Ch 3 Student.pptx
... • Molecular compounds form between two nonmetals – The atoms in molecular compounds don’t form ions – they share electrons. For this reason the same combination of elements can form a number of different molecular compounds. ...
... • Molecular compounds form between two nonmetals – The atoms in molecular compounds don’t form ions – they share electrons. For this reason the same combination of elements can form a number of different molecular compounds. ...
Selective Oxidation Reactions of Natural Compounds with
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
... Methyltrioxorhenium (CH3ReO3, MTO) in the presence of H2O2 has proven itself as an efficient and versatile oxidation catalyst with interesting selectivity towards natural compounds, which can be oxidized under quite mild conditions [3–21]. In previous work [22] we have observed good regio- and stere ...
CHEM 263 Oct 14 revised
... Phenol has a pKa value of 10 (given this information, you should immediately recognize that it is more much acidic (about 6 orders of magnitude) than water (pKa 15.7) and methanol (pKa 16) since it has lower pKa value). As phenol is more acidic, this means that its conjugate anion is more stable. Th ...
... Phenol has a pKa value of 10 (given this information, you should immediately recognize that it is more much acidic (about 6 orders of magnitude) than water (pKa 15.7) and methanol (pKa 16) since it has lower pKa value). As phenol is more acidic, this means that its conjugate anion is more stable. Th ...
organic chemistry reaction scheme
... *Note: Lithium aluminium hydride (or Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III)), LiAlH4, is one of the few reagents that can reduce an acid to an alcohol; the initial product is an alkoxide which the alcohol is liberated by hydrolysis. The –H ion acts as a nucleophile, and can attack the carbon atom of the ...
... *Note: Lithium aluminium hydride (or Lithium tetrahydridoaluminate(III)), LiAlH4, is one of the few reagents that can reduce an acid to an alcohol; the initial product is an alkoxide which the alcohol is liberated by hydrolysis. The –H ion acts as a nucleophile, and can attack the carbon atom of the ...
Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers
... (1) Menthol is a naturally occurring terpene alcohol with a minty odor. (2) THC, the active ingredient in marijuana, contains phenol, cyclic ether and halogen functional groups. (3) Ether-type anesthetics in use today are usually halogenated compounds. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the ...
... (1) Menthol is a naturally occurring terpene alcohol with a minty odor. (2) THC, the active ingredient in marijuana, contains phenol, cyclic ether and halogen functional groups. (3) Ether-type anesthetics in use today are usually halogenated compounds. a) All three statements are true. b) Two of the ...
Click Here - GBN Pharmacy
... Halogen Compounds-Aromatic: Nomenclature, low reactivity of halo benzenes towards nucleophilic substitution, arenes. UNIT – V Alcohols: Nomenclature, classification, general methods of preparation, physical properties, hydrogen bonding, characteristic nucleophilic substitution reactions (replacement ...
... Halogen Compounds-Aromatic: Nomenclature, low reactivity of halo benzenes towards nucleophilic substitution, arenes. UNIT – V Alcohols: Nomenclature, classification, general methods of preparation, physical properties, hydrogen bonding, characteristic nucleophilic substitution reactions (replacement ...
Lipids I do pdf
... Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. ...
... Organic compounds present in living organisms, insoluble in water but able to be extracted by organic solvents such as: chloroform, acetone, benzene. ...
CHM230 - Preparation of Methyl Benzoate Preparation of Methyl
... The ester group is an important functional group that can be synthesized in a number of different ways. The low-molecular-weight esters have very pleasant odors and indeed are the major components of the flavor and odor aspects of a number of fruits. Although the natural flavor may contain nearly a ...
... The ester group is an important functional group that can be synthesized in a number of different ways. The low-molecular-weight esters have very pleasant odors and indeed are the major components of the flavor and odor aspects of a number of fruits. Although the natural flavor may contain nearly a ...
Ex. 29 Answer
... The intermolecular attractions in alkanes are van der Waals’ forces. The number of electrons in one alkane molecule increases as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule increases. Hence the strength of van der Waals’ forces between alkane molecules also increases. More heat is needed to separate ...
... The intermolecular attractions in alkanes are van der Waals’ forces. The number of electrons in one alkane molecule increases as the number of carbon atoms in the molecule increases. Hence the strength of van der Waals’ forces between alkane molecules also increases. More heat is needed to separate ...
Organic Chemistry Lecture Outline Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid
... Organic Chemistry Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions ...
