CHEM 2412
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
SORAN UNIVERSITY
... Subject: Organic and the biochemistry Organic chemistry will help the students to understand the meaning of the hydrocarbon compounds which also called organic compounds, such as alkane, alkene, etc. and how can the students differentiated between these organic families, by understanding their (nome ...
... Subject: Organic and the biochemistry Organic chemistry will help the students to understand the meaning of the hydrocarbon compounds which also called organic compounds, such as alkane, alkene, etc. and how can the students differentiated between these organic families, by understanding their (nome ...
Carbohydrates (cont.)
... RNA or protein molecules that act as biological catalysts Work by a “lock-and-key” method with its substrate – the reactant being catalyzed Substrate will only “fit” if shape of active site is a match Once enzyme is done, it releases the product(s) and can be used over + over again Mail fail ...
... RNA or protein molecules that act as biological catalysts Work by a “lock-and-key” method with its substrate – the reactant being catalyzed Substrate will only “fit” if shape of active site is a match Once enzyme is done, it releases the product(s) and can be used over + over again Mail fail ...
Chemical Properties of Organic Compounds
... mL of water to a 1mL sample of each alcohol in separate test tubes. Shake each test tube to ensure mixing. Is a homogenous solution formed or do separate liquid layers remain? Repeat the two tests using hexane instead of water as the solvent. Draw some conclusions about the effect of the length of t ...
... mL of water to a 1mL sample of each alcohol in separate test tubes. Shake each test tube to ensure mixing. Is a homogenous solution formed or do separate liquid layers remain? Repeat the two tests using hexane instead of water as the solvent. Draw some conclusions about the effect of the length of t ...
Carbon
... • Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror image ...
... • Isomers are compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror image ...
Redox reactions
... Oxidation of secondary alcohols • Secondary alcohols such as propan-2-ol are oxidised to the corresponding ketones, such as propanone • Unlike aldehydes, ketones are not easily oxidised, and so no further oxidation takes place ...
... Oxidation of secondary alcohols • Secondary alcohols such as propan-2-ol are oxidised to the corresponding ketones, such as propanone • Unlike aldehydes, ketones are not easily oxidised, and so no further oxidation takes place ...
Organic Reactions
... • Esterification is the most common type of condensation reaction on the regents exam. • Protein synthesis is a commonly cited example of condensation. ...
... • Esterification is the most common type of condensation reaction on the regents exam. • Protein synthesis is a commonly cited example of condensation. ...
Document
... test-tube rack. To each of the tubes, add 1 mL of a carboxylic acid and 1 mL of an alcohol, as listed in Table 50.1. In the case of the solid carb oxylic acid, salicylic acid, add 1 g of acid and 1 ml of alcohol to the tnbe. 2. CAUTION: Keep containers of alcohols and carbo.vylic acMs away from flam ...
... test-tube rack. To each of the tubes, add 1 mL of a carboxylic acid and 1 mL of an alcohol, as listed in Table 50.1. In the case of the solid carb oxylic acid, salicylic acid, add 1 g of acid and 1 ml of alcohol to the tnbe. 2. CAUTION: Keep containers of alcohols and carbo.vylic acMs away from flam ...
CH CH Formula Weight = 86.1748114
... Peaks separated by 14 mass units Get smaller and smaller towards right Peaks separated by 14 mass units Get smaller and smaller towards right but some unusually high peaks Tertiary and secondary carbocations are more stable so MS peaks may be higher than usual ...
... Peaks separated by 14 mass units Get smaller and smaller towards right Peaks separated by 14 mass units Get smaller and smaller towards right but some unusually high peaks Tertiary and secondary carbocations are more stable so MS peaks may be higher than usual ...
CHEMISTRY 263
... Do Not turn in, answers available in "Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry" for Solomons. This is available in the Bookstore or can be borrowed from Cameron Library's Reserve Reading Room Chapter 11: 11.2 to11.4; 11.9; 11.13 to 11.16; 11.25 to 11.27; 11.34 Chapter 22: 22.1; 22. ...
... Do Not turn in, answers available in "Study Guide and Solutions Manual for Organic Chemistry" for Solomons. This is available in the Bookstore or can be borrowed from Cameron Library's Reserve Reading Room Chapter 11: 11.2 to11.4; 11.9; 11.13 to 11.16; 11.25 to 11.27; 11.34 Chapter 22: 22.1; 22. ...
Organic Chem WS - mvhs
... Ex: CH2=CH-CH2=CH3 1-butene Alkynes: contain one or more C-C triple covalent bonds. Practice: 1. How many H atoms in Ethane, Ethene, Ethyne ...
... Ex: CH2=CH-CH2=CH3 1-butene Alkynes: contain one or more C-C triple covalent bonds. Practice: 1. How many H atoms in Ethane, Ethene, Ethyne ...
Contents CONCEPT Introduction to Structure of Atom Dalton`s
... Classification of Organic Compounds based on structure Priority order of functional groups IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Prefixes and suffixes for functional groups Compounds Derivation of structural formula from a given IUPAC name and vice-versa Structural isomerism Stereochemistry and stereoisomer ...
