Abdominal Sonography Part 1 Lecture 1 Liver . Normal
... The two anterior leaves of the coronary ligaments join to become the Falciform ligament in the anterior surface of the liver (the two posterior leaves become the lesser omentum, which encircle the porta hepatis). FL is an anteroposterior fold of parietal peritoneum extending from the bare area o ...
... The two anterior leaves of the coronary ligaments join to become the Falciform ligament in the anterior surface of the liver (the two posterior leaves become the lesser omentum, which encircle the porta hepatis). FL is an anteroposterior fold of parietal peritoneum extending from the bare area o ...
Unit 2 Objectives - Chemistry of Life
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH a ...
... 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 Explain the role of enzymes as catalysts that lower the activation energy of biochemical reactions. Identify factors, such as pH a ...
eprint_3_16309_960
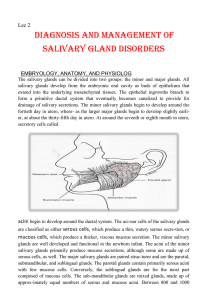
... anterosuperior aspect of the parotid to form Stensen's duct, which is the major duct of the parotid gland. Stensen's duct is about 1 to 3 mm in diam-eter and 6 cm in length. Occasionally, a normal anatomic variation occurs in which an accessory parotid duct may aid Stensen's duct in drainage of sali ...
... anterosuperior aspect of the parotid to form Stensen's duct, which is the major duct of the parotid gland. Stensen's duct is about 1 to 3 mm in diam-eter and 6 cm in length. Occasionally, a normal anatomic variation occurs in which an accessory parotid duct may aid Stensen's duct in drainage of sali ...
By Dr. harith dahham
... • Submandibular ganglion. • Deep part of the submandibular salivary gland. • Submandibular duct. • Hypoglossal nerve. • Suprahyoid artery. ...
... • Submandibular ganglion. • Deep part of the submandibular salivary gland. • Submandibular duct. • Hypoglossal nerve. • Suprahyoid artery. ...
Introduction
... Second, dietary fiber is associated with reduced insulin secretion because of its low glycemic effect on blood glucose. Most soluble fibers decrease the rate of glucose absorption and attenuate the rise of plasma glucose and insulin levels, leading to a reduced level of cholesterol synthesis in the ...
... Second, dietary fiber is associated with reduced insulin secretion because of its low glycemic effect on blood glucose. Most soluble fibers decrease the rate of glucose absorption and attenuate the rise of plasma glucose and insulin levels, leading to a reduced level of cholesterol synthesis in the ...
Unit 02 Dry Lab Questions – A Use the following case has 4 question.
... a. NO. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh courses laterally across the iliacus muscles toward the anterior superior iliac spines where it passes posterior to the inguinal ligament and enters the thigh. It would not be severed in a horizontal c-section incision. b. YES. The OB has cut the ilioh ...
... a. NO. The lateral cutaneous nerve of the thigh courses laterally across the iliacus muscles toward the anterior superior iliac spines where it passes posterior to the inguinal ligament and enters the thigh. It would not be severed in a horizontal c-section incision. b. YES. The OB has cut the ilioh ...
Assiut university researches Functional Morphological Study of the
... versa. While, in the budgerigar, the brain case exhibits a high kinesis due to the presence of movable naso-frontal hinge. 2) The brain case of the budgerigar is characterized by the appearance of the suborbital arch which is considered as a parrot-specific structure surrounding the eye. C. The quad ...
... versa. While, in the budgerigar, the brain case exhibits a high kinesis due to the presence of movable naso-frontal hinge. 2) The brain case of the budgerigar is characterized by the appearance of the suborbital arch which is considered as a parrot-specific structure surrounding the eye. C. The quad ...
File
... 5. Cuneiform cartilages: are 2 small rodshaped cartilages in the Aryepiglottic folds to strengthen them. 6. Epiglottis: is leaf-shaped lamina of elastic cartilage lies behind root of tongue. Its stalk is attached to back of thyroid cartilage and its sides are attached to arytenoid cartilages by Arye ...
