SPECTRA Q - the British School of Bahrain
... A tablet of ibuprofen contains a very small quantity of the drug and the remainder of the tablet material is unreactive. In an analysis 50 tablets were reacted with 100.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol dm–3 aqueous sodium hydroxide, an excess. The ibuprofen reacted as a weak acid. When the reaction was complete, t ...
... A tablet of ibuprofen contains a very small quantity of the drug and the remainder of the tablet material is unreactive. In an analysis 50 tablets were reacted with 100.0 cm3 of 1.00 mol dm–3 aqueous sodium hydroxide, an excess. The ibuprofen reacted as a weak acid. When the reaction was complete, t ...
Assessment of bioactive compounds from five wild edible fruits
... vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, enzymes, phytonutrients and other nutrients. In humans they can have a beneficial effect because of the positive biological responses they elicit, often reducing the risk of chronic disease. Foods with high phytonutrient content are sometimes called “super foods” si ...
... vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, enzymes, phytonutrients and other nutrients. In humans they can have a beneficial effect because of the positive biological responses they elicit, often reducing the risk of chronic disease. Foods with high phytonutrient content are sometimes called “super foods” si ...
Chapter 25 The Chemistry of Life: Organic Chemistry 25.1 Some
... Hydrocarbons are relatively unreactive; for an organic molecule to be reactive it needs something additional. ...
... Hydrocarbons are relatively unreactive; for an organic molecule to be reactive it needs something additional. ...
Organic Chemistry
... Cracking: large molecules broken down to smaller ones by breaking carbon-carbon bonds. Pyrolysis (thermal cracking): The process that produces cracking at high temperatures. ...
... Cracking: large molecules broken down to smaller ones by breaking carbon-carbon bonds. Pyrolysis (thermal cracking): The process that produces cracking at high temperatures. ...
Organic Chemistry Syllabus and Course Outline
... structure and function of molecules, the major classes of reactions, reaction energetics and mechanisms, synthesis of organic compounds, and how to determine structure via various spectroscopic techniques. Several themes are prevalent in each unit of study: nomenclature, chemical and physical proper ...
... structure and function of molecules, the major classes of reactions, reaction energetics and mechanisms, synthesis of organic compounds, and how to determine structure via various spectroscopic techniques. Several themes are prevalent in each unit of study: nomenclature, chemical and physical proper ...
Carbohydrates important reactions
... I. Chemical reactions of - COOH group Oxidation As noted above, sugars may be classified as reducing or non-reducing based on their reactivity with Tollens', Benedict's or Fehling's reagents. If a sugar is oxidized by these reagents it is called reducing, since the oxidant (Ag(+) or Cu(+2)) is reduc ...
... I. Chemical reactions of - COOH group Oxidation As noted above, sugars may be classified as reducing or non-reducing based on their reactivity with Tollens', Benedict's or Fehling's reagents. If a sugar is oxidized by these reagents it is called reducing, since the oxidant (Ag(+) or Cu(+2)) is reduc ...
16565 Demonstrate knowledge of organic compounds
... Physical properties of a homologous series are identified in relation to trends. ...
... Physical properties of a homologous series are identified in relation to trends. ...
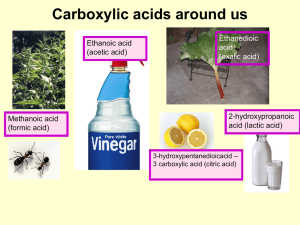
Unit4_Carboxylic Acid ppt
... Acids are named according to standard IUPAC rules But, many are still known under their trivial names, some having been called after characteristic properties or their origin. Formula HCOOH CH3COOH C6H5COOH ...
... Acids are named according to standard IUPAC rules But, many are still known under their trivial names, some having been called after characteristic properties or their origin. Formula HCOOH CH3COOH C6H5COOH ...
ether - TeacherWeb
... Naming Ethers • Identify the two alkyl groups in the chain. • Write the prefix of the shorter alkyl chain, then the suffix – oxy, followed by the complete name of the longer alkyl chain (alkane name). • A number is required to indicate the carbon in which the oxygen is attached to in the longer cha ...
