
Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... Increasing order of acidity is ethanol < water < phenol. The phenoxide ion obtained after the removal of a proton is stabilised by resonance whereas the ethoxide ion obtained after the removal of a proton is destabilised by ‘+I’ effect of —C2H5 group. Therefore phenol is stronger acid than ethanol. ...
... Increasing order of acidity is ethanol < water < phenol. The phenoxide ion obtained after the removal of a proton is stabilised by resonance whereas the ethoxide ion obtained after the removal of a proton is destabilised by ‘+I’ effect of —C2H5 group. Therefore phenol is stronger acid than ethanol. ...
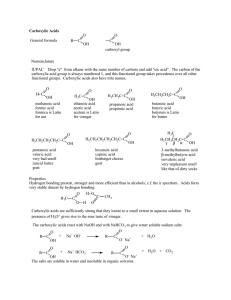
Carboxylic Acids General formula R C O OH C O OH carboxyl group
... Although they both contain the -OH group, carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alchols. This is due to the resonance stabilization of the anion formed from a carboxylic acid by loss of a proton: ...
... Although they both contain the -OH group, carboxylic acids are stronger acids than alchols. This is due to the resonance stabilization of the anion formed from a carboxylic acid by loss of a proton: ...
CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 9, 11, and 15-22, with 24-28 being addressed in research papers. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step s ...
... Course Content: Organic Chemistry I will cover chapters 9, 11, and 15-22, with 24-28 being addressed in research papers. Special emphasis will be placed on aromatic compounds, carbonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, amines, phenols, spectroscopy, structure and reactivity, biomolecules and multi-step s ...
2008 Periodic Table of the Elements Instructions: Read carefully all
... At Standard Temperature and Pressure 22.4 L of Chlorine gas Cl2 will have a mass of: a) 35.45g b) 22.4g c) 28.0g d) 70.9g ...
... At Standard Temperature and Pressure 22.4 L of Chlorine gas Cl2 will have a mass of: a) 35.45g b) 22.4g c) 28.0g d) 70.9g ...
Efficient one pot synthesis of N-alkyl and N-aryl imides
... Imide derivatives have been found to possess a broad spectrum of biological activities. A variety of methods have been reported for the preparation of this class of compound. However, in spite of their potential utility, some of the reported methods suffer from drawbacks such as long reaction times, ...
... Imide derivatives have been found to possess a broad spectrum of biological activities. A variety of methods have been reported for the preparation of this class of compound. However, in spite of their potential utility, some of the reported methods suffer from drawbacks such as long reaction times, ...
ID of Alcohol Lab
... Each unknown is one of the alcohols in the chart below. First, use the name of the alcohol to sketch the structural formula. Next, determine from the structural formula if the alcohol is a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol. Finally, use the boiling point, Lucas test & Chromic Acid test data fr ...
... Each unknown is one of the alcohols in the chart below. First, use the name of the alcohol to sketch the structural formula. Next, determine from the structural formula if the alcohol is a primary, secondary, or tertiary alcohol. Finally, use the boiling point, Lucas test & Chromic Acid test data fr ...
AP Biology - cloudfront.net
... Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of one another. Not being able to superimpose one molecule on top of the other simply means that the two molecules are not equivalent or identical. For a compound to form an enantiomeric pair, it must have chiral molecules. Chiral molecules must not h ...
... Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of one another. Not being able to superimpose one molecule on top of the other simply means that the two molecules are not equivalent or identical. For a compound to form an enantiomeric pair, it must have chiral molecules. Chiral molecules must not h ...
Ch. 4 Carbon
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
... Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. ...
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH CH3 - CH2-CH2
... Named using the ending –ol. –O-H group gets the lowest possible number Alcohols are oxidised to carboxylic acids when treated with strong oxidising agents Alcohol molecules have a non-polar hydrocarbon end and a polar –O-H section Alcohols are solvents for polar and non-polar solutes Classification ...
... Named using the ending –ol. –O-H group gets the lowest possible number Alcohols are oxidised to carboxylic acids when treated with strong oxidising agents Alcohol molecules have a non-polar hydrocarbon end and a polar –O-H section Alcohols are solvents for polar and non-polar solutes Classification ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... COURSE OBJECTIVES: Upon completion of CHEM 2310, the student will be able to: 1. understand and explain the important role carbon compounds play in life systems; 2. explain the role of carbon compounds in our economy and in our dally life; 3. describe covalent bonding as it applies to organic compou ...
... COURSE OBJECTIVES: Upon completion of CHEM 2310, the student will be able to: 1. understand and explain the important role carbon compounds play in life systems; 2. explain the role of carbon compounds in our economy and in our dally life; 3. describe covalent bonding as it applies to organic compou ...
polymer - MrSimonPorter
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
polymer - MrSimonPorter
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
... Ethanoic acid C2H3OOH Propanoic acid C3H5OOH Butanoic acid C4H7OOH Pentanoic acid C5H9OOH Hexanoic acid C6H11OOH ...
