Unit 6 web
... More Complex Organic Molecules • Contain atoms other than C and H • To understand their properties, they are grouped according to the nature of these atoms and how they are bonded • Classified according to reactivity and function, hence “functional groups” ...
... More Complex Organic Molecules • Contain atoms other than C and H • To understand their properties, they are grouped according to the nature of these atoms and how they are bonded • Classified according to reactivity and function, hence “functional groups” ...
CARBON COMPOUNDS - SMK Raja Perempuan Ipoh
... The melting point of alcohol is higher than alkane and alkene due to the presence of hydroxyl group. This is because –OH group forms hydrogen bonding that is stronger than the bonds between molecules of alcohol. Methanol, ethanol and propanol dissolve in water. The solubility of other alcohols decre ...
... The melting point of alcohol is higher than alkane and alkene due to the presence of hydroxyl group. This is because –OH group forms hydrogen bonding that is stronger than the bonds between molecules of alcohol. Methanol, ethanol and propanol dissolve in water. The solubility of other alcohols decre ...
Essential Oils Composition
... • Aliphatic Compounds are non-aromatic organic compounds. The chain of C-atoms may be straight, branched, saturated, or unsaturated. • Aliphatic Compounds : Aliphatic of Hidrocarbon, alcohol, aldehydes, ketones, or ester • Hidrocarbon compounds occur abundantly in foodstuffs such as fruit, but contr ...
... • Aliphatic Compounds are non-aromatic organic compounds. The chain of C-atoms may be straight, branched, saturated, or unsaturated. • Aliphatic Compounds : Aliphatic of Hidrocarbon, alcohol, aldehydes, ketones, or ester • Hidrocarbon compounds occur abundantly in foodstuffs such as fruit, but contr ...
Organic and Biochemistry
... The name of the alkane varies according to the number of C atoms present in the chain. We can make a table of members of a homologous series of straight-chain alkanes. • In this table each member differs by one CH2 unit. • The names each end in - ane. • The prefix assigned indicates the number of ca ...
... The name of the alkane varies according to the number of C atoms present in the chain. We can make a table of members of a homologous series of straight-chain alkanes. • In this table each member differs by one CH2 unit. • The names each end in - ane. • The prefix assigned indicates the number of ca ...
diazonium salt
... diazonium salts are stable enough to be stored in aqueous solution at 0–5°C for reasonable periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss of nitrogen from an alkyl diazonium ion. Stability is due to: interaction with the ar ...
... diazonium salts are stable enough to be stored in aqueous solution at 0–5°C for reasonable periods of time. Loss of nitrogen from an aryl diazonium ion generates an unstable aryl cation and is much slower than loss of nitrogen from an alkyl diazonium ion. Stability is due to: interaction with the ar ...
الشريحة 1 - Systematic Approach to Teaching
... • Alcohols are prepared:From alkene by hydration, 2) From alkyl halide by SN using aqueous NaOH, 3) From aldehydes or ketones by reduction using NaBH4 or Li Al H4. & 4) From Acids or esters by reduction using Li Al H4. • * Amines are prepared from alkyl halides using NH3 or NaNH2. • * Amines could b ...
... • Alcohols are prepared:From alkene by hydration, 2) From alkyl halide by SN using aqueous NaOH, 3) From aldehydes or ketones by reduction using NaBH4 or Li Al H4. & 4) From Acids or esters by reduction using Li Al H4. • * Amines are prepared from alkyl halides using NH3 or NaNH2. • * Amines could b ...
File
... the ketones (and is usually indicated via number.) • The main industrial use for ketones is as solvents and varnishes (propanone is the solvent used for nail varnish remover) ...
... the ketones (and is usually indicated via number.) • The main industrial use for ketones is as solvents and varnishes (propanone is the solvent used for nail varnish remover) ...
Esters, fats and oils
... To prevent oil and water components separating into layers, a soap-like molecule known as an emulsifier is added. ...