... Classification of Organic Compounds based on structure Priority order of functional groups IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Prefixes and suffixes for functional groups Compounds Derivation of structural formula from a given IUPAC name and vice-versa Structural isomerism Stereochemistry and stereoisomer ...
ttl>.`
... A number of derivativesof the parent phenol are used today as antiseptics. Many mouthwashesand throat lozengesinclude alkyl-substituted phenols as their uciive ingredients for pain relief (seefigure). The compound 4-hexylresorcinol has a superior antibacterial action to that of phenol. It is also mu ...
... A number of derivativesof the parent phenol are used today as antiseptics. Many mouthwashesand throat lozengesinclude alkyl-substituted phenols as their uciive ingredients for pain relief (seefigure). The compound 4-hexylresorcinol has a superior antibacterial action to that of phenol. It is also mu ...
Organic Chemistry Powerpoint Honors
... electrons between carbon atoms are shared evenly around the ring. An aromatic compound is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring or other ring in which the bonding is like that of ...
... electrons between carbon atoms are shared evenly around the ring. An aromatic compound is an organic compound that contains a benzene ring or other ring in which the bonding is like that of ...
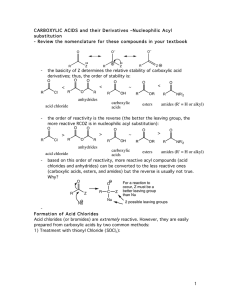
carboxylic acids esters amides (R
... be used to acetylate functional groups such as alcohols and amines. Acetylation can modify both the chemistry and biological activity of a compound. In the case of aspirin, for example, acetylation of the relatively acidic phenol alcohol of salicylic acid leads to a compound that doesn’t dissolve yo ...
... be used to acetylate functional groups such as alcohols and amines. Acetylation can modify both the chemistry and biological activity of a compound. In the case of aspirin, for example, acetylation of the relatively acidic phenol alcohol of salicylic acid leads to a compound that doesn’t dissolve yo ...
Document
... itself to form long chains or rings of carbon atoms. • Carbon forms strong bonds to other nonmetals such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and the halogens. • Several million (11 million-plus) are known, and the number continues to grow rapidly. • Carbon is the most important compound to the bi ...
... itself to form long chains or rings of carbon atoms. • Carbon forms strong bonds to other nonmetals such as hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, and the halogens. • Several million (11 million-plus) are known, and the number continues to grow rapidly. • Carbon is the most important compound to the bi ...
CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 13 – 20, 22, and 23. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step synthesis. Laboratory is included and chapter ...
Friedel-Crafts Alkylations (Exp.II)
... 4. is soluble in dilute HCl solution? 5. is soluble only in conc H2SO4? 6. is not soluble in any of the above solvents? ...
... 4. is soluble in dilute HCl solution? 5. is soluble only in conc H2SO4? 6. is not soluble in any of the above solvents? ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Compare saturated and unsaturated compounds and explain why the latter are more reactive. Draw the structural formula of benzene and explain the circle inside it. Explain what a functional group is and list several important examples. Compare inorganic acids, bases, and salts with their organic equi ...
... Compare saturated and unsaturated compounds and explain why the latter are more reactive. Draw the structural formula of benzene and explain the circle inside it. Explain what a functional group is and list several important examples. Compare inorganic acids, bases, and salts with their organic equi ...
File
... • Physical state: Methanoic acid and ethanoic acid are liquids, while propanoic acid and butanoic acid are solids due to H bonding • Short chain carboxylic acids are soluble in water due to the polar COOH group • Carboxylic acids are soluble in non-polar solvents such as cyclohexane • Boiling points ...
... • Physical state: Methanoic acid and ethanoic acid are liquids, while propanoic acid and butanoic acid are solids due to H bonding • Short chain carboxylic acids are soluble in water due to the polar COOH group • Carboxylic acids are soluble in non-polar solvents such as cyclohexane • Boiling points ...
Alcohols and Phenols - faculty at Chemeketa
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel additive, produced in large quantities Ethanol, CH3CH2OH, called ethyl alcohol, is a solvent, fuel, bevera ...
... They are important solvents and synthesis intermediates Phenols contain an OH group connected to a carbon in a benzene ring Methanol, CH3OH, called methyl alcohol, is a common solvent, a fuel additive, produced in large quantities Ethanol, CH3CH2OH, called ethyl alcohol, is a solvent, fuel, bevera ...
Organic Synthesis of aromatic compounds
... • Explain that synthetic molecules often contain a mixture of optical isomers, whereas natural molecules often have only one optical isomer. • Explain that the synthesis of a pharmaceutical that is a single optical isomer increases costs, reduces side effects and improves pharmacological activity. • ...
... • Explain that synthetic molecules often contain a mixture of optical isomers, whereas natural molecules often have only one optical isomer. • Explain that the synthesis of a pharmaceutical that is a single optical isomer increases costs, reduces side effects and improves pharmacological activity. • ...
BSc-Chemistry-II
... Nomenclature, structure and bonding, physical properties, acidity of carboxylic acids, effects of substituents on acid strength. Preparation of carboxylic acids. Reactions of carboxylic acids. Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction. Reduction of carboxylic acids. Mechanism of decarboxylation, esterificatio ...
... Nomenclature, structure and bonding, physical properties, acidity of carboxylic acids, effects of substituents on acid strength. Preparation of carboxylic acids. Reactions of carboxylic acids. Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky reaction. Reduction of carboxylic acids. Mechanism of decarboxylation, esterificatio ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.