Tongji Univesity School of Medicine
... 40. Severance of the occulomotor nerve can cause which of the following conditions? A. Complete ptosis B. Abduction of the eyeball C. A constricted pupil D. Impaired lacrimal secretion E. Paralysis of the ciliary muscle Which of the following cranial nerves contains only sensory fibers? A. facial n ...
... 40. Severance of the occulomotor nerve can cause which of the following conditions? A. Complete ptosis B. Abduction of the eyeball C. A constricted pupil D. Impaired lacrimal secretion E. Paralysis of the ciliary muscle Which of the following cranial nerves contains only sensory fibers? A. facial n ...
The Respiratory System in the Head and Neck The Nose The nose
... Note that maxillary and sphenoidal sinuses are present in rudimentary form at birth, enlarge appreciably after the eighth year, and are fully formed in adolescence. Crossing of Air and Food Pathways in the Pharynx It is in the pharynx that the air and food pathways cross. This is made possible by th ...
... Note that maxillary and sphenoidal sinuses are present in rudimentary form at birth, enlarge appreciably after the eighth year, and are fully formed in adolescence. Crossing of Air and Food Pathways in the Pharynx It is in the pharynx that the air and food pathways cross. This is made possible by th ...
Unit 29: Posterior Abdominal Wall
... Locate and clean the branches of the lumbar plexus (Plates 259, 478, 479; 2.72, 2.73, 2.82B, Table 2.6-p. 165). Like all of the somatic nerve plexuses, it is formed from anterior primary rami. The genitofemoral nerve has already been seen on the anterior surface of the psoas muscles. This nerve divi ...
... Locate and clean the branches of the lumbar plexus (Plates 259, 478, 479; 2.72, 2.73, 2.82B, Table 2.6-p. 165). Like all of the somatic nerve plexuses, it is formed from anterior primary rami. The genitofemoral nerve has already been seen on the anterior surface of the psoas muscles. This nerve divi ...
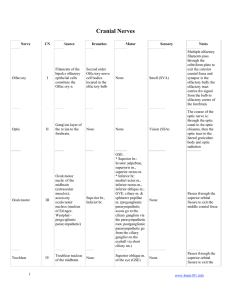
Cranial Nerves
... muscle of the respiratory tree & gut (proximal to the left colic flexure), heart; secretomotor: mucous glands of the larynx, respiratory tree, pharynx and gut; secretomotor to digestive glands ...
... muscle of the respiratory tree & gut (proximal to the left colic flexure), heart; secretomotor: mucous glands of the larynx, respiratory tree, pharynx and gut; secretomotor to digestive glands ...
In vitro gastrointestinal digestion study of a novel bio-tofu
... Thus, enzymatic modification of proteins by MTGase could lead to firmer matrices that are digested to a lower extent which may help in controlling energy intake. Although the study of milk and soy proteins have been conducted, little information is available on the properties of the mixed gels, expe ...
... Thus, enzymatic modification of proteins by MTGase could lead to firmer matrices that are digested to a lower extent which may help in controlling energy intake. Although the study of milk and soy proteins have been conducted, little information is available on the properties of the mixed gels, expe ...
Why do we yawn?
... Providing an extensive area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood. To move the air from the exchanged surfaces of the lungs. To protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration, temperature changes, or other environmental variations and to defend the respiratory system and other tissues fr ...
... Providing an extensive area for gas exchange between air and circulating blood. To move the air from the exchanged surfaces of the lungs. To protect respiratory surfaces from dehydration, temperature changes, or other environmental variations and to defend the respiratory system and other tissues fr ...
Correlative Body Systems
... • Triploblastic animals that possess a pseudocoelom are called pseudocoelomates ...
... • Triploblastic animals that possess a pseudocoelom are called pseudocoelomates ...
7. The Tongue - UCLA Linguistics
... noting where this muscle attaches.) From this point, the muscle fibers fan out posteriorly and superiorly (backwards and upwards) to form the inferior portion of the tongue. In addition to these four muscles, we will also note two other muscles. The first is the palatoglossus muscle, a small muscle ...