... 5. Cuneiform cartilages: are 2 small rodshaped cartilages in the Aryepiglottic folds to strengthen them. 6. Epiglottis: is leaf-shaped lamina of elastic cartilage lies behind root of tongue. Its stalk is attached to back of thyroid cartilage and its sides are attached to arytenoid cartilages by Arye ...
Abdominopelvic Cavity and Peritoneum - Dr. Sholley
... by one or more mesenteries are said to be intraperitoneal (but this does not mean they are within the peritoneal cavity). ...
... by one or more mesenteries are said to be intraperitoneal (but this does not mean they are within the peritoneal cavity). ...
1. The gastroesophageal junction occurs at - NYCC SP-01
... 97. The portion of the eye that extends from the iris to the lens is: a) posterior segment b)anterior segment c) posterior chamber d) anterior chamber 98. Which of the following is not directly affiliated with the right atrium: a) inferior vena cava b)superior vena cava c) coronary sinus d) pulmonar ...
... 97. The portion of the eye that extends from the iris to the lens is: a) posterior segment b)anterior segment c) posterior chamber d) anterior chamber 98. Which of the following is not directly affiliated with the right atrium: a) inferior vena cava b)superior vena cava c) coronary sinus d) pulmonar ...
muscles of facial expression
... • Nerve supply : Buccal branch of the facial nerve . • Action : Compresses the cheeks and lips against the teeth . ...
... • Nerve supply : Buccal branch of the facial nerve . • Action : Compresses the cheeks and lips against the teeth . ...
Lecture 2 - cholesterol _CVS block
... Most important animal steroid Mainitains membrane fluidity Has an insulating effect on nerve fibres Cholesterol is the parent molecule for – Bile acids and bile salts – Steroid hormones and – vitamin D3 ...
... Most important animal steroid Mainitains membrane fluidity Has an insulating effect on nerve fibres Cholesterol is the parent molecule for – Bile acids and bile salts – Steroid hormones and – vitamin D3 ...
Face and Related Structures Anatomy
... Demonstrates difficulty closing the left eye and inability to raise the left corner of mouth; C) Demonstrates drooping at the left corner of mouth and inability to completely close the left eye. These findings are the result of idiopathic peripheral cranial nerve 7 palsy (Bell's palsy). ...
... Demonstrates difficulty closing the left eye and inability to raise the left corner of mouth; C) Demonstrates drooping at the left corner of mouth and inability to completely close the left eye. These findings are the result of idiopathic peripheral cranial nerve 7 palsy (Bell's palsy). ...
Unit 10 ~ Learning Guide Name
... 5. Planaria belong to the Class _________________________ of the Phylum ______________________________ and are free-living. (2 marks) 6. Free-living species do not require a ______________ to survive whereas __________________________ species require a host to survive. Free-living species tend to ha ...
... 5. Planaria belong to the Class _________________________ of the Phylum ______________________________ and are free-living. (2 marks) 6. Free-living species do not require a ______________ to survive whereas __________________________ species require a host to survive. Free-living species tend to ha ...
Intestinal Protein digestion in vitro Assay
... and Schils, R. L. M. 1994. Rumen degradation and intestinal digestion of grass and clover at two maturity levels during the season in dairy cows. Grass Forage Sci 49, 378-390. Stern, M. D., Bach, A., and Calsamiglia, S. 1997. Alternative techniques for measuring nutrient digestion in ruminants. J An ...
... and Schils, R. L. M. 1994. Rumen degradation and intestinal digestion of grass and clover at two maturity levels during the season in dairy cows. Grass Forage Sci 49, 378-390. Stern, M. D., Bach, A., and Calsamiglia, S. 1997. Alternative techniques for measuring nutrient digestion in ruminants. J An ...
Document
... The transverse facial vein joins the Superficial temporal vein within the parotid gland. Lymph Drainage of the Face Lymph from the forehead and the anterior part of the face drains into the submandibular lymph nodes. A few buccal lymph nodes may be present along the course of these lymph vessels. Th ...
