Department of LD - Covenant University
... All class assignments to be submitted promptly Pay attention to class work Active participation in all activities No Academic dishonesty - Plagiarism, Improper collaboration in group work, copy or using unauthorized aids in tests and examinations TOPICS FOR ASSIGNMENTS 1. In the qualitative test for ...
... All class assignments to be submitted promptly Pay attention to class work Active participation in all activities No Academic dishonesty - Plagiarism, Improper collaboration in group work, copy or using unauthorized aids in tests and examinations TOPICS FOR ASSIGNMENTS 1. In the qualitative test for ...
CHEM 203 Topics Discussed on Nov. 25 Toxic and carcinogenic
... IMPORTANT: PCC is used ONLY in anhydrous (=water-free) media, while Jones rgt. is an aqueous solution. This seemingly minor difference has a major influence on the course of the reaction of primary alcohols with the two reagents. The Jones reagent: oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids a ...
... IMPORTANT: PCC is used ONLY in anhydrous (=water-free) media, while Jones rgt. is an aqueous solution. This seemingly minor difference has a major influence on the course of the reaction of primary alcohols with the two reagents. The Jones reagent: oxidation of primary alcohols to carboxylic acids a ...
07 Aromatic compounds. Acids of arom.s.,their salts, esters,amides
... This reaction may be used for assay of vitamin K. For this reason reduce obtained 2-methyl-1,4- naphthoquinone to 1,4-dioxi-2-methylnaphtaline and titrate with 0.2N Ce(SO4)3 using a o-phenantroline as an indicator. ...
... This reaction may be used for assay of vitamin K. For this reason reduce obtained 2-methyl-1,4- naphthoquinone to 1,4-dioxi-2-methylnaphtaline and titrate with 0.2N Ce(SO4)3 using a o-phenantroline as an indicator. ...
Document
... B. When alcohols are oxidized with potassium permanganate, in the presence of sulphuric acid, the colour of the reaction mixture changes form orange to green. C. 2-cetopentanoic acid and oxalic acid are obtained when 1-methyl-1, 4cyclohexadiene is oxidized, with KMnO4, in presence of sulphuric acid. ...
... B. When alcohols are oxidized with potassium permanganate, in the presence of sulphuric acid, the colour of the reaction mixture changes form orange to green. C. 2-cetopentanoic acid and oxalic acid are obtained when 1-methyl-1, 4cyclohexadiene is oxidized, with KMnO4, in presence of sulphuric acid. ...
Final Study Guide
... compounds and draw their structural formulas. You will need to be very familiar with the organic reactions we have studies over the course, including those of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, thiols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines and amides. ...
... compounds and draw their structural formulas. You will need to be very familiar with the organic reactions we have studies over the course, including those of alkenes, alkynes, alcohols, phenols, ethers, thiols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines and amides. ...
Carboxylic Acid Questions 1.-Arrange the following in order of (i
... First, note that we have an homologous series of C3 to C6 acids we are trying to make. Here is a scheme collecting possible syntheses together (based on the more important reactions) ...
... First, note that we have an homologous series of C3 to C6 acids we are trying to make. Here is a scheme collecting possible syntheses together (based on the more important reactions) ...
UNIT_3_PART_5[3]
... When the metal involved in the ionic bond has more than one oxidations state/possible charge we need to identify which ion it is. This usually occurs with the transition metals. Any ion that appears on your common ion sheet more than once is one of these types of metals. There are 2 ways to do thi ...
... When the metal involved in the ionic bond has more than one oxidations state/possible charge we need to identify which ion it is. This usually occurs with the transition metals. Any ion that appears on your common ion sheet more than once is one of these types of metals. There are 2 ways to do thi ...
Carboxylic Acids - University of Nebraska Omaha
... • Fischer esterification is an equilibrium reaction. • By careful control of experimental conditions, it is possible to prepare esters in high yield. • If the alcohol is inexpensive relative to the carboxylic acid, it can be used in excess to drive the equilibrium to the right (toward ester ...