... Organic Chemistry Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives and Nu Acyl Substitutions ...
Lecture 16 Aromatic Diazonium Salts
... The reactive intermediate depends on the reaction conditions. Under acidic conditions, the diazonium salt is believed to decompose into aryl cation and nitrogen. The aryl cation is highly reactive and attacked by the aryl ring that leads to cyclization. On the other hand, under neutral and basic con ...
... The reactive intermediate depends on the reaction conditions. Under acidic conditions, the diazonium salt is believed to decompose into aryl cation and nitrogen. The aryl cation is highly reactive and attacked by the aryl ring that leads to cyclization. On the other hand, under neutral and basic con ...
notes 11/28/16 Monday
... laboratory synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although ...
... laboratory synthesis, however, dehydrogenation is not practical, and cost is not as large a factor as it would be in industry. Most labs would have chromium trioxide or sodium dichromate available, and the chromic acid oxidation would be simple. PCC and the Swern oxidation would also work, although ...
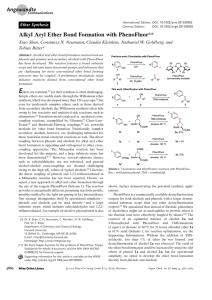
Alkyl Aryl Ether Bond Formation with PhenoFluor
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
... bond formation is appealing and orthogonal to other crosscoupling approaches. The Mitsunobu reaction has been developed for this purpose, and a large substrate scope has been demonstrated.[6, 7] However, several substrate classes, such as salicylaldehydes, are not tolerated, and general alcohol–alco ...
Abstract OXIDATIVE TRANSFORMATIONS AND CYCLIZATIONS
... Section II. One-pot synthesis of 2-Substituted Quinazolines and Oxazines via Oxidative Dehydrogenation using NaOCl Quinazolines are important class of compounds frequently found in alkaloids and in many bioactive compounds. Quinazoline ring structure is an essential component in few anticancer drugs ...
... Section II. One-pot synthesis of 2-Substituted Quinazolines and Oxazines via Oxidative Dehydrogenation using NaOCl Quinazolines are important class of compounds frequently found in alkaloids and in many bioactive compounds. Quinazoline ring structure is an essential component in few anticancer drugs ...
Reactions of carboxymethylalginic acid with some N
... Reaction of H-form of carboxymethylalginic acid with aromatic amines and hydrazides of pyridinecarboxylic acids forms corresponding N-arylamides and acylhydrazides. The influence of time, temperature of reaction, solvent nature and structure of nucleophiles on the amount of aromatic fragments entere ...
... Reaction of H-form of carboxymethylalginic acid with aromatic amines and hydrazides of pyridinecarboxylic acids forms corresponding N-arylamides and acylhydrazides. The influence of time, temperature of reaction, solvent nature and structure of nucleophiles on the amount of aromatic fragments entere ...
ORGANIC NOMENCLATURE
... The aliphatics may be alkanes, alkenes or alkynes; aromatic hydrocarbons contain one or more benzene rings. It is important that students get a good grasp of the convention used in naming the simplest class, the alkanes, as the naming of other classes is an extension of alkane nomenclature. ...
... The aliphatics may be alkanes, alkenes or alkynes; aromatic hydrocarbons contain one or more benzene rings. It is important that students get a good grasp of the convention used in naming the simplest class, the alkanes, as the naming of other classes is an extension of alkane nomenclature. ...
Organic Chemistry Durham School Board March
... distinguish among the different classes of organic compounds, including alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, ethers, amines, and amides, by name and by structural formula; describe some physical properties of the classes of organic compounds in terms of solubility in different sol ...
... distinguish among the different classes of organic compounds, including alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, ethers, amines, and amides, by name and by structural formula; describe some physical properties of the classes of organic compounds in terms of solubility in different sol ...
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND CARBOXYLATE SALTS Carboxylic
... The salts of the long-chain fatty acids are known as soaps. They are extremely useful as they help oil and water mix together. Glycerol is a useful by-product of this reaction as it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which us ...
... The salts of the long-chain fatty acids are known as soaps. They are extremely useful as they help oil and water mix together. Glycerol is a useful by-product of this reaction as it can be used to make pharmaceuticals and cosmetics. So the alkaline hydrolysis of fats and oils produces soap, which us ...