... Naming Ethers • Identify the two alkyl groups in the chain. • Write the prefix of the shorter alkyl chain, then the suffix – oxy, followed by the complete name of the longer alkyl chain (alkane name). • A number is required to indicate the carbon in which the oxygen is attached to in the longer cha ...
04_Lecture_Presentation_PC
... molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror images of each other ...
... molecular formula but different structures and properties – Structural isomers have different covalent arrangements of their atoms – Cis-trans isomers have the same covalent bonds but differ in spatial arrangements – Enantiomers are isomers that are mirror images of each other ...
chemistry 2 - waiukucollegescience
... In order to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propene a student said it was necessary to use bromine water rather than acidified potassium permanganate. Discuss this statement. ...
... In order to distinguish between propan-1-ol and propene a student said it was necessary to use bromine water rather than acidified potassium permanganate. Discuss this statement. ...
polar covalent bond
... – Since alkanes are insoluble and less dense than water, they float on top of the water. ...
... – Since alkanes are insoluble and less dense than water, they float on top of the water. ...
Sequence Rules for Specifying Configuration Sequence Rules for
... Have identical melting points, solubilities, and densities Differ in sign of their rotation of plane-polarized light • The meso isomer is diastereomeric with the (+) and (-) forms • It has no mirror-image relationship to (+)- and (-)-tartaric acids • Is a different compound ...
... Have identical melting points, solubilities, and densities Differ in sign of their rotation of plane-polarized light • The meso isomer is diastereomeric with the (+) and (-) forms • It has no mirror-image relationship to (+)- and (-)-tartaric acids • Is a different compound ...
Organic Chemistry - Moorpark College
... PHENOLS For a phenol, R-OH ,the R is an aryl group (based on a benzene ring, C6H5OH). The simplest phenol is phenol (C6H5OH) where the group name comes from. ETHER The general formula for an ether is R-O-R The R and R' may be the same or different. The simplest ether is dimethyl ether For complicate ...
... PHENOLS For a phenol, R-OH ,the R is an aryl group (based on a benzene ring, C6H5OH). The simplest phenol is phenol (C6H5OH) where the group name comes from. ETHER The general formula for an ether is R-O-R The R and R' may be the same or different. The simplest ether is dimethyl ether For complicate ...
Programma III year
... Drug analysis, laboratory III year, Module Prof. Barbato. aa. 2015-2016 1. Elementary analysis: calcination, HCN analysis of organic molecules of pharmacological interest. 1.A Laboratory practical exercise: Minimum formula of compounds from HCN analysis data, examples. 1.B Laboratory practical exerc ...
... Drug analysis, laboratory III year, Module Prof. Barbato. aa. 2015-2016 1. Elementary analysis: calcination, HCN analysis of organic molecules of pharmacological interest. 1.A Laboratory practical exercise: Minimum formula of compounds from HCN analysis data, examples. 1.B Laboratory practical exerc ...
CHAPTER 1: ORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... - based on cycloalkanes: ex menthol and chlosterol - based on benzene: ex phenol - use hydroxyl prefix for naming Properties of Alcohols - bp higher than parent alkanes – due to polarity - smaller ones much more soluble in water than parent alkanes – due to polarity - if alkyl chain is long, then no ...
... - based on cycloalkanes: ex menthol and chlosterol - based on benzene: ex phenol - use hydroxyl prefix for naming Properties of Alcohols - bp higher than parent alkanes – due to polarity - smaller ones much more soluble in water than parent alkanes – due to polarity - if alkyl chain is long, then no ...
