Experiment 5b Fermentation of carbohydrates Advisor
... after partial oxidation, as electron acceptor. Fermenting organisms gain fewer ATP molecules from each molecule of food they oxidize than aerobically respiring organisms. They excrete large quantities of only partially oxidized products during growth. These products may be used as indicator compound ...
... after partial oxidation, as electron acceptor. Fermenting organisms gain fewer ATP molecules from each molecule of food they oxidize than aerobically respiring organisms. They excrete large quantities of only partially oxidized products during growth. These products may be used as indicator compound ...
activity 1-071510 - ids
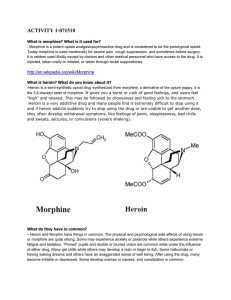
... heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
... heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
Regents Unit 15b: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, & Esters
... over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
... over corresponding alkane. • Also can form hydrogen bonds with water so the smaller acids are pretty soluble. ...
Biochem basics POGIL
... in your body, everything in a plant, everything in a virus, etc. is made of atoms. The structures and properties of the molecules in an organism determine the features and properties of the organism. Which molecules are polar, which are nonpolar? Which molecules have acidic properties, which have ba ...
... in your body, everything in a plant, everything in a virus, etc. is made of atoms. The structures and properties of the molecules in an organism determine the features and properties of the organism. Which molecules are polar, which are nonpolar? Which molecules have acidic properties, which have ba ...
Naming organic compounds
... Ketones Ketones also contain a carbonyl functional group, but in ketones it is never on the end of a carbon chain. Ketones end in the letters '-one'. The naming rules apply, as before. For example: ...
... Ketones Ketones also contain a carbonyl functional group, but in ketones it is never on the end of a carbon chain. Ketones end in the letters '-one'. The naming rules apply, as before. For example: ...
10.3 Alcohols
... longest continuous chain that includes the carbon attached to the -OH group. • Number the carbons in this chain so that the carbon attached to the -OH group has the lowest number. • Drop the -e ending from the name of the parent alkane and replace it with –ol • Alcohols containing two or three -OH g ...
... longest continuous chain that includes the carbon attached to the -OH group. • Number the carbons in this chain so that the carbon attached to the -OH group has the lowest number. • Drop the -e ending from the name of the parent alkane and replace it with –ol • Alcohols containing two or three -OH g ...
4.4 Formation of Esters from Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
... reaction because it breaks up the ester and adds a water molecule in the process. Note that a water molecule is removed in the process of forming the ester from the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. The water comes from removing an OH group on the carboxylic acid and combining it with a H. One can sh ...
... reaction because it breaks up the ester and adds a water molecule in the process. Note that a water molecule is removed in the process of forming the ester from the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. The water comes from removing an OH group on the carboxylic acid and combining it with a H. One can sh ...
Proceedings of the Indiana Academy of Science
... and toxic solvents, and expensive glassware. Furthermore, their completion requires longer than 50 minutes. Such constraints limit the number of organic synthesis experiments, in which products are isolated, purified, and characterized, that are amenable for use in high school. The student's laborat ...
... and toxic solvents, and expensive glassware. Furthermore, their completion requires longer than 50 minutes. Such constraints limit the number of organic synthesis experiments, in which products are isolated, purified, and characterized, that are amenable for use in high school. The student's laborat ...
Module 02.indd
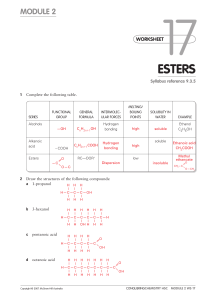
... For esters having the same number of carbon atoms in the molecule, does boiling point depend significantly upon the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group (as opposed to the number in the acyl group—that is, in the ‘anoate’ part of the molecule)? Justify your answer. For esters with the same tota ...
... For esters having the same number of carbon atoms in the molecule, does boiling point depend significantly upon the number of carbon atoms in the alkyl group (as opposed to the number in the acyl group—that is, in the ‘anoate’ part of the molecule)? Justify your answer. For esters with the same tota ...
INTRODUCTION
... Secondary alcohols (OH attached to a non-terminal carbon) may be oxidized in a single stage to the corresponding ketone. The general reaction is: secondary alcohol + oxidizing agent ketone ...
... Secondary alcohols (OH attached to a non-terminal carbon) may be oxidized in a single stage to the corresponding ketone. The general reaction is: secondary alcohol + oxidizing agent ketone ...
Chemistry Project on Carboxyl Acids
... Carboxylic acids are polar. As they are both hydrogen-bond acceptors (the carbonyl) and hydrogen-bond donors (the hydroxyl), they also participate in hydrogen bonding. Smaller carboxylic acids (1 to 5 carbons) are soluble with water, whereas higher carboxylic acids are less soluble due to the increa ...
