PP Aldehyde and ketone
... contains a copper(II) complex ion giving a blue solution on warming, it will oxidise aliphatic (but not aromatic) aldehydes the copper(II) is reduced to copper(I) a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, is formed ...
... contains a copper(II) complex ion giving a blue solution on warming, it will oxidise aliphatic (but not aromatic) aldehydes the copper(II) is reduced to copper(I) a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, is formed ...
Chapter 23: Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions
... hydrocarbons of similar shape and size. Also, because of polarity and hydrogen bonding, ethanol is completely miscible with water. In fact, once they are mixed, it is difficult to separate water and ethanol completely. Distillation is used to remove ethanol from water, but even after that process is ...
... hydrocarbons of similar shape and size. Also, because of polarity and hydrogen bonding, ethanol is completely miscible with water. In fact, once they are mixed, it is difficult to separate water and ethanol completely. Distillation is used to remove ethanol from water, but even after that process is ...
Document
... • by careful control of experimental conditions, it is possible to prepare esters in high yield • if the alcohol is inexpensive relative to the carboxylic acid, it can be used in excess to drive the equilibrium to the right • alternatively, water can be removed by azeotropic distillation and a Dean- ...
... • by careful control of experimental conditions, it is possible to prepare esters in high yield • if the alcohol is inexpensive relative to the carboxylic acid, it can be used in excess to drive the equilibrium to the right • alternatively, water can be removed by azeotropic distillation and a Dean- ...
Chapter 1--Title
... used to make any of the other derivatives Since acyl chlorides are easily made from carboxylic acids they provide a way to synthesize any acyl compound from a carboxylic acid Acyl chlorides react readily with water, but this is not a synthetically useful reaction ...
... used to make any of the other derivatives Since acyl chlorides are easily made from carboxylic acids they provide a way to synthesize any acyl compound from a carboxylic acid Acyl chlorides react readily with water, but this is not a synthetically useful reaction ...
Study Guide Exam 2 and 3 Sp2011
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
... If you are trying to determine if an amine is a primary, secondary or tertiary, you now replace the C with the N and the OH with lone pair of electrons on the picture for alcohols. Depending on how many other carbon atoms are bound to the nitrogen determines if it is primary, secondary or tertiary. ...
Alcohols
... methyl alcohol (methanol, or wood alcohol). As little as 10 mL of methanol has been known to cause permanent blindness, and 30 ml has resulted in death!!! ...
... methyl alcohol (methanol, or wood alcohol). As little as 10 mL of methanol has been known to cause permanent blindness, and 30 ml has resulted in death!!! ...
Dr.Farshid Zand Department of chemistry Organic Chem 233 L San
... Compounds or the Merck Index for the original literature on each of your possible compounds. The procedures given in the older literature may give you improved isolation or recrystallization procedures as compared to the general methods given below. You may need to consult with your instructor for a ...
... Compounds or the Merck Index for the original literature on each of your possible compounds. The procedures given in the older literature may give you improved isolation or recrystallization procedures as compared to the general methods given below. You may need to consult with your instructor for a ...
Page 1 - WordPress.com
... Predict the m/z values of the two most abundant fragments in the mass spectrum of pentan-2-one. Fragment 1 .................................................Fragment 2 ...
... Predict the m/z values of the two most abundant fragments in the mass spectrum of pentan-2-one. Fragment 1 .................................................Fragment 2 ...
© NCERT not to be republished
... shaking till a definite dark colour of iodine persists. Allow the reactants to remain at room temperature for 2-3 minutes. If no iodoform separates, warm the reaction mixture in a water bath at 60°C. Add more drops of potassium iodide–iodine reagent. If colour of iodine disappears continue addition ...
... shaking till a definite dark colour of iodine persists. Allow the reactants to remain at room temperature for 2-3 minutes. If no iodoform separates, warm the reaction mixture in a water bath at 60°C. Add more drops of potassium iodide–iodine reagent. If colour of iodine disappears continue addition ...