DECARBOXYLATION OF CARBON COMPOUNDS - USRA
... Conclusion: Simple carbon compounds that are oxidized, such as oxalates, acetates, and mellitic acid, will undergo decarboxylation to produce CO2 at temperatures as low as 150° C under inert conditions (i.e., He), but in the presence of 99.99% oxygen, the CO2 evolution can be shifted to lower temper ...
... Conclusion: Simple carbon compounds that are oxidized, such as oxalates, acetates, and mellitic acid, will undergo decarboxylation to produce CO2 at temperatures as low as 150° C under inert conditions (i.e., He), but in the presence of 99.99% oxygen, the CO2 evolution can be shifted to lower temper ...
Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... a) Structural Isomers • Differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms • The number of possible isomers increases as the number of carbon skeleton increases in size E.g. C4H10 has 2 isomers C8H18 has 18 isomers C20H42 has 366319 isomers ...
... a) Structural Isomers • Differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms • The number of possible isomers increases as the number of carbon skeleton increases in size E.g. C4H10 has 2 isomers C8H18 has 18 isomers C20H42 has 366319 isomers ...
CARBON AND ITS COMPOUNDS
... shell. (Duplet) Thus N shares three of its valence electrons with each H atom to form NH3. CH4: - Atomic number of C is 6. Its electronic configuration is 2,4 and thus requires four electron to complete its octet(8). Atomic number of H is 1. Its electronic configuration is 1 and thus requires 1 elec ...
... shell. (Duplet) Thus N shares three of its valence electrons with each H atom to form NH3. CH4: - Atomic number of C is 6. Its electronic configuration is 2,4 and thus requires four electron to complete its octet(8). Atomic number of H is 1. Its electronic configuration is 1 and thus requires 1 elec ...
Text Questions from Corwin
... 5. What is the difference between a hydrocarbon and a hydrocarbon derivative? a hydrocarbon contains only H and C; a derivative has H and C, but also other elements 6. What does a saturated hydrocarbon have? a single bond between each of its carbon atoms 7. Why can a carbon atom bond to as many as f ...
... 5. What is the difference between a hydrocarbon and a hydrocarbon derivative? a hydrocarbon contains only H and C; a derivative has H and C, but also other elements 6. What does a saturated hydrocarbon have? a single bond between each of its carbon atoms 7. Why can a carbon atom bond to as many as f ...
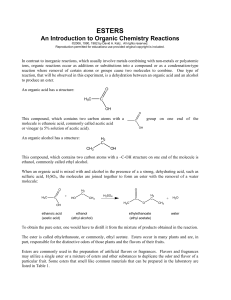
Esters - chymist.com
... Organic alcohols are flammable. Avoid flames. Never heat any of the materials in this experiment directly, use a water bath. If passing esters around for individuals to smell, use small quantities with a piece of glass wool in the container to prevent splashing or spilling. ...
... Organic alcohols are flammable. Avoid flames. Never heat any of the materials in this experiment directly, use a water bath. If passing esters around for individuals to smell, use small quantities with a piece of glass wool in the container to prevent splashing or spilling. ...
4.79 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... What is Organic Chemistry? Organic chemistry is the field of science that studies the structure, properties, composition of hydrocarbons (compounds containing carbon and hydrogen). These compounds may contain some other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen and halogens. ...
... What is Organic Chemistry? Organic chemistry is the field of science that studies the structure, properties, composition of hydrocarbons (compounds containing carbon and hydrogen). These compounds may contain some other elements, including oxygen, nitrogen and halogens. ...
Lecture syllabus - Linfield College
... - teach foundational principles that underlie the chemical and physical behavior of compounds constructed mainly of carbon atoms - foster scientific critical thinking skills - provide experience in common laboratory techniques and “chemical common sense” in the laboratory - provide practice in writi ...
... - teach foundational principles that underlie the chemical and physical behavior of compounds constructed mainly of carbon atoms - foster scientific critical thinking skills - provide experience in common laboratory techniques and “chemical common sense” in the laboratory - provide practice in writi ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.