... To prevent oil and water components separating into layers, a soap-like molecule known as an emulsifier is added. ...
Organic Chemistry Notes
... alcohols (e.g., pentan-2-ol), carboxylic acids (e.g., pentanoic acid) and esters (e.g., methyl pentanoate), and with multiple occurrences of the functional group limited to halogens (e.g., 2bromo-1-chloropentane) and alcohols (e.g., pentane-2,3-diol) You will identify types of compounds from the hyd ...
... alcohols (e.g., pentan-2-ol), carboxylic acids (e.g., pentanoic acid) and esters (e.g., methyl pentanoate), and with multiple occurrences of the functional group limited to halogens (e.g., 2bromo-1-chloropentane) and alcohols (e.g., pentane-2,3-diol) You will identify types of compounds from the hyd ...
Aspirin - Community Colleges of Spokane
... In this experiment, you will synthesize acetylsalicylic acid from salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. In order to understand this synthesis, you should become familiar with the four functional groups involved. Functional groups are used as a means of classifying the vast number organic compounds. K ...
... In this experiment, you will synthesize acetylsalicylic acid from salicylic acid and acetic anhydride. In order to understand this synthesis, you should become familiar with the four functional groups involved. Functional groups are used as a means of classifying the vast number organic compounds. K ...
Chapter 4 – Carbon
... •Sulfhydryl groups help stabilize the structure of proteins. •A phosphate group (-OPO32-) consists of phosphorus bound to four O atoms (three with single bonds and one with a double bond). •A phosphate group connects to the C backbone via one of its O atoms. •Phosphate groups are anions with two neg ...
... •Sulfhydryl groups help stabilize the structure of proteins. •A phosphate group (-OPO32-) consists of phosphorus bound to four O atoms (three with single bonds and one with a double bond). •A phosphate group connects to the C backbone via one of its O atoms. •Phosphate groups are anions with two neg ...
Biehl PPT Part2
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
... From ethyl benzene? Side-chain oxidation!!!! Appears as if we could start with benzoic acid and introduce ethyl group by EtLi. ...
Chapter 2. CLASSIFICATION AND NOMENCLATURE OF ORGANIC
... Heterocyclic compounds. They contain a cyclic skeleton having at least one heteroatom, an atom that is not carbon. The most common heteroatoms are nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. More than one heteroatom may be present and these atoms may be identical or different. The structures of some natural hetero ...
... Heterocyclic compounds. They contain a cyclic skeleton having at least one heteroatom, an atom that is not carbon. The most common heteroatoms are nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. More than one heteroatom may be present and these atoms may be identical or different. The structures of some natural hetero ...
Carbonyl Compounds Prior Knowledge
... be able to apply IUPAC rules for nomenclature to alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms understand that alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary understand that tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidised understand that primar ...
... be able to apply IUPAC rules for nomenclature to alcohols, aldehydes, ketones and carboxylic acids limited to chains with up to 6 carbon atoms understand that alcohols can be classified as primary, secondary or tertiary understand that tertiary alcohols are not easily oxidised understand that primar ...
Hydrogen bonding
... • Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride) has the formula SOCl2. • The two other products of the reaction (sulphur dioxide and HCl) are both gases. That means that they separate themselves from the reaction mixture. ...
... • Sulphur dichloride oxide (thionyl chloride) has the formula SOCl2. • The two other products of the reaction (sulphur dioxide and HCl) are both gases. That means that they separate themselves from the reaction mixture. ...
Solution 1. - TutorBreeze.com
... (vii) Ketal :- Dialkoxyalkanes are called ketals. In Ketals , the two alkoxy groups are present on the same carbon within the chain. ...
... (vii) Ketal :- Dialkoxyalkanes are called ketals. In Ketals , the two alkoxy groups are present on the same carbon within the chain. ...
organic chemistry - Mr. Walsh`s AP Chemistry
... - hydrocarbons are classified according to whether or not they have multiple bonds 1. Alkanes suffix -ane All bonds in carbon chain or ring are single bonds 2. Alkenes suffix -ene Hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds between carbon atoms 3. Alkynes suffix -yne Hydrocarbon has one or more triple ...