... • Fischer esterification is an equilibrium reaction. • By careful control of experimental conditions, it is possible to prepare esters in high yield. • If the alcohol is inexpensive relative to the carboxylic acid, it can be used in excess to drive the equilibrium to the right (toward ester ...
Alcohols: Structure and Physical Properties
... Oxidation of methanol produces the aldehyde methanal ...
... Oxidation of methanol produces the aldehyde methanal ...
Day 8
... 12. Now, have each member of your group take a carbon atom and add 4 bonds. Add a hydrogen, chlorine (green), bromine (orange) and iodine (purple) to each stick. Compare your molecules by trying to superimpose them on each other (all atoms line up when one molecule is placed over the other). Did any ...
... 12. Now, have each member of your group take a carbon atom and add 4 bonds. Add a hydrogen, chlorine (green), bromine (orange) and iodine (purple) to each stick. Compare your molecules by trying to superimpose them on each other (all atoms line up when one molecule is placed over the other). Did any ...
Lecture 2
... Ethanol in alcoholic beverages has been consumed by humans since prehistoric times. The consumption of large doses of ethanol causes drunkenness (intoxication). Depending upon the dose and the regularity of its consumption, ethanol can cause acute respiratory failure or death. Because ethanol impair ...
... Ethanol in alcoholic beverages has been consumed by humans since prehistoric times. The consumption of large doses of ethanol causes drunkenness (intoxication). Depending upon the dose and the regularity of its consumption, ethanol can cause acute respiratory failure or death. Because ethanol impair ...
Problem Set 12-2: Organic Chemistry
... 8. Which of the 12 functional groups are soluble in water? Alcohol, carboxylic acids, amides, amines, aldehydes and ketones, esters. Solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. 9. Give 3 factors that determine solubility in water. Polarity of molecule Ability to form hydrogen bonds Len ...
... 8. Which of the 12 functional groups are soluble in water? Alcohol, carboxylic acids, amides, amines, aldehydes and ketones, esters. Solubility decreases with the length of the carbon chain. 9. Give 3 factors that determine solubility in water. Polarity of molecule Ability to form hydrogen bonds Len ...
Organic_Chemistry - TangHua2012-2013
... How many carbons are there in carboxylic acid? The number of carbons Prefixes Prefix + oic + Acid That is how the name comes from! ...
... How many carbons are there in carboxylic acid? The number of carbons Prefixes Prefix + oic + Acid That is how the name comes from! ...
Organic Chemistry
... molecules. Functional groups can have decisive influence on the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Molecules are classified on the basis of their functional groups. Alcohols, for example, have the subunit C-O-H. All alcohols tend to be somewhat hydrophilic, usually form esters, a ...
... molecules. Functional groups can have decisive influence on the chemical and physical properties of organic compounds. Molecules are classified on the basis of their functional groups. Alcohols, for example, have the subunit C-O-H. All alcohols tend to be somewhat hydrophilic, usually form esters, a ...
Alcohol, Aldehydes and Acids
... the alcohol in beverages. It can also be made from ethene by the addition of water for nonbeverage use, like an additive to gassoline to make "gasahol." 2-Propanol (better known as isopropyl alcohol) is in (with some water) rubbing alcohol. It is also used in gasoline to prevent freezing of the gas ...
... the alcohol in beverages. It can also be made from ethene by the addition of water for nonbeverage use, like an additive to gassoline to make "gasahol." 2-Propanol (better known as isopropyl alcohol) is in (with some water) rubbing alcohol. It is also used in gasoline to prevent freezing of the gas ...
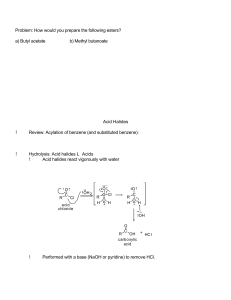
Problem: How would you prepare the following esters? a) Butyl
... The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated by using a gentler reducing agent such as lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride. O CCl 1. LiAlH(OC)CH3) 3, ether ...
... The aldehyde intermediate can be isolated by using a gentler reducing agent such as lithium tri-tert-butoxyaluminum hydride. O CCl 1. LiAlH(OC)CH3) 3, ether ...
