Organic Chemistry The chemistry of carbon compounds. Carbon
... This test used to distinguish between alcohols according to rate of reaction 30> 20> 10> methanol Tertiary alcohol reacts directly with Lucas reagent. 3- Oxidation by cold KMnO4 KMnO4/ H2O ...
... This test used to distinguish between alcohols according to rate of reaction 30> 20> 10> methanol Tertiary alcohol reacts directly with Lucas reagent. 3- Oxidation by cold KMnO4 KMnO4/ H2O ...
Pre-AP Chemistry
... Many foods and consumer products contain artificial flavors as additives. Many of these flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid ...
... Many foods and consumer products contain artificial flavors as additives. Many of these flavors are organic molecules called esters that are synthesized in the lab. Chemists discovered about two hundred years ago that these compounds could be produced when an alcohol was reacted with an organic acid ...
Chapter 20 - people.vcu.edu
... Even if you don’t know this mechanism for this class, your prehealth standardized tests will expect you to know it. o Overall: Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water o Step 1: protonation of carbonyl to “activate” it for attack. ...
... Even if you don’t know this mechanism for this class, your prehealth standardized tests will expect you to know it. o Overall: Carboxylic acid + alcohol → ester + water o Step 1: protonation of carbonyl to “activate” it for attack. ...
Unit 6 part 1 notes on Naming Compounds
... Write symbol of cation followed by symbol of anion along with their oxidation numbers. Use the oxidation number of the charge of each ion as the subscript for the other ion. If a subscript is 1 omit it. If the subscripts are the same, reduce them. Subscripts must be simplified in an ionic formula ...
... Write symbol of cation followed by symbol of anion along with their oxidation numbers. Use the oxidation number of the charge of each ion as the subscript for the other ion. If a subscript is 1 omit it. If the subscripts are the same, reduce them. Subscripts must be simplified in an ionic formula ...
SCH4U Unit Test Name
... 2. When two alcohols undergo a self condensation, what is formed? a. liquid alcohol d. an aldehyde b. a ketone e. an ether c. an ester ...
... 2. When two alcohols undergo a self condensation, what is formed? a. liquid alcohol d. an aldehyde b. a ketone e. an ether c. an ester ...
organic chem ppt notes
... compounds are known as enantiomers. Even though very similar still, different enantiomers of the same chiral drug can have very different pharmological effects, mainly because the proteins they bind to are also chiral. ...
... compounds are known as enantiomers. Even though very similar still, different enantiomers of the same chiral drug can have very different pharmological effects, mainly because the proteins they bind to are also chiral. ...
Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Reading: Wade
... dissolution in this case is driven by entropy, since solution is a more disordered state than either solvent or solute alone. 4. Non polar solutes do not dissolve in polar solvents, because non-polar molecules disrupt the stable H-bond network or water, resulting in an energetic penalty. Furthermor ...
... dissolution in this case is driven by entropy, since solution is a more disordered state than either solvent or solute alone. 4. Non polar solutes do not dissolve in polar solvents, because non-polar molecules disrupt the stable H-bond network or water, resulting in an energetic penalty. Furthermor ...
Organic Chemistry: Organic Halides and Alcohols
... Question: Glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) is more viscous than water, and can lower the freezing point of water. When added to biological samples, it helps to keep the tissues from freezing, thereby reducing damage. From your knowledge of the molecular structure of glycerol, suggest reasons to accoun ...
... Question: Glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) is more viscous than water, and can lower the freezing point of water. When added to biological samples, it helps to keep the tissues from freezing, thereby reducing damage. From your knowledge of the molecular structure of glycerol, suggest reasons to accoun ...
Unit 15 Organic Chemistry Notes
... Halogen name is shortened to end in -o There can be more than 1 halogen added to a hydrocarbon (replace more than 1 H) Prefixes to indicate number ...
... Halogen name is shortened to end in -o There can be more than 1 halogen added to a hydrocarbon (replace more than 1 H) Prefixes to indicate number ...
Islamic University of Gaza Biochemistry School of Nursing Midterm
... the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has three or more carbon atoms attached to it. (incorrect) three 10. The product of the oxi ...
... the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has three or more carbon atoms attached to it. (incorrect) three 10. The product of the oxi ...