... - hydrocarbons are classified according to whether or not they have multiple bonds 1. Alkanes suffix -ane All bonds in carbon chain or ring are single bonds 2. Alkenes suffix -ene Hydrocarbon has one or more double bonds between carbon atoms 3. Alkynes suffix -yne Hydrocarbon has one or more triple ...
Elias lecture chemistry of chlorine 2016 nov
... On dilution in water, however, a cloudy liquid forms. This consists of droplets of pine oil containing dissolved PCMX. These are held dispersed in water by a layer of soap molecules arranged with their tails in the pine oil and their heads in the water, Figure 13. These droplets are big enough to sc ...
... On dilution in water, however, a cloudy liquid forms. This consists of droplets of pine oil containing dissolved PCMX. These are held dispersed in water by a layer of soap molecules arranged with their tails in the pine oil and their heads in the water, Figure 13. These droplets are big enough to sc ...
Lesson 1 Theme: Classification and nomenclature of organic
... Heterocyclic compounds. They contain a cyclic skeleton having at least one heteroatom, an atom that is not carbon. The most common heteroatoms are nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. More than one heteroatom may be present and these atoms may be identical or different. The structures of some natural hetero ...
... Heterocyclic compounds. They contain a cyclic skeleton having at least one heteroatom, an atom that is not carbon. The most common heteroatoms are nitrogen, oxygen, or sulfur. More than one heteroatom may be present and these atoms may be identical or different. The structures of some natural hetero ...
MALLOTUS PHILIPPENSIS Research Article
... against the fungi such as A. flavus and C. albicans may be due to the presence of secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, phenolic groups and steroids as suggested by previous reports25,26,27. The significant activity of the results against the fungi, A. flavus and Can ...
... against the fungi such as A. flavus and C. albicans may be due to the presence of secondary metabolites such as flavonoids, phenolic groups and steroids as suggested by previous reports25,26,27. The significant activity of the results against the fungi, A. flavus and Can ...
2202 Chapter 9 10 11 Partial
... represented by an italicized "o" meta- means positions 1 and 3 and is represented by an italicized "m" para- means positions 1 and 4 and is represented by an italicized "p" ...
... represented by an italicized "o" meta- means positions 1 and 3 and is represented by an italicized "m" para- means positions 1 and 4 and is represented by an italicized "p" ...
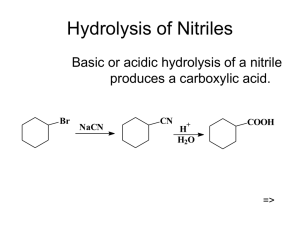
Hydrolysis of Nitriles
... Mechanism is nucleophilic addition of the alcohol to the carbonyl as chloride ion leaves, then deprotonation. O ...
... Mechanism is nucleophilic addition of the alcohol to the carbonyl as chloride ion leaves, then deprotonation. O ...
23 • Organic Chemistry
... Given a formula, you can tell that it contains only single bonds because it fits the alkane formula. As the molecules increase in size, they tend to be liquids and ...
... Given a formula, you can tell that it contains only single bonds because it fits the alkane formula. As the molecules increase in size, they tend to be liquids and ...
Carboxylic Acids
... Carboxylic acids are generally characterized by their distinctive smell or sour/tangy taste. They are found in citrus filled fruits such as apples, rhubarb, grapes and other fruits with high acidity Carboxylic acids are also produced when an alcohol is oxidized accordingly. This creates the double b ...
... Carboxylic acids are generally characterized by their distinctive smell or sour/tangy taste. They are found in citrus filled fruits such as apples, rhubarb, grapes and other fruits with high acidity Carboxylic acids are also produced when an alcohol is oxidized accordingly. This creates the double b ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.