Document
... These endodermal buds grow laterally into the pericardioperitoneal canals, the primordia of the pleural cavities. Together with the surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, the bronchial buds differentiate into the bronchi and their ramifications in the lungs. ...
... These endodermal buds grow laterally into the pericardioperitoneal canals, the primordia of the pleural cavities. Together with the surrounding splanchnic mesenchyme, the bronchial buds differentiate into the bronchi and their ramifications in the lungs. ...
Anatomy - head and neck
... 25. Which of the following does not drain into the middle meatus of the nose? a. Maxillary sinus b. Ethmoidal sinus c. Sphenoid sinus d. Nasolacrimal duct e. Frontal sinus f. a + c g. c + d h. b + c + d i. All of the above drain into the middle meatus 26. The first vertebra that can be palpated at ...
... 25. Which of the following does not drain into the middle meatus of the nose? a. Maxillary sinus b. Ethmoidal sinus c. Sphenoid sinus d. Nasolacrimal duct e. Frontal sinus f. a + c g. c + d h. b + c + d i. All of the above drain into the middle meatus 26. The first vertebra that can be palpated at ...
Vegetarian Protezyme Forte Natural Non-Animal
... Proteolytic enzymes are naturally present in many unprocessed foods, and studies show that many of these enzymes are absorbed in the intestine to varying degrees, and in fact remain active after entering the circulatory system. Absorption tends to be better in the absence of protein-containing foods ...
... Proteolytic enzymes are naturally present in many unprocessed foods, and studies show that many of these enzymes are absorbed in the intestine to varying degrees, and in fact remain active after entering the circulatory system. Absorption tends to be better in the absence of protein-containing foods ...
File
... Scalene muscles: (Anterior, middle and posterior) 2- Extensor of the neck Trapezius muscle Splenius capitis 3- The infrahyoid muscles (strap muscles) Are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are; the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyr ...
... Scalene muscles: (Anterior, middle and posterior) 2- Extensor of the neck Trapezius muscle Splenius capitis 3- The infrahyoid muscles (strap muscles) Are a group of four pairs of muscles in the anterior (frontal) part of the neck. The four infrahyoid muscles are; the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, thyr ...
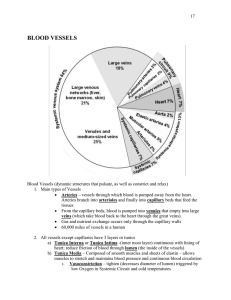
marking the start and the end of an artery 3) Branches
... 3) Branches (1st ,2nd, 3rd… in grade, from a large D to a small D) Parietal and visceral branches exist in the trunk. ...
... 3) Branches (1st ,2nd, 3rd… in grade, from a large D to a small D) Parietal and visceral branches exist in the trunk. ...
THE CRANIAL NERVES - anderson1.k12.sc.us
... muscles, baroreceptors (stretch) in carotid sinus, chemoreceptors in carotid bodies motor: from nuclei in medulla, exit thru jugular foramen, innervate stylopharyngeus muscle (elevates pharynx & larynx) parasympathetic: motor: stimulate parotid gland to secrete saliva ...
... muscles, baroreceptors (stretch) in carotid sinus, chemoreceptors in carotid bodies motor: from nuclei in medulla, exit thru jugular foramen, innervate stylopharyngeus muscle (elevates pharynx & larynx) parasympathetic: motor: stimulate parotid gland to secrete saliva ...
The Deuterostomes
... A point of emphasis in our discussion of the evolution of the central nervous system has been the presence in many invertebrate phyla of ventral nerve cords A ventral nerve cord persists in the hemichordates, but is accompanied by a dorsal nerve cord The dorsal nerve cord is hollow because it is for ...
... A point of emphasis in our discussion of the evolution of the central nervous system has been the presence in many invertebrate phyla of ventral nerve cords A ventral nerve cord persists in the hemichordates, but is accompanied by a dorsal nerve cord The dorsal nerve cord is hollow because it is for ...
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
... pterygomandibular raphe, mandible and lateral surface of the tongue. It is overlapped on its outside by the middle pharyngeal constrictor posteriorly and laterally, but anteriorly there is a gap through which the stylopharyngeus muscle and glossopharyngeal nerve enter the wall of the pharynx. The mi ...
... pterygomandibular raphe, mandible and lateral surface of the tongue. It is overlapped on its outside by the middle pharyngeal constrictor posteriorly and laterally, but anteriorly there is a gap through which the stylopharyngeus muscle and glossopharyngeal nerve enter the wall of the pharynx. The mi ...
Gross 2 notes C
... Deglutition is not possible if you have a hole in your palate. You cannot nurse either since you cannot create a vacuum. (cleft palate) ...
... Deglutition is not possible if you have a hole in your palate. You cannot nurse either since you cannot create a vacuum. (cleft palate) ...
The Cranial Nerves
... Sensations from skin at back of ear, external acoustic meatus, part of tympanic membrane, larynx, trachea, espophagus, thoracic and abdominal viscera Sensations from bararoceptors and chemoreceptors Special sensory – taste from epiglottis and pharynx Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production v ...
... Sensations from skin at back of ear, external acoustic meatus, part of tympanic membrane, larynx, trachea, espophagus, thoracic and abdominal viscera Sensations from bararoceptors and chemoreceptors Special sensory – taste from epiglottis and pharynx Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production v ...
Sono Facts
... When the pancreatic duct is visualized, which portion of the pancreas are you scanning through? ...
... When the pancreatic duct is visualized, which portion of the pancreas are you scanning through? ...
Document
... 22- ----------------- are substances produced by specialized cells of the body and carried by bloodstream where it affect other specialized cells. a- Enzymes b- Hormones c- Vitamins d- Isoenzymes 23- --------------- play an essential role in body metabolism , a deficiency or excess may lead to serio ...