... Carboxylic acids are polar. As they are both hydrogen-bond acceptors (the carbonyl) and hydrogen-bond donors (the hydroxyl), they also participate in hydrogen bonding. Smaller carboxylic acids (1 to 5 carbons) are soluble with water, whereas higher carboxylic acids are less soluble due to the increa ...
Chapter 22 HEIN
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Alcohols 3. Form the parent alcohol name by replacing the final –e of the corresponding alkane by –ol. When isomers are possible, locate the position of the –OH group by placing the number (hyphenated) of the carbon atom to which the –OH is bonded immediately before the paren ...
... IUPAC Rules for Naming Alcohols 3. Form the parent alcohol name by replacing the final –e of the corresponding alkane by –ol. When isomers are possible, locate the position of the –OH group by placing the number (hyphenated) of the carbon atom to which the –OH is bonded immediately before the paren ...
Ch03macromolecules - Environmental
... Structural differences create important functional significance ...
... Structural differences create important functional significance ...
Organic/Biological Chemistry
... • Organic compounds that contain one carbon atom that is attached to four different atoms or groups are chiral. • The carbon atom attached to the four different moieties is called a stereogenic carbon. ...
... • Organic compounds that contain one carbon atom that is attached to four different atoms or groups are chiral. • The carbon atom attached to the four different moieties is called a stereogenic carbon. ...
formic (methanoic) acid
... In this reaction between acetic acid and water, the hydrogen ion from the acid is transferred to water, producing the hydronium ion and the acetate ion. Because the reaction has increased the hydrogen ion concentration (really hydronium-ion concentration) of the water, acetic acid is an acid. The ac ...
... In this reaction between acetic acid and water, the hydrogen ion from the acid is transferred to water, producing the hydronium ion and the acetate ion. Because the reaction has increased the hydrogen ion concentration (really hydronium-ion concentration) of the water, acetic acid is an acid. The ac ...
Chapter 13 – Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, and Thioethers
... bind in only one way before the reaction begins. This ensures only one product comes out and that product may not be the one preferred by standard organic methods. Oxidation In an oxidation one of two things will happen. Either an external reagent will remove two hydrogen atoms (resulting in the con ...
... bind in only one way before the reaction begins. This ensures only one product comes out and that product may not be the one preferred by standard organic methods. Oxidation In an oxidation one of two things will happen. Either an external reagent will remove two hydrogen atoms (resulting in the con ...
102 Lecture Ch17
... (except PCC, which forms aldehydes) • Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with most oxidizing agents, such as Tollens’reagent (AgNO3/NH3) - alcohols do not react with Tollens CrO3 OH ...
... (except PCC, which forms aldehydes) • Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with most oxidizing agents, such as Tollens’reagent (AgNO3/NH3) - alcohols do not react with Tollens CrO3 OH ...
Lect 9 Alcohols
... catalyst of phosphoric acid under high temperature and pressure of 50-120 atm. • Methanol is produced from synthesis gas, where carbon monoxide and 2 equivalents of hydrogen gas are combined to produce methanol using a copper, zinc oxide and aluminium oxide catalyst at 250°C and a pressure of 50-100 ...
... catalyst of phosphoric acid under high temperature and pressure of 50-120 atm. • Methanol is produced from synthesis gas, where carbon monoxide and 2 equivalents of hydrogen gas are combined to produce methanol using a copper, zinc oxide and aluminium oxide catalyst at 250°C and a pressure of 50-100 ...
Part B: Short Written Response - bourre-chem-11
... ______22. Aldehydes and ketones both contain the carbonyl group(an O double bonded to a carbon). How are they different? a) aldehydes have the carbonyls attached at the end of the carbon chain while ketones have the carbonyl attached in the middle somewhere b) ketones have the carbonyls attached at ...
... ______22. Aldehydes and ketones both contain the carbonyl group(an O double bonded to a carbon). How are they different? a) aldehydes have the carbonyls attached at the end of the carbon chain while ketones have the carbonyl attached in the middle somewhere b) ketones have the carbonyls attached at ...
shyam_organic
... METHODS OF SEPERATION OF MONOFUNCTIONAL ORGANIC COMPOUNDS . I) Seperation based on differences In chemical properties of the Compounds: 1. Toluene and Aniline : Extraction with dil. HCl ; Aniline passes into the aqueous layer as salt and may be recovered by neutralization. 2. Phenol and Toluene : Se ...
... METHODS OF SEPERATION OF MONOFUNCTIONAL ORGANIC COMPOUNDS . I) Seperation based on differences In chemical properties of the Compounds: 1. Toluene and Aniline : Extraction with dil. HCl ; Aniline passes into the aqueous layer as salt and may be recovered by neutralization. 2. Phenol and Toluene : Se ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.