inner ear
... Outer Eye: Vascular Tunic Functions: Provides route for blood and lymphatic vessels that supply eye Regulates amount of light that enters eye Controls shape of lens, essential to focusing images on retina Secretes and reabsorbs aqueous humor ...
... Outer Eye: Vascular Tunic Functions: Provides route for blood and lymphatic vessels that supply eye Regulates amount of light that enters eye Controls shape of lens, essential to focusing images on retina Secretes and reabsorbs aqueous humor ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
... List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
Thyroid, Parathyroid and Suprarenal Glands
... List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
... List the blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the thyroid gland. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the parathyroid glands. Describe the shape, position, blood supply & lymphatic drainage of the adenal glands. ...
Development anatomy of the respiratory organ
... • The interstitial space is rich with cells and the proportion of collagen and elastic fibers is still small. This matrix, though, plays an important role for the growth and differentiation of the epithelium that lies above it (9). At the end of this phase the interstitial fibroblasts begin with the ...
... • The interstitial space is rich with cells and the proportion of collagen and elastic fibers is still small. This matrix, though, plays an important role for the growth and differentiation of the epithelium that lies above it (9). At the end of this phase the interstitial fibroblasts begin with the ...
Slide ()
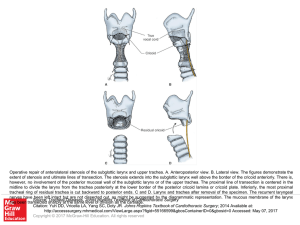
... extent of stenosis and ultimate lines of transection. The stenosis extends into the subglottic larynx well above the border of the cricoid anteriorly. There is, however, no involvement of the posterior mucosal wall of the subglottic larynx or of the upper trachea. The proximal line of transection is ...
... extent of stenosis and ultimate lines of transection. The stenosis extends into the subglottic larynx well above the border of the cricoid anteriorly. There is, however, no involvement of the posterior mucosal wall of the subglottic larynx or of the upper trachea. The proximal line of transection is ...
2nd year Anatomy - Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University
... Anterior abdominal wall ( layers of the abdominal wall, characters of the abdominal fascia, origin, insertion, direction of fibers, nerve supply and action of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the structures related to the abdominal muscles, formation and contents of the rectus sheath and ...
... Anterior abdominal wall ( layers of the abdominal wall, characters of the abdominal fascia, origin, insertion, direction of fibers, nerve supply and action of the muscles of the anterior abdominal wall, the structures related to the abdominal muscles, formation and contents of the rectus sheath and ...
Skull and Face - Faculty of Science, Mahidol University
... Stylohyoid Muscle • Origin, styloid process • Insertion, hyoid bone (two slips) • Nerve, CN VII ...
... Stylohyoid Muscle • Origin, styloid process • Insertion, hyoid bone (two slips) • Nerve, CN VII ...
Liver Function Tests slides 2009
... The production rate of bilirubin is increased, exceeding the excretory capacity of the liver. Overproduction of bilirubin occurs in all forms of hemolytic anemia, less commonly, in conditions where ...
... The production rate of bilirubin is increased, exceeding the excretory capacity of the liver. Overproduction of bilirubin occurs in all forms of hemolytic anemia, less commonly, in conditions where ...
anatomy review notes
... It arises from the greater and lesser horns of the hyoid bone. The borderline between the superior and the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle is marked by the stylopharyngeus muscle (entering the pharynx between them). The glossopharyngeal nerve runs along the stylopharyngeus muscle. Inferior ...
... It arises from the greater and lesser horns of the hyoid bone. The borderline between the superior and the middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle is marked by the stylopharyngeus muscle (entering the pharynx between them). The glossopharyngeal nerve runs along the stylopharyngeus muscle. Inferior ...
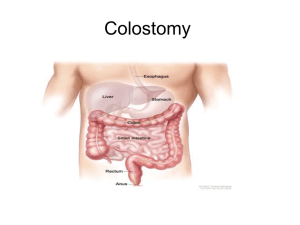
COLOSTOMY 1 2121
... -Monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respirations, and temperature. • -The patient is instructed how to support the operative site during deep breathing and coughing, and given pain medication as necessary. -Fluid intake and output is measured, and the operative site is observed for color and amoun ...
... -Monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respirations, and temperature. • -The patient is instructed how to support the operative site during deep breathing and coughing, and given pain medication as necessary. -Fluid intake and output is measured, and the operative site is observed for color and amoun ...
The trigeminal nerve Ophthalmic division Maxillary division
... branch supplies the anterior part of the middle cranial fossa. The maxillary nerve goes to the nasal region (ptyerygopalatine fossa) where it is joined by hitchhikers from the facial nerve (pterygopalatine ganglion). These parasympathetic and taste nerves supply the palatine, nasal and lachrymal gla ...
... branch supplies the anterior part of the middle cranial fossa. The maxillary nerve goes to the nasal region (ptyerygopalatine fossa) where it is joined by hitchhikers from the facial nerve (pterygopalatine ganglion). These parasympathetic and taste nerves supply the palatine, nasal and lachrymal gla ...
Region 16: Kidneys and Retroperitoneal Structures Abdominal aorta
... --ends at level of T8 where it passes through the diaphragm --lies to the right of the aorta --has tributaries --important collateral routes b/w superior and inferior vena cava include *thoracoepigastric veins *ascending lumbar veins: change to azygos vein on right and hemiazygos on left Lymphatics ...
... --ends at level of T8 where it passes through the diaphragm --lies to the right of the aorta --has tributaries --important collateral routes b/w superior and inferior vena cava include *thoracoepigastric veins *ascending lumbar veins: change to azygos vein on right and hemiazygos on left Lymphatics ...