... noting where this muscle attaches.) From this point, the muscle fibers fan out posteriorly and superiorly (backwards and upwards) to form the inferior portion of the tongue. In addition to these four muscles, we will also note two other muscles. The first is the palatoglossus muscle, a small muscle ...
Neurology 1 Cranial Nerves
... 3. Special Visceral Efferent (SVE) Activates Muscles of face, palate, mouth, pharynx and larynx Excludes eye and tongue muscles 4. Special Visceral Afferent (SVA) Mediates visceral sensation of taste from tongue Olfaction from Nose 5. General Visceral Afferent (GVA) Mediates sensory innervation from ...
... 3. Special Visceral Efferent (SVE) Activates Muscles of face, palate, mouth, pharynx and larynx Excludes eye and tongue muscles 4. Special Visceral Afferent (SVA) Mediates visceral sensation of taste from tongue Olfaction from Nose 5. General Visceral Afferent (GVA) Mediates sensory innervation from ...
Anatomy and Embryology of the Pharynx
... By end of 4th week, four pairs of arches are visible on the surface (not 5th and 6th ) and a buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures forming communication between primitive oral cavity and foregut ...
... By end of 4th week, four pairs of arches are visible on the surface (not 5th and 6th ) and a buccopharyngeal membrane ruptures forming communication between primitive oral cavity and foregut ...
LAC.SYSTEM I-ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY, CONGENITAL
... More common condition leading to epiphora in small children (non-canalization of the NLD cord) Managed by massages and simple antibiotics till the age of 6 months in the hope of spontaneous ...
... More common condition leading to epiphora in small children (non-canalization of the NLD cord) Managed by massages and simple antibiotics till the age of 6 months in the hope of spontaneous ...
Ultrasound examination of the normal pancreas
... The pancreas is a challenge for the beginner in ultrasonography, but patience, perseverance and experience will lead to a complete and correct evaluation of the organ in almost all cases. A correct examination of the pancreas requires the patient’s fasting 7 to 8 hours before the examination. Transv ...
... The pancreas is a challenge for the beginner in ultrasonography, but patience, perseverance and experience will lead to a complete and correct evaluation of the organ in almost all cases. A correct examination of the pancreas requires the patient’s fasting 7 to 8 hours before the examination. Transv ...
muscles involved in respiration
... diaphragm & innervates it from abdominal surface • Action: contraction (descent) of diaphragm increase vertical diameter of thoracic cavity (essential for ...
... diaphragm & innervates it from abdominal surface • Action: contraction (descent) of diaphragm increase vertical diameter of thoracic cavity (essential for ...
The rectum
... That part of the rectum that lies below the middle valve has a much wider diameter than the upper third and is known as the ampulla of the rectum. ...
... That part of the rectum that lies below the middle valve has a much wider diameter than the upper third and is known as the ampulla of the rectum. ...
exam 4
... B) the subclavian artery becomes the axillary artery when it passes the 1st rib C) the femoral artery becomes the popliteal artery when it passes through the adductor hiatus D) the axillary artery becomes the brachial artery when it passes the teres major muscle E) the sigmoid sinus becomes the inte ...
... B) the subclavian artery becomes the axillary artery when it passes the 1st rib C) the femoral artery becomes the popliteal artery when it passes through the adductor hiatus D) the axillary artery becomes the brachial artery when it passes the teres major muscle E) the sigmoid sinus becomes the inte ...
14-Nasal cavity
... Distinct smells are far more numerous than tastes The sense of smell plays a major role in the flavor of foods and it is common for individuals who lose their sense of smell to report that food loses its taste. (food seems somewhat tasteless when a person has cold) Most air breathed in normall ...
... Distinct smells are far more numerous than tastes The sense of smell plays a major role in the flavor of foods and it is common for individuals who lose their sense of smell to report that food loses its taste. (food seems somewhat tasteless when a person has cold) Most air breathed in normall ...