Synthesizing Organic Compounds
... There are many reasons why chemists create new organic substances. They may be synthesized as part of research or to demonstrate a new type of reaction. Others are synthesized if a compound is needed with specific chemical and physical properties. Large amounts of some synthetic compounds are routin ...
... There are many reasons why chemists create new organic substances. They may be synthesized as part of research or to demonstrate a new type of reaction. Others are synthesized if a compound is needed with specific chemical and physical properties. Large amounts of some synthetic compounds are routin ...
Chapter 4
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
AP Biology Functional Groups of Carbon
... between molecules. (See module on energetics) – DNA and RNA have backbones made of phosphates alternating with a deoxyribose or ribose monosaccharide. – Molecules that accept Hydrogen such as NAD+ or FAD+ contain phosphates. ...
... between molecules. (See module on energetics) – DNA and RNA have backbones made of phosphates alternating with a deoxyribose or ribose monosaccharide. – Molecules that accept Hydrogen such as NAD+ or FAD+ contain phosphates. ...
Biochemistry Carbon Compounds
... • The structure of a functional group is drawn with one bond to the side that does not appear to be connected to anything. This is to indicate that the functional group is bonded to some larger molecule. The functional group is not a molecule and it does not exist all by itself. • A carboxyl group h ...
... • The structure of a functional group is drawn with one bond to the side that does not appear to be connected to anything. This is to indicate that the functional group is bonded to some larger molecule. The functional group is not a molecule and it does not exist all by itself. • A carboxyl group h ...
Biochemistry 1. Which statement describes a similarity between all
... Their ability to replicate identical copies ensures continuation of the species. ...
... Their ability to replicate identical copies ensures continuation of the species. ...
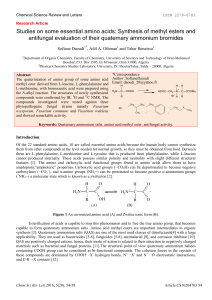
Studies on some essential amino acids: Synthesis of methyl esters
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
... capable to form quaternary ammonium salts. Amino acid methyl esters are important intermediates in organic synthesis [3]. Quaternary ammonium salts (QAS) are one of the most used classes of disinfectants[4] with a large applicability. They are used as bactericides [5-6], fungicides [5-8], antimalari ...
C3 3.1-3.4 part 1 Alcohols, carboxlic acids and esters progress ticket
... Organic compounds such as ethyl propanoate are used in perfumes. Give two properties of these compounds that make them suitable for use in perfumes. ...
... Organic compounds such as ethyl propanoate are used in perfumes. Give two properties of these compounds that make them suitable for use in perfumes. ...
Antimicrobial Agents Suitable for Use in Lab. Animal Facility
... From AALAS Reference Directory 2007 ...
... From AALAS Reference Directory 2007 ...
Carbon Chemistry
... • Notice how the CH2 units repeat. • A very large carbon-based molecule made of repeating units is called a polymer. • Polymers can be thousands of atoms long. ...
... • Notice how the CH2 units repeat. • A very large carbon-based molecule made of repeating units is called a polymer. • Polymers can be thousands of atoms long. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... c) Why oxymercuration-demercuration method of preparation of alcohols follows anti addition. ...
... c) Why oxymercuration-demercuration method of preparation of alcohols follows anti addition. ...
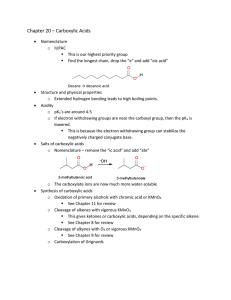
Carboxylic Acids
... on the alkyl portion of the acid. Electron withdrawing groups make the molecule more acidic (by stabilizing the negative charge on the conjugate base), while electron-donating groups make it less acidic, by destabilizing that same charge. You should know this relationship already! It’s the same one ...
... on the alkyl portion of the acid. Electron withdrawing groups make the molecule more acidic (by stabilizing the negative charge on the conjugate base), while electron-donating groups make it less acidic, by destabilizing that same charge. You should know this relationship already! It’s the same one ...
Organic Chemistry PPT
... Saturated means that all the carbon bonds are taken. They are solid at room temperature and bad for you. Unsaturated means that there is at least one double bond with the carbon. They are liquid at room temp. and are better for you. ...
... Saturated means that all the carbon bonds are taken. They are solid at room temperature and bad for you. Unsaturated means that there is at least one double bond with the carbon. They are liquid at room temp. and are better for you. ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.