Chapter 12. Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
... potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) also give red ppt. of CU2O. (d) Schiff’s reagent It is an aqueous solution of magenta or pink coloured rosaniline hydrochloride which has been decolourised by passing SO2, Aldehyde ...
... potassium tartrate which is also called, Rochelle salt.] (c) Benedict solution With it, aldehydes (except benzaldehyde) also give red ppt. of CU2O. (d) Schiff’s reagent It is an aqueous solution of magenta or pink coloured rosaniline hydrochloride which has been decolourised by passing SO2, Aldehyde ...
COMPOUNDS OF CARBON CONTAINING NITROGEN
... You know that aliphatic amines contain one or more alkyl groups in place of hydrogen atoms of ammonia. Since alkyl groups are electron releasing groups, they increase the electron density on nitrogen. This makes the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom to be easily available for sharing and hence ...
... You know that aliphatic amines contain one or more alkyl groups in place of hydrogen atoms of ammonia. Since alkyl groups are electron releasing groups, they increase the electron density on nitrogen. This makes the lone pair of electrons on nitrogen atom to be easily available for sharing and hence ...
m4 carbonyl
... contains a copper(II) complex ion giving a blue solution on warming, it will oxidise aliphatic (but not aromatic) aldehydes the copper(II) is reduced to copper(I) a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, is formed ...
... contains a copper(II) complex ion giving a blue solution on warming, it will oxidise aliphatic (but not aromatic) aldehydes the copper(II) is reduced to copper(I) a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, is formed ...
TYPES OF HYBRIDIZATION AND GEOMETRY OF MOLECULES
... The Factors affecting acidity of carboxylic acids. The different ways to make carboxylic acids Salt formation reactions of carboxylic acids The nucleophilic substitution reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the specific products formed in each case. The chemistry of carboxylic acid derivatives ...
... The Factors affecting acidity of carboxylic acids. The different ways to make carboxylic acids Salt formation reactions of carboxylic acids The nucleophilic substitution reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the specific products formed in each case. The chemistry of carboxylic acid derivatives ...
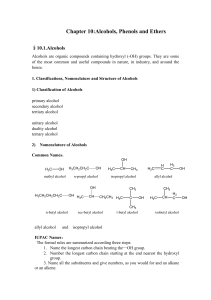
Chapter 10:Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
... absorptions for ethers. Most ethers give a moderate to strong C-O stretch around 1000 to 2000cm-1(in the fingerprint region), but many compounds other than ethers give similar absorptions. Nevertheless, the IR spetrum can be useful because it shows the absence of carbonyl(C=O) groups. If the molecu ...
... absorptions for ethers. Most ethers give a moderate to strong C-O stretch around 1000 to 2000cm-1(in the fingerprint region), but many compounds other than ethers give similar absorptions. Nevertheless, the IR spetrum can be useful because it shows the absence of carbonyl(C=O) groups. If the molecu ...
chapter20(10-27-14)
... • Other alcohols Ethylene glycol (ethane-1,2-diol) – automotive antifreeze Phenol (benzenol) – production of adhesives and plastics ...
... • Other alcohols Ethylene glycol (ethane-1,2-diol) – automotive antifreeze Phenol (benzenol) – production of adhesives and plastics ...
Lectures 36-38 - U of L Class Index
... Calculating pH of an Acidic Solution A strong acid, HA, (pKa < 0) dissociates fully in water: A stronger acid than H3O+ (pKa = 0) generates H3O+ and conj. base, A-. This effect is known as solvent leveling: No acid stronger than the conjugate acid of the solvent can exist in any solution of that so ...
... Calculating pH of an Acidic Solution A strong acid, HA, (pKa < 0) dissociates fully in water: A stronger acid than H3O+ (pKa = 0) generates H3O+ and conj. base, A-. This effect is known as solvent leveling: No acid stronger than the conjugate acid of the solvent can exist in any solution of that so ...
chapter 8-carboxyl compounds
... - the aromatic nucleus (benzene ring) and multiple bonds are electron-withdrawing groups and possess negative inductive ...