Practice Exam 2
... NOTE: PLEASE NOTE THAT THIS PRACTICE TEST IS ONLY MEANT TO GIVE YOU AN IDEA OF THE TYPES OF QUESTIONS THAT I WILL ASK. REMEMBER, THE NUMBER AND NATURE OF THE TOPICS I COVER IN A PARTICULAR YEAR VARIES BASED ON TIME AND NUMEROUS OTHER FACTORS. AS AN EXAMPLE, I SEE THAT THERE IS VERY LITTLE FROM CH 7, ...
... NOTE: PLEASE NOTE THAT THIS PRACTICE TEST IS ONLY MEANT TO GIVE YOU AN IDEA OF THE TYPES OF QUESTIONS THAT I WILL ASK. REMEMBER, THE NUMBER AND NATURE OF THE TOPICS I COVER IN A PARTICULAR YEAR VARIES BASED ON TIME AND NUMEROUS OTHER FACTORS. AS AN EXAMPLE, I SEE THAT THERE IS VERY LITTLE FROM CH 7, ...
unit 6 alcohols
... NaBH4 reduces aldehydes and ketones but not acids and esters. Alcohol, ether, or water is the solvent. ...
... NaBH4 reduces aldehydes and ketones but not acids and esters. Alcohol, ether, or water is the solvent. ...
Aromatic compounds
... • Alkylation and acylation of benzene known as Friedel-Crafts rxns • In alkylation carbocation is electrophile • Formed by removing halide from alkyl halide with Lewis acid catalyst (i.e. AlCl3) • Or formed by adding proton to an alkene ...
... • Alkylation and acylation of benzene known as Friedel-Crafts rxns • In alkylation carbocation is electrophile • Formed by removing halide from alkyl halide with Lewis acid catalyst (i.e. AlCl3) • Or formed by adding proton to an alkene ...
Chapter 14: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers This chapter is the first of
... The polar hydroxyl functional group dominates the physical properties of methanol. The molecule is completely soluble in water (polar) but only partially so in hexane (nonpolar). Conversely, the nonpolar portion of 1-octanol dominates its physical properties; it is infinitely soluble in hexane and h ...
... The polar hydroxyl functional group dominates the physical properties of methanol. The molecule is completely soluble in water (polar) but only partially so in hexane (nonpolar). Conversely, the nonpolar portion of 1-octanol dominates its physical properties; it is infinitely soluble in hexane and h ...
J. Org. Chem. 2001, 66, 1672
... The aliphatic carboxylic group was efficiently reduced to the methyl group by HSiEt3 in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of a direct exhaustive reduction of aliphatic carboxylic function. Aliphatic aldehydes, acyl chlorides, anhyd ...
... The aliphatic carboxylic group was efficiently reduced to the methyl group by HSiEt3 in the presence of catalytic amounts of B(C6F5)3. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first example of a direct exhaustive reduction of aliphatic carboxylic function. Aliphatic aldehydes, acyl chlorides, anhyd ...
Compounds Containing a C=O (Carbonyl) Group
... reaction at the α-carbon. A C—H bond on the α carbon to a carbonyl group is more acidic than many other C—H bonds, because reaction with base forms a resonance-stabilized enolate anion. ...
... reaction at the α-carbon. A C—H bond on the α carbon to a carbonyl group is more acidic than many other C—H bonds, because reaction with base forms a resonance-stabilized enolate anion. ...
Phenols

In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of a hydroxyl group (—OH) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest of the class is phenol, which is also called carbolic acid C6H5OH. Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule.Synonyms are arenols or aryl alcohols.Phenolic compounds are synthesized industrially; they also are produced by plants and microorganisms, with variation between and within species.Although similar to alcohols, phenols have unique properties and are not classified as alcohols (since the hydroxyl group is not bonded to a saturated carbon atom). They have higher acidities due to the aromatic ring's tight coupling with the oxygen and a relatively loose bond between the oxygen and hydrogen. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12).Loss of a positive hydrogen ion (H+) from the hydroxyl group of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides, although the term aryloxides is preferred according to the IUPAC Gold Book. Phenols can have two or more hydroxy groups bonded to the aromatic ring(s) in the same molecule. The simplest examples are the three benzenediols, each having two hydroxy groups on a benzene ring.Organisms that synthesize phenolic compounds do so in response to ecological pressures such as pathogen and insect attack, UV radiation and wounding. As they are present in food consumed in human diets and in plants used in traditional medicine of several cultures, their role in human health and disease is a subject of research.ref name=Klepacka Some phenols are germicidal and are used in formulating disinfectants. Others possess estrogenic or endocrine disrupting activity.