the order of the amino acids in the chain. ...
A Novel Scoring Function for Predicting the Conformation of Pairs of
... Many pairs of helices in transmembrane (TM) proteins are tightly packed. We present a scoring function and a computational methodology for predicting the tertiary fold of a pair of α-helices, such that its chances of being tightly packed are maximized. Since the number of TM protein structures solve ...
... Many pairs of helices in transmembrane (TM) proteins are tightly packed. We present a scoring function and a computational methodology for predicting the tertiary fold of a pair of α-helices, such that its chances of being tightly packed are maximized. Since the number of TM protein structures solve ...
Module 5
... (or motifs) common to homologous proteins. These motifs, usually of the order of 10-20 amino acids in length, usually correspond to key functional or structural elements, often domains, and are extremely useful in identifying such features in new uncharacterized proteins. There is a number of such s ...
... (or motifs) common to homologous proteins. These motifs, usually of the order of 10-20 amino acids in length, usually correspond to key functional or structural elements, often domains, and are extremely useful in identifying such features in new uncharacterized proteins. There is a number of such s ...
Representations of 3D Structures
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
... lengths/angles and standard information about atom-atom interactions such as minimum distance (i.e. Van der Waals radii) •With all this information you can generate a model of the structure. Important: NMR gives you a number of possible solutions (all almost identical, rmsd <1Å), This can range from ...
Atomic models of complexes - Cryo
... Atomic models of complexes 10 Å structure of HBV Fitting of FAB ...
... Atomic models of complexes 10 Å structure of HBV Fitting of FAB ...
Slide 1
... Highly insoluble regions represent positions for protein insertion into the membrane. ...
... Highly insoluble regions represent positions for protein insertion into the membrane. ...
Tools for BioInformatics - Computer Science
... Ab initio -- based on energy minimization fold recognition -- sequence -> secondary structure, then align secondary structures with corresponding secondary structures in related proteins, etc. statistical -- based on “hidden patterns”; similar patterns -> similar structure ...
... Ab initio -- based on energy minimization fold recognition -- sequence -> secondary structure, then align secondary structures with corresponding secondary structures in related proteins, etc. statistical -- based on “hidden patterns”; similar patterns -> similar structure ...
Computational Molecular Biology 2012
... b) How many of these substitutions are conservative ones according to the default substitution matrix (BLOSUM62) used in BLAST programs for proteins? 7) One of the 8 RNA fragments of the influenza A genome codes for a polymerase called PB1 of about 750 amino acids. It has been recently determined th ...
... b) How many of these substitutions are conservative ones according to the default substitution matrix (BLOSUM62) used in BLAST programs for proteins? 7) One of the 8 RNA fragments of the influenza A genome codes for a polymerase called PB1 of about 750 amino acids. It has been recently determined th ...
Homology modeling

Homology modeling, also known as comparative modeling of protein, refers to constructing an atomic-resolution model of the ""target"" protein from its amino acid sequence and an experimental three-dimensional structure of a related homologous protein (the ""template""). Homology modeling relies on the identification of one or more known protein structures likely to resemble the structure of the query sequence, and on the production of an alignment that maps residues in the query sequence to residues in the template sequence. It has been shown that protein structures are more conserved than protein sequences amongst homologues, but sequences falling below a 20% sequence identity can have very different structure.Evolutionarily related proteins have similar sequences and naturally occurring homologous proteins have similar protein structure.It has been shown that three-dimensional protein structure is evolutionarily more conserved than would be expected on the basis of sequence conservation alone.The sequence alignment and template structure are then used to produce a structural model of the target. Because protein structures are more conserved than DNA sequences, detectable levels of sequence similarity usually imply significant structural similarity.The quality of the homology model is dependent on the quality of the sequence alignment and template structure. The approach can be complicated by the presence of alignment gaps (commonly called indels) that indicate a structural region present in the target but not in the template, and by structure gaps in the template that arise from poor resolution in the experimental procedure (usually X-ray crystallography) used to solve the structure. Model quality declines with decreasing sequence identity; a typical model has ~1–2 Å root mean square deviation between the matched Cα atoms at 70% sequence identity but only 2–4 Å agreement at 25% sequence identity. However, the errors are significantly higher in the loop regions, where the amino acid sequences of the target and template proteins may be completely different.Regions of the model that were constructed without a template, usually by loop modeling, are generally much less accurate than the rest of the model. Errors in side chain packing and position also increase with decreasing identity, and variations in these packing configurations have been suggested as a major reason for poor model quality at low identity. Taken together, these various atomic-position errors are significant and impede the use of homology models for purposes that require atomic-resolution data, such as drug design and protein–protein interaction predictions; even the quaternary structure of a protein may be difficult to predict from homology models of its subunit(s). Nevertheless, homology models can be useful in reaching qualitative conclusions about the biochemistry of the query sequence, especially in formulating hypotheses about why certain residues are conserved, which may in turn lead to experiments to test those hypotheses. For example, the spatial arrangement of conserved residues may suggest whether a particular residue is conserved to stabilize the folding, to participate in binding some small molecule, or to foster association with another protein or nucleic acid. Homology modeling can produce high-quality structural models when the target and template are closely related, which has inspired the formation of a structural genomics consortium dedicated to the production of representative experimental structures for all classes of protein folds. The chief inaccuracies in homology modeling, which worsen with lower sequence identity, derive from errors in the initial sequence alignment and from improper template selection. Like other methods of structure prediction, current practice in homology modeling is assessed in a biennial large-scale experiment known as the Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, or CASP.