Lecture 1: RDCH 710 Introduction
... * Isostructural with KPu(C8H8)2 orthorhombic unit cell Reactions with other K complexes K2RC8H7; R=ethanol, butanol • Reactions with NpI3 Formation of mono- and diMeCP ...
... * Isostructural with KPu(C8H8)2 orthorhombic unit cell Reactions with other K complexes K2RC8H7; R=ethanol, butanol • Reactions with NpI3 Formation of mono- and diMeCP ...
Classifying Organic Molecules
... 12. Take your non-nitrogen pile and sort out those cards that have -OH attached to most carbons. Be aware that organic chemists use many shortcuts in drawing complex molecules. They often do not include the letter C for carbon in ring structures. How many cards did you find? 13. What are the two for ...
... 12. Take your non-nitrogen pile and sort out those cards that have -OH attached to most carbons. Be aware that organic chemists use many shortcuts in drawing complex molecules. They often do not include the letter C for carbon in ring structures. How many cards did you find? 13. What are the two for ...
Organic Chemistry Unit Test
... 1. We did two labs involving esters. In the first, we made a series of esters. In the second, we made two polyesters. Describe at least 3 ‘real world’ uses that you could imagine for the products of either of these labs based on your observations and data table. (3 marks) ...
... 1. We did two labs involving esters. In the first, we made a series of esters. In the second, we made two polyesters. Describe at least 3 ‘real world’ uses that you could imagine for the products of either of these labs based on your observations and data table. (3 marks) ...
Name: David Kett Id Number: 0564591
... If the intermolecular forces between the molecules of one substance are roughly the same as the intermolecular forces between the molecules of another substance, then the two substances will most likely dissolve in each other. Thus, polar substances such as water can dissolve other polar substances ...
... If the intermolecular forces between the molecules of one substance are roughly the same as the intermolecular forces between the molecules of another substance, then the two substances will most likely dissolve in each other. Thus, polar substances such as water can dissolve other polar substances ...
sOLUBILITY
... less than 5 carbons) with a polar functional group such as carboxylic acid, amine, alcohol, aldehyde, or ketone. Low MW carboxylic acids ...
... less than 5 carbons) with a polar functional group such as carboxylic acid, amine, alcohol, aldehyde, or ketone. Low MW carboxylic acids ...
Pre-lab 2: Naming and Modeling Organic Compounds
... 1. alkenes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing carboncarbon double bonds with three electron groups. 2. alkynes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing carboncarbon triple bonds with two electron groups. 3. ring: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons may form rings with the root n ...
... 1. alkenes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing carboncarbon double bonds with three electron groups. 2. alkynes: These are unsaturated hydrocarbons containing carboncarbon triple bonds with two electron groups. 3. ring: saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons may form rings with the root n ...
File
... Addition reactions Alkynes • two-stage process: • alkyne→ alkene→ alkane • possibility of isomers being produced. • compared to an alkene, complete addition to an alkyne will require twice the quantity of • halogen (1) • hydrogen (2) • hydrogen halide (3) ...
... Addition reactions Alkynes • two-stage process: • alkyne→ alkene→ alkane • possibility of isomers being produced. • compared to an alkene, complete addition to an alkyne will require twice the quantity of • halogen (1) • hydrogen (2) • hydrogen halide (3) ...
Derivatization reagents
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
... ● Purified, dried and packaged under nitrogen in convenient 50mL Hypo-Vial Sample Storage Vials ● Supplied with elastomer septa, allowing immediate access to the sample without exposure to moisture and oxygen ● Use polar solvents (acetonitrile, dimethylformamide, dimethylsulfoxide, pyridine, tetrahy ...
alcohols!
... • Resveratrol-one of many phenols found in red wine-lowers bad cholesterol • BHT-butylated hydroxytoluene/ BHAbutylated hydroxyanisole • Found in cereal and other snacks-fat is oxidized easily and cereal becomes soft and yucky • BHT and BHA are antioxidants. They are sacrificial molecules. When O2 ...
... • Resveratrol-one of many phenols found in red wine-lowers bad cholesterol • BHT-butylated hydroxytoluene/ BHAbutylated hydroxyanisole • Found in cereal and other snacks-fat is oxidized easily and cereal becomes soft and yucky • BHT and BHA are antioxidants. They are sacrificial molecules. When O2 ...