... 22- ----------------- are substances produced by specialized cells of the body and carried by bloodstream where it affect other specialized cells. a- Enzymes b- Hormones c- Vitamins d- Isoenzymes 23- --------------- play an essential role in body metabolism , a deficiency or excess may lead to serio ...
Circulatory System Part 3
... Fenestrated capillaries – (fenestra = windows) abundant in small intestine, kidneys, endocrine glands – allows slightly larger things to pass through Endothelial cells (lining) have oval pores called fenestra ...
... Fenestrated capillaries – (fenestra = windows) abundant in small intestine, kidneys, endocrine glands – allows slightly larger things to pass through Endothelial cells (lining) have oval pores called fenestra ...
abdomen - WordPress.com
... Venous drainage: submucosal veins L gastric vein portal venous system oesophageal veins systemic venous system Nerve supply: oesophageal nerve plexus from vagal trunks and thoracic sympathetic trunks (from greater splanchnic nerves and periarterial plexuses) 3 constrictions 1) Cervical: at p ...
... Venous drainage: submucosal veins L gastric vein portal venous system oesophageal veins systemic venous system Nerve supply: oesophageal nerve plexus from vagal trunks and thoracic sympathetic trunks (from greater splanchnic nerves and periarterial plexuses) 3 constrictions 1) Cervical: at p ...
Antihyperlipidemic Drugs
... What are lipoproteins? And the transport of Cholesterol & Triglycerides Since blood and other body fluids are watery, so fats need a special transport system to travel around the body. They are carried from one place to another mixing with protein particles, called lipoproteins. There are four ( ...
... What are lipoproteins? And the transport of Cholesterol & Triglycerides Since blood and other body fluids are watery, so fats need a special transport system to travel around the body. They are carried from one place to another mixing with protein particles, called lipoproteins. There are four ( ...
Document
... Present in tissues and lipoproteins either as a free cholesterol or cholesteryl ester, Lipoproteins transport free cholesterol in the circulation, where it readily equilibrates with cholesterol in other lipoproteins and in membranes, Cholesteryl ester is a storage form of cholesterol in most tissues ...
... Present in tissues and lipoproteins either as a free cholesterol or cholesteryl ester, Lipoproteins transport free cholesterol in the circulation, where it readily equilibrates with cholesterol in other lipoproteins and in membranes, Cholesteryl ester is a storage form of cholesterol in most tissues ...
Roundworms - Advanced
... • hydrostatic skeleton: A structure consisting of a fluid-filled cavity surrounded by muscles; it is used to change an organism’s shape and produce movement. • phasmid: One of a pair of circular depressions situated laterally at the posterior end of nematodes and believed to be chemoreceptors. • pse ...
... • hydrostatic skeleton: A structure consisting of a fluid-filled cavity surrounded by muscles; it is used to change an organism’s shape and produce movement. • phasmid: One of a pair of circular depressions situated laterally at the posterior end of nematodes and believed to be chemoreceptors. • pse ...
Anatomy – Whole Block Review
... o The area where the liver is continuous with the diaphragm. It has not peritoneum. Because the peritoneum does not unite at the bare area, two recesses are formed. What are they? o Subphrenic Recess o Hepatorenal Recess (right kidney) What part of the liver has the most Islets of Langerhans? o The ...
... o The area where the liver is continuous with the diaphragm. It has not peritoneum. Because the peritoneum does not unite at the bare area, two recesses are formed. What are they? o Subphrenic Recess o Hepatorenal Recess (right kidney) What part of the liver has the most Islets of Langerhans? o The ...
Bovine mammary glands
... The inguinal canal -orifice in the body cavity in the inguinal region where blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves enter and leave the body wall to supply the skin in the posterior part of the animal. As the external pudic artery passes out of the body cavity it becomes the mammary artery. Onc ...
... The inguinal canal -orifice in the body cavity in the inguinal region where blood vessels, lymph vessels and nerves enter and leave the body wall to supply the skin in the posterior part of the animal. As the external pudic artery passes out of the body cavity it becomes the mammary artery. Onc ...
Anatomy_of_the_Larynx
... 3. SLN course inferior and anterior where it runs behind carotid and splits into external and internal branches 4. external branch courses over pharyngeal constrictors, closely associated with superior thyroid artery to innervate cricothyroid muscle ii. Internal branch 1. fibers end in nucleus solit ...
... 3. SLN course inferior and anterior where it runs behind carotid and splits into external and internal branches 4. external branch courses over pharyngeal constrictors, closely associated with superior thyroid artery to innervate cricothyroid muscle ii. Internal branch 1. fibers end in nucleus solit ...
Anatomy, Function, and Evaluation of the Salivary Glands
... The temporal branch traverses parallel to the superficial temporal vessels across the zygoma to supply the The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) provides visceral frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle, the orbicu- secretory innervation to the parotid gland. The nerve laris oculi, the corrugato ...
... The temporal branch traverses parallel to the superficial temporal vessels across the zygoma to supply the The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) provides visceral frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle, the orbicu- secretory innervation to the parotid gland. The nerve laris oculi, the corrugato ...
Anatomy, Function, and Evaluation of the Salivary Glands
... The temporal branch traverses parallel to the superficial temporal vessels across the zygoma to supply the The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) provides visceral frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle, the orbicu- secretory innervation to the parotid gland. The nerve laris oculi, the corrugato ...
... The temporal branch traverses parallel to the superficial temporal vessels across the zygoma to supply the The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) provides visceral frontal belly of the occipitofrontalis muscle, the orbicu- secretory innervation to the parotid gland. The nerve laris oculi, the corrugato ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.