... - the aromatic nucleus (benzene ring) and multiple bonds are electron-withdrawing groups and possess negative inductive ...
Biosynthesis of 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid (2
... nitrilase from Acidovorax facilis 72W for the synthesis of 3-hydroxy carboxylic acids [28]. Although an efficient acetone cyanohydrin-hydrolyzing enzymatic system could be developed in the future, it has to be stressed that this route is only partially based on biotechnology as the nitrile will obvi ...
... nitrilase from Acidovorax facilis 72W for the synthesis of 3-hydroxy carboxylic acids [28]. Although an efficient acetone cyanohydrin-hydrolyzing enzymatic system could be developed in the future, it has to be stressed that this route is only partially based on biotechnology as the nitrile will obvi ...
SECONDARY METABOLISM: THE BUILDING BLOCKS AND
... is the product from three acetyl-CoA molecules, but only five of mevalonate’s six carbons are used, the carboxyl group being lost. The alternative precursor deoxyxylulose phosphate, a straight-chain sugar derivative, undergoes a skeletal rearrangement to form the branchedchain isoprene unit. • C6 C3 ...
... is the product from three acetyl-CoA molecules, but only five of mevalonate’s six carbons are used, the carboxyl group being lost. The alternative precursor deoxyxylulose phosphate, a straight-chain sugar derivative, undergoes a skeletal rearrangement to form the branchedchain isoprene unit. • C6 C3 ...
NITRO COMPOUNDS
... For nitrating compounds containing electron attracting or deactivating group such as – COOH or when it is desired to introduce more than one nitro group a suitably strong nitrating mixture has to employed and the reaction is carried out at higher temperature . Nitro benzene and m-dinitrobenzene can ...
... For nitrating compounds containing electron attracting or deactivating group such as – COOH or when it is desired to introduce more than one nitro group a suitably strong nitrating mixture has to employed and the reaction is carried out at higher temperature . Nitro benzene and m-dinitrobenzene can ...
A Straightforward Route to Enantiopure Pyrrolizidines and
... special comments regarding preparative applicability of such esters. It is noteworthy that the experiment described is, to the best of our knowledge, the first example for preparation of an alkyl trichloromethanesulfonate on this route starting from an alcohol. In addition to this initial aim, the u ...
... special comments regarding preparative applicability of such esters. It is noteworthy that the experiment described is, to the best of our knowledge, the first example for preparation of an alkyl trichloromethanesulfonate on this route starting from an alcohol. In addition to this initial aim, the u ...
Learning Guide for Chapter 24
... "hydrolysis" comes from "hydro" meaning water and "lysis" meaning to cut, implying that these compounds are cut with water. Acid chlorides, anhydrides - react easily with water. Reactions involving these functional groups must be kept dry in order to avoid this side reaction. During the work-up the ...
... "hydrolysis" comes from "hydro" meaning water and "lysis" meaning to cut, implying that these compounds are cut with water. Acid chlorides, anhydrides - react easily with water. Reactions involving these functional groups must be kept dry in order to avoid this side reaction. During the work-up the ...
United States Patent Boyle et aI.
... MESO-MONOIODO-SUBSTITUTED TETRAMACROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR MAKING AND USING THE SAME ...
... MESO-MONOIODO-SUBSTITUTED TETRAMACROCYCLIC COMPOUNDS AND METHODS FOR MAKING AND USING THE SAME ...
Carboxylic Acids And Their Derivatives
... The Factors affecting acidity of carboxylic acids. The different ways to make carboxylic acids Salt formation reactions of carboxylic acids The nucleophilic substitution reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the specific products formed in each case. The chemistry of carboxylic acid derivatives ...
... The Factors affecting acidity of carboxylic acids. The different ways to make carboxylic acids Salt formation reactions of carboxylic acids The nucleophilic substitution reactions at the carbonyl carbon and the specific products formed in each case. The chemistry of carboxylic acid derivatives ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.