Chapter 18 - Hope Charter School
... 1) Very reactive, so most don’t exist and if they do, it isn’t for long 2) They can be synthesized from other organic compounds 3) Melting and boiling points increase with increasing chain lengths 4) Similar properties to Alkenes 5) melting and boiling points are higher than alkanes 6) they undergo ...
... 1) Very reactive, so most don’t exist and if they do, it isn’t for long 2) They can be synthesized from other organic compounds 3) Melting and boiling points increase with increasing chain lengths 4) Similar properties to Alkenes 5) melting and boiling points are higher than alkanes 6) they undergo ...
Ch 20 review - Organic Chemistry at CU Boulder
... Sulfonic acids are even more acidic because they have three possible resonance forms, and also a bigger partial positive charge on sulfur. They usually have pKas around -3. These are compounds that we saw how to make by sulfonation reactions in Ch. 16. ...
... Sulfonic acids are even more acidic because they have three possible resonance forms, and also a bigger partial positive charge on sulfur. They usually have pKas around -3. These are compounds that we saw how to make by sulfonation reactions in Ch. 16. ...
Skill Sheet 19-C Naming Chemical Compounds
... forming the compound, the numbers of atoms of each element in one molecule, and even some indication, perhaps, of the arrangement of the atoms when they form the molecule. In addition to having a unique chemical formula, each compound has a unique name. These names provide scientists with valuable i ...
... forming the compound, the numbers of atoms of each element in one molecule, and even some indication, perhaps, of the arrangement of the atoms when they form the molecule. In addition to having a unique chemical formula, each compound has a unique name. These names provide scientists with valuable i ...
chromomixes (2)
... Used to analyze metal ions and organic compounds in solutions. It uses liquids which may incorporate hydrophilic, insoluble molecules. ...
... Used to analyze metal ions and organic compounds in solutions. It uses liquids which may incorporate hydrophilic, insoluble molecules. ...
CrO3/Al2O3: Rapid oxidation of alcohols to carbonyl compounds in
... to carboxylic acids, which is common in the some other reagents, was not observed. One of the interesting features of this reagent was its ability to convert hydrobenzoin to benzoin contrasting to the results obtained by many other reagents, which cleaved the carbon-carbon bond to give the correspon ...
... to carboxylic acids, which is common in the some other reagents, was not observed. One of the interesting features of this reagent was its ability to convert hydrobenzoin to benzoin contrasting to the results obtained by many other reagents, which cleaved the carbon-carbon bond to give the correspon ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... (b)What are ambidentate ligands ? Explain with example. 12. (a)Give the resonating structures of NO2 & N2O5 . (b)Complete the following reactions: (i) 4Al + 3O2 → (ii)C2H4 + O2 OR Write the steps involved in Contact’s process 13. For the reaction: NO2 (g) + CO2 (g) → CO2 (g) + NO(g) The proposed mec ...
... (b)What are ambidentate ligands ? Explain with example. 12. (a)Give the resonating structures of NO2 & N2O5 . (b)Complete the following reactions: (i) 4Al + 3O2 → (ii)C2H4 + O2 OR Write the steps involved in Contact’s process 13. For the reaction: NO2 (g) + CO2 (g) → CO2 (g) + NO(g) The proposed mec ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Identify the compound with the molecular mass 72 which responds to iodoform test. It absorbs in UV spectrum at 275 nm (max is 17). In IR spectrum the various bands obtained are i) 2941 ii) 1715 and iii) 1460 cm-1. In mass spectrum, the fragmentations are obtained at m/e values of 72, 43 (maximum in ...
... Identify the compound with the molecular mass 72 which responds to iodoform test. It absorbs in UV spectrum at 275 nm (max is 17). In IR spectrum the various bands obtained are i) 2941 ii) 1715 and iii) 1460 cm-1. In mass spectrum, the fragmentations are obtained at m/e values of 72, 43 (maximum in ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.






![UNIT_3_PART_5[3]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013887813_1-e384d1258759e65beb0bedcc6881c6f9-300x300.png)