1-Nose, Nasal Cavity, Paranasal Sinuses,2017-02
... 2- Opening of the oral cavity. 3- Laryngeal inlet. o The muscles are arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. Explanation: The pharynx is made up of muscles that cover/make up the posterior and lateral walls. But they do not cover the anterior wall that’s why it is deficient. Instead the anteri ...
... 2- Opening of the oral cavity. 3- Laryngeal inlet. o The muscles are arranged in circular and longitudinal layers. Explanation: The pharynx is made up of muscles that cover/make up the posterior and lateral walls. But they do not cover the anterior wall that’s why it is deficient. Instead the anteri ...
ABDOMEN MCQs Regarding divisions of anterior abdominal wall
... A. Falciform ligament contains the obliterated left umbilical vein B. Median umbilical fold contains the obliterated right umbilical vein C. Medial umbilical ligament contain the obliterated umbilical artery D. Lateral umbilical fold contains the inferior epigastric vessels E. All of the above 15. T ...
... A. Falciform ligament contains the obliterated left umbilical vein B. Median umbilical fold contains the obliterated right umbilical vein C. Medial umbilical ligament contain the obliterated umbilical artery D. Lateral umbilical fold contains the inferior epigastric vessels E. All of the above 15. T ...
REAL Health Solutions!
... word ─ LIFE. Without systemic enzymes, LIFE itself is not possible, not for people, plants, or animals.** Enzymes are the single most important essential for every reaction taking place in a living organism because every second of everyday life changes and renews itself. Restoring proper levels of s ...
... word ─ LIFE. Without systemic enzymes, LIFE itself is not possible, not for people, plants, or animals.** Enzymes are the single most important essential for every reaction taking place in a living organism because every second of everyday life changes and renews itself. Restoring proper levels of s ...
Anatomy of Respiratory System
... Pharynx, oral cavity, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses act as resonating chambers that add quality to the sound Muscles of the face, tongue, and lips help with enunciation of words ...
... Pharynx, oral cavity, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses act as resonating chambers that add quality to the sound Muscles of the face, tongue, and lips help with enunciation of words ...
Structure and physical-chemical properties of enzymes
... •The enzyme cannot differentiate between the two compounds •When inhibitor binds, prevents the substrate from binding •Inhibitor can be released by increasing substrate concentration ...
... •The enzyme cannot differentiate between the two compounds •When inhibitor binds, prevents the substrate from binding •Inhibitor can be released by increasing substrate concentration ...
Feeding I: Structure and Function of Mouthparts
... laterally behind the mandibles. They are held in place by a single point of articulation with the head capsule and membraneous connections that allow freedom of movement. • The main body of the maxilla is composed of the proximally located cardo and the distally located stipes. Distally on the stip ...
... laterally behind the mandibles. They are held in place by a single point of articulation with the head capsule and membraneous connections that allow freedom of movement. • The main body of the maxilla is composed of the proximally located cardo and the distally located stipes. Distally on the stip ...
Muscles of Respiration
... SCM, levator scapulae, and upper fibers of the trapezius, the iliocostalis thoracis, subclavius, and omohyoid. The serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi are accessory muscles of respiration with the upper extremities elevated. Accessory muscles of expiration include the interosseous internal interc ...
... SCM, levator scapulae, and upper fibers of the trapezius, the iliocostalis thoracis, subclavius, and omohyoid. The serratus anterior and latissimus dorsi are accessory muscles of respiration with the upper extremities elevated. Accessory muscles of expiration include the interosseous internal interc ...
02/01/05 1 Cellulose-Degrading Symbioses BI 358 I. Intro: Guts of
... (1) Carbohydrates show slide (a) Ruminant diet is almost all carbos (i) over ½ is cellulose or hemicellulose (ii) 25% is soluble sugars (2) Symbionts break carbos down to monosaccharides (3) Ferment these sugars by glycolysis (4) synthesize VFAs from pyruvate (a) if symbiont oxidized them all the wa ...
... (1) Carbohydrates show slide (a) Ruminant diet is almost all carbos (i) over ½ is cellulose or hemicellulose (ii) 25% is soluble sugars (2) Symbionts break carbos down to monosaccharides (3) Ferment these sugars by glycolysis (4) synthesize VFAs from pyruvate (a) if symbiont oxidized them all the wa ...
The Palate - كلية طب الاسنان
... And from this origin the triangular muscle passes down between the medial and lateral pterygoid plates converging to a tendon that turns medially around the pterygoid hamulus شص. The tendon, together with the tendon of the opposite side, expands to form the palatine aponeurosis. When the muscles ...
... And from this origin the triangular muscle passes down between the medial and lateral pterygoid plates converging to a tendon that turns medially around the pterygoid hamulus شص. The tendon, together with the tendon of the opposite side, expands to form the palatine aponeurosis. When the muscles ...
Cranial nerves
... foramina in cribriform plate Distributes to mucosa of superior part of lateral and septal walls of ...
... foramina in cribriform plate Distributes to mucosa of superior part of lateral and septal walls of ...
Anatomy - head and neck
... 25. Which of the following does not drain into the middle meatus of the nose? a. Maxillary sinus b. Ethmoidal sinus c. Sphenoid sinus d. Nasolacrimal duct e. Frontal sinus f. a + c g. c + d h. b + c + d i. All of the above drain into the middle meatus 26. The first vertebra that can be palpated at ...
... 25. Which of the following does not drain into the middle meatus of the nose? a. Maxillary sinus b. Ethmoidal sinus c. Sphenoid sinus d. Nasolacrimal duct e. Frontal sinus f. a + c g. c + d h. b + c + d i. All of the above drain into the middle meatus 26. The first vertebra that can be palpated at ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.