... The transverse facial vein joins the Superficial temporal vein within the parotid gland. Lymph Drainage of the Face Lymph from the forehead and the anterior part of the face drains into the submandibular lymph nodes. A few buccal lymph nodes may be present along the course of these lymph vessels. Th ...
8.1_Respiratory_Anatomy_
... D. Components - The respiratory system includes all the organs and structures through which air passes to reach the small chambers (alveoli) within the lungs where external respiration occurs. Some of these structures (the oral cavity and portions of the pharynx) are also part of the digestive syste ...
... D. Components - The respiratory system includes all the organs and structures through which air passes to reach the small chambers (alveoli) within the lungs where external respiration occurs. Some of these structures (the oral cavity and portions of the pharynx) are also part of the digestive syste ...
Ⅰ.In the following questions, selecting the best response :( 1 marks
... C. the lateral border of the femoral triangle is formed by the lateral border of sartorius muscle D. the femoral canal lies medial to the femoral vein. E. at the apex of the femoral triangle, the femoral vessels pass into the popliteal fossa. 12. Which nerve passes through the quadrilateral foramen? ...
... C. the lateral border of the femoral triangle is formed by the lateral border of sartorius muscle D. the femoral canal lies medial to the femoral vein. E. at the apex of the femoral triangle, the femoral vessels pass into the popliteal fossa. 12. Which nerve passes through the quadrilateral foramen? ...
Cholesterol and Heart Disease
... cholesterol overproduction results from defect in the control mechanisms that normally regulate cholesterol biosynthesis. • In 1974, Brown and Goldstein demonstrated that the lesion in FH cells is a defect in LDL binding to a receptor on the surface. ...
... cholesterol overproduction results from defect in the control mechanisms that normally regulate cholesterol biosynthesis. • In 1974, Brown and Goldstein demonstrated that the lesion in FH cells is a defect in LDL binding to a receptor on the surface. ...
Summary
... The laryngeal mucosa is lined by stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium extending from the laryngeal vestibule to the caudal edge of the vocal fold.While, the remainder of the epithelium is respiratory epithelium which is pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells. A tra ...
... The laryngeal mucosa is lined by stratified squamous non keratinized epithelium extending from the laryngeal vestibule to the caudal edge of the vocal fold.While, the remainder of the epithelium is respiratory epithelium which is pseudostratified columnar ciliated epithelium with goblet cells. A tra ...
Document
... drains to the upper deep cervical chain. Whereas, the subglottis drains to the prelaryngeal, pretracheal and the lower deep cervical chain. Hence, the incidence of metastatic lymphadenopathy is higher in supraglottic and subglottic tumours, making the prognosis worse. ...
... drains to the upper deep cervical chain. Whereas, the subglottis drains to the prelaryngeal, pretracheal and the lower deep cervical chain. Hence, the incidence of metastatic lymphadenopathy is higher in supraglottic and subglottic tumours, making the prognosis worse. ...
Document
... drains to the upper deep cervical chain. Whereas, the subglottis drains to the prelaryngeal, pretracheal and the lower deep cervical chain. Hence, the incidence of metastatic lymphadenopathy is higher in supraglottic and subglottic tumours, making the prognosis worse. ...
... drains to the upper deep cervical chain. Whereas, the subglottis drains to the prelaryngeal, pretracheal and the lower deep cervical chain. Hence, the incidence of metastatic lymphadenopathy is higher in supraglottic and subglottic tumours, making the prognosis worse. ...
Root of the Neck
... for this artery; the confusion concerns the veins of the same names; the supreme intercostal vein drains the first intercostal space and then empties into the brachiocephalic while the superior/highest intercostal vein drains ...
... for this artery; the confusion concerns the veins of the same names; the supreme intercostal vein drains the first intercostal space and then empties into the brachiocephalic while the superior/highest intercostal vein drains ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.