WM4 Instrumental analysis
... which electromagnetic radiation is transmitted through a sample of substance. Frequency ranges absorbed give clues about functional groups which are present. IR spectrum of salicylic acid gives evidence of C=O and –OH groups. ...
... which electromagnetic radiation is transmitted through a sample of substance. Frequency ranges absorbed give clues about functional groups which are present. IR spectrum of salicylic acid gives evidence of C=O and –OH groups. ...
Slide 1
... A crown ether specifically binds certain metal ions or organic molecules to form a host–guest complex, an example of molecular recognition ...
... A crown ether specifically binds certain metal ions or organic molecules to form a host–guest complex, an example of molecular recognition ...
aldehyde,ketones and Haloalkanes
... (i) The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxymethane. (ii) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol (iii) o – and p – nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. [3] Q.12 Name the reagent which are used in the following conversions: Write chemical reaction also. [3] (i) A primary alcohol t ...
... (i) The boiling point of ethanol is higher than that of methoxymethane. (ii) Phenol is more acidic than ethanol (iii) o – and p – nitrophenols are more acidic than phenol. [3] Q.12 Name the reagent which are used in the following conversions: Write chemical reaction also. [3] (i) A primary alcohol t ...
Dess-Martin Periodinane
... One of the mildest reagents for the selective oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. High yields can be obtained at ambient temperatures, under neutral conditions, in chloroform, dichloromethane or acetonitrile: J. Org. Chem., 48, 4155 (1983); J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 7 ...
... One of the mildest reagents for the selective oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. High yields can be obtained at ambient temperatures, under neutral conditions, in chloroform, dichloromethane or acetonitrile: J. Org. Chem., 48, 4155 (1983); J. Am. Chem. Soc., 113, 7 ...
Biologists nowadays depend upon chemists for
... 3. What is the molecular formula for methyl alcohol?________________________________________ 5. What is the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in glycerol?_____________________________ Build a model of each molecule (Methyl & Ethyl Alcohol & Glycerol. Have different classmates inspect your mode ...
... 3. What is the molecular formula for methyl alcohol?________________________________________ 5. What is the ratio of hydrogen atoms to oxygen atoms in glycerol?_____________________________ Build a model of each molecule (Methyl & Ethyl Alcohol & Glycerol. Have different classmates inspect your mode ...
+ [O] - MrFisherChemistry
... Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
... Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
Unknowns
... 1. What are desirable properties of a derivative? 2. What is the purpose of preparing a derivative? →Prepare two good derivatives of each unknown. Recrystallize from ethanol/water. ...
... 1. What are desirable properties of a derivative? 2. What is the purpose of preparing a derivative? →Prepare two good derivatives of each unknown. Recrystallize from ethanol/water. ...
Organic Chemistry - City University of New York
... concepts of hybridization of atomic orbitals and the theory of resonance, developed in the 1930s, provided the first adequate description of benzene’s structure. • The carbon skeleton is a planar regular hexagon. • All C-C-C and H-C-C bond angles 120°. ...
... concepts of hybridization of atomic orbitals and the theory of resonance, developed in the 1930s, provided the first adequate description of benzene’s structure. • The carbon skeleton is a planar regular hexagon. • All C-C-C and H-C-C bond angles 120°. ...
Alcohols - ChemistryHSC
... Alcohols Functional group: -OH. Hydroxyl group covalently bonded to an alkyl chain or benzene ring (called phenols) Many naturally occurring in nature: glucose C6H12O6, glycerol C3H8O3 Most common alcohol is ethanol, which has been produced for thousands of years – Egyptian workers given beer ration ...
... Alcohols Functional group: -OH. Hydroxyl group covalently bonded to an alkyl chain or benzene ring (called phenols) Many naturally occurring in nature: glucose C6H12O6, glycerol C3H8O3 Most common alcohol is ethanol, which has been produced for thousands of years – Egyptian workers given beer ration ...
Organic Functional Groups
... to form an alkene, condensation (with c. acids ester) as well as oxidation reactions (can make ketones, aldehydes, c. acids) Nomenclature suffix = “ol”, prefix = “hydroxyl” Eg. CH3CH2CH2OH = 1-propanol OH ...
... to form an alkene, condensation (with c. acids ester) as well as oxidation reactions (can make ketones, aldehydes, c. acids) Nomenclature suffix = “ol”, prefix = “hydroxyl” Eg. CH3CH2CH2OH = 1-propanol OH ...
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry
... COURSE OBJECTIVES: Upon completion of CHEM 2310, the student will be able to: 1. understand and explain the important role carbon compounds play in life systems; 2. explain the role of carbon compounds in our economy and in our dally life; 3. describe covalent bonding as it applies to organic compou ...
... COURSE OBJECTIVES: Upon completion of CHEM 2310, the student will be able to: 1. understand and explain the important role carbon compounds play in life systems; 2. explain the role of carbon compounds in our economy and in our dally life; 3. describe covalent bonding as it applies to organic compou ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.
















![+ [O] - MrFisherChemistry](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194573_1-9c1e57b3af8f6a74ecb3216d2ce704f3-300x300.png)