MBBS first Prof. Syllabus, uploaded on 2014-05-17
... Large intestine, Extrahepatic biliary Apparatus, Posterior wall of abdomen, Kidney, Introduction to pelvis, Pelvic diaphragm, Pelvic peritoneum, Nerves of pelvis, Urinary Bladder, Rectum and anal canal, Uterus, Ovary, Urogenital triangle, Superficial structures of anterior abdominal wall, Anterolate ...
... Large intestine, Extrahepatic biliary Apparatus, Posterior wall of abdomen, Kidney, Introduction to pelvis, Pelvic diaphragm, Pelvic peritoneum, Nerves of pelvis, Urinary Bladder, Rectum and anal canal, Uterus, Ovary, Urogenital triangle, Superficial structures of anterior abdominal wall, Anterolate ...
CO-ENZYMES i.
... --------------------------------------------Enzyme: protein catalysts that increase the rate of reactions without being changed in the overall process. Occurrence: Enzymes are produced by all living organisms including humans and present only in small amounts. ...
... --------------------------------------------Enzyme: protein catalysts that increase the rate of reactions without being changed in the overall process. Occurrence: Enzymes are produced by all living organisms including humans and present only in small amounts. ...
ANAT__OF__EAR__1
... oropharynx are separated by the strong mobile, membranous-muscular soft palate. The uvula hangs from the soft palate in the midline. From the palate stretch down on each side two folds of mucous membrane and muscle to meet the side of the tongue. These are the pillars of the fauces; they are known a ...
... oropharynx are separated by the strong mobile, membranous-muscular soft palate. The uvula hangs from the soft palate in the midline. From the palate stretch down on each side two folds of mucous membrane and muscle to meet the side of the tongue. These are the pillars of the fauces; they are known a ...
anatomy of female reproductive organs
... iliac artery. In the young adult they are almond shaped, solid, a greyish pink and approximately 3cm long, 1.5cm wide and 1 cm thick. In the child, the ovaries are small structures, approximately 1.5cm long. They have a smooth surface. After the menopause, no active follicles are present and the ova ...
... iliac artery. In the young adult they are almond shaped, solid, a greyish pink and approximately 3cm long, 1.5cm wide and 1 cm thick. In the child, the ovaries are small structures, approximately 1.5cm long. They have a smooth surface. After the menopause, no active follicles are present and the ova ...
BioN04 Enzymes 2015 v2
... intestine are produced in the pancreas as the zymogens trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and proelastase. • These enzymes are inactive when they are synthesized so that they do not digest the pancreas. • Each zymogen has a polypeptide segment at one end that is not present in the active enzymes. • The ...
... intestine are produced in the pancreas as the zymogens trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen, and proelastase. • These enzymes are inactive when they are synthesized so that they do not digest the pancreas. • Each zymogen has a polypeptide segment at one end that is not present in the active enzymes. • The ...
y. - كلية طب الاسنان
... fascia. The investing layer الطبقة المغلقةof deep cervical fascia splits to envelope the gland and the inner leaf صفحةpasses up to the base of the skull. The outer leaf extends superiorly as the parotidomasseteric fascia and reaches up to the zygomatic arch. On the gland, the fascia tends to be ...
... fascia. The investing layer الطبقة المغلقةof deep cervical fascia splits to envelope the gland and the inner leaf صفحةpasses up to the base of the skull. The outer leaf extends superiorly as the parotidomasseteric fascia and reaches up to the zygomatic arch. On the gland, the fascia tends to be ...
Spleen - 05blocks
... its normal size. Many disorders, including infections, anemias, can cause an enlarged spleen. Enlarged spleen extends downward and medially (due to the presence of the phrenico-colic ligament that prevents its direct downward descent). The splenic notch(s) may be felt by palpation through the anteri ...
... its normal size. Many disorders, including infections, anemias, can cause an enlarged spleen. Enlarged spleen extends downward and medially (due to the presence of the phrenico-colic ligament that prevents its direct downward descent). The splenic notch(s) may be felt by palpation through the anteri ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.