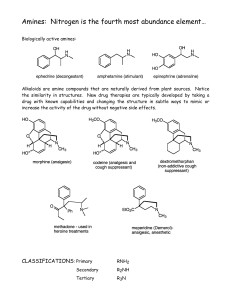
Amines: Nitrogen is the fourth most abundance element…
... We can use acid-base chemistry to separate them. Consider their characteristics: naphthalene is a neutral organic compound without any acidic nor basic functionality. Benzoic acid has an acidic proton that reacts with bases. Pyridine is a base that reacts with acids. Let’s separate them. Add aqueou ...
... We can use acid-base chemistry to separate them. Consider their characteristics: naphthalene is a neutral organic compound without any acidic nor basic functionality. Benzoic acid has an acidic proton that reacts with bases. Pyridine is a base that reacts with acids. Let’s separate them. Add aqueou ...
Alcohols/Wade: Reactions
... 6. What simple chemical test can you use to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds? Write the test and the observation. a) 1-butanol and 2-butanol ...
... 6. What simple chemical test can you use to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds? Write the test and the observation. a) 1-butanol and 2-butanol ...
reactions of functional groups of organic compounds with
... Try to write the reactions in the ionic form: ...
... Try to write the reactions in the ionic form: ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 1. Background and Properties
... and halides consist of alkyl and/or aryl groups bonded to hydroxyl, alkoxyl, amino and halo substituents respectively. If these same functional groups are attached to an acyl group (RCO–) their properties are substantially changed, and they are designated ...
... and halides consist of alkyl and/or aryl groups bonded to hydroxyl, alkoxyl, amino and halo substituents respectively. If these same functional groups are attached to an acyl group (RCO–) their properties are substantially changed, and they are designated ...
Laboratory Disinfectants - University of Kentucky`s Environmental
... Ethanol (ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH) and 2-propanol (isopropyl alcohol, (CH3)2CHOH) have similar disinfectant properties. They are active against vegetative bacteria, fungi, and lipid-containing viruses but not against spores. Their action on non-lipid-containing viruses is variable. For highest effectiv ...
... Ethanol (ethyl alcohol, C2H5OH) and 2-propanol (isopropyl alcohol, (CH3)2CHOH) have similar disinfectant properties. They are active against vegetative bacteria, fungi, and lipid-containing viruses but not against spores. Their action on non-lipid-containing viruses is variable. For highest effectiv ...
877-Alcohols Carboxylic acids and Esters Presentation
... Q Why not write C2H6O? The formula gives us clues about the structure of the molecule The oxygen and hydrogen in the alcohol functional group are bonded and so are written together ...
... Q Why not write C2H6O? The formula gives us clues about the structure of the molecule The oxygen and hydrogen in the alcohol functional group are bonded and so are written together ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... Reactions of Phenols ¾ Some reactions like aliphatic alcohols: phenol + carboxylic acid → ester phenol + aq. NaOH → phenoxide ion ¾ Reactions that are peculiar to phenols are: Oxidation of phenols to quinones Electrophilic aromatic substitution of phenols ...
... Reactions of Phenols ¾ Some reactions like aliphatic alcohols: phenol + carboxylic acid → ester phenol + aq. NaOH → phenoxide ion ¾ Reactions that are peculiar to phenols are: Oxidation of phenols to quinones Electrophilic aromatic substitution of phenols ...
to get Period 1 8
... and air conditioners. But soon Freon was found to damage the environment. The use of it as banned in the United States. Although, a very hazardous compound that contains halogens, named trichlyobroethane, is continued to be used in dry-cleaning solutions. For it can cause severe health problems. ...
... and air conditioners. But soon Freon was found to damage the environment. The use of it as banned in the United States. Although, a very hazardous compound that contains halogens, named trichlyobroethane, is continued to be used in dry-cleaning solutions. For it can cause severe health problems. ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-18
... the most significant being the ability to form hydrogen bonds. The formation of hydrogen bonds between amines, and between amines and water, accounts for their higher boiling points (than alkanes) and their water solubility. b. Reactions of Amines. Since amines are derivatives of ammonia, they are ...
... the most significant being the ability to form hydrogen bonds. The formation of hydrogen bonds between amines, and between amines and water, accounts for their higher boiling points (than alkanes) and their water solubility. b. Reactions of Amines. Since amines are derivatives of ammonia, they are ...
CHEM 2412
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
... Nomenclature and drawing of alkynes; Physical properties of alkynes; Hybridization and bond lengths, scharacter; Acidity of terminal alkynes; Acetylide formation and reactions with alkyl halides and carbonyl compounds; Elimination reactions used to form alkynes (terminal/internal isomerization); Add ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.