ZOO 115 Invertebrate Zoology
... Gametes released and mature in coelom Gametes transferred and stored in nephridia until ...
... Gametes released and mature in coelom Gametes transferred and stored in nephridia until ...
Section II: The Liver
... Protein synthesis – The liver synthesizes (builds) several important proteins, including enzymes, hormones, clotting factors, and immune factors. Liver enzymes called aminotransferases or transaminases (ALT and AST) break down amino acids from digested food and rebuild them into new proteins needed ...
... Protein synthesis – The liver synthesizes (builds) several important proteins, including enzymes, hormones, clotting factors, and immune factors. Liver enzymes called aminotransferases or transaminases (ALT and AST) break down amino acids from digested food and rebuild them into new proteins needed ...
colitis - Acorn House Veterinary Surgery
... red and white blood cells, mineral and electrolyte levels; blood tests to check that the pancreas is producing the correct digestive enzymes; culture and microscope examination of the faeces; colonoscopy with biopsies of the colon under general anaesthetic. If the above investigations find a specifi ...
... red and white blood cells, mineral and electrolyte levels; blood tests to check that the pancreas is producing the correct digestive enzymes; culture and microscope examination of the faeces; colonoscopy with biopsies of the colon under general anaesthetic. If the above investigations find a specifi ...
Segments of liver
... Falciform ligament: This is a sickle shaped fold of peritoneum which ascends from umbilicus to liver and connects the anteroposterior surface of liver to the anterior abdominal wall and to the under surface of diaphragm. Its free margin contains ligament teres and small paraumbilical veins (liga ...
... Falciform ligament: This is a sickle shaped fold of peritoneum which ascends from umbilicus to liver and connects the anteroposterior surface of liver to the anterior abdominal wall and to the under surface of diaphragm. Its free margin contains ligament teres and small paraumbilical veins (liga ...
The Cranial Nerves
... Sensations from skin at back of ear, external acoustic meatus, part of tympanic membrane, larynx, trachea, espophagus, thoracic and abdominal viscera Sensations from bararoceptors and chemoreceptors Special sensory – taste from epiglottis and pharynx Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production v ...
... Sensations from skin at back of ear, external acoustic meatus, part of tympanic membrane, larynx, trachea, espophagus, thoracic and abdominal viscera Sensations from bararoceptors and chemoreceptors Special sensory – taste from epiglottis and pharynx Somatic motor – Swallowing and voice production v ...
Plasma Enzymes
... comparison to tissues No known functions Their substrates are absent from the blood Different organs e.g. liver, heart, brain and skeletal muscles Different enzymes increase in different organ diseases ALT, AST, CK, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, acid phosphatase and amylase, ...
... comparison to tissues No known functions Their substrates are absent from the blood Different organs e.g. liver, heart, brain and skeletal muscles Different enzymes increase in different organ diseases ALT, AST, CK, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, acid phosphatase and amylase, ...
Immunohistochemical localization of fatty acid transporters and
... mouse model with genetic deletion of CD36 did not affect the essential expression of MCT1 or fatty acid binding proteins in the sebaceous glands. The epidermis of the skin intensely expresses MCT1 in the basal layer, where GLUT1 with a sufficient expression is also provided (20). Cellular localizat ...
... mouse model with genetic deletion of CD36 did not affect the essential expression of MCT1 or fatty acid binding proteins in the sebaceous glands. The epidermis of the skin intensely expresses MCT1 in the basal layer, where GLUT1 with a sufficient expression is also provided (20). Cellular localizat ...
Learning objectives Liver Liver HEPATIC LOBES Left lobe,
... Falciform ligament: This is a sickle shaped fold of peritoneum which ascends from umbilicus to liver and connects the anteroposterior surface of liver to the anterior abdominal wall and to the under surface of diaphragm. Its free margin contains ligament teres and small paraumbilical veins (liga ...
... Falciform ligament: This is a sickle shaped fold of peritoneum which ascends from umbilicus to liver and connects the anteroposterior surface of liver to the anterior abdominal wall and to the under surface of diaphragm. Its free margin contains ligament teres and small paraumbilical veins (liga ...
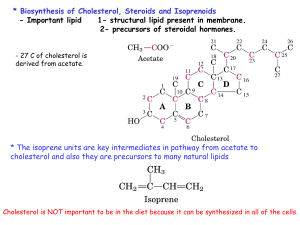
S17 Cholesterol And Steroids Biosynthesis
... To be moved from one part to another they should carried as plasma lipoprotein. Plasma lipoproteins - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid sol ...
... To be moved from one part to another they should carried as plasma lipoprotein. Plasma lipoproteins - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid sol ...
14steriod
... To be moved from one part to another they should carried as plasma lipoprotein. Plasma lipoproteins - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid sol ...
... To be moved from one part to another they should carried as plasma lipoprotein. Plasma lipoproteins - Macromolecular complexes of lipids and specific proteins called apolipoprotein with a various combination of phospholipids, cholesterol, cholesterol esters and TG. * Function : to keep the lipid sol ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Instructions External Anatomy
... 11 Observe the palate on the roof of the mouth. The anterior part of the palate is the hard palate, while the posterior part is the soft palate. 12 Locate the epiglottis, a cone-shaped structure at the back of the mouth. Above the epiglottis, find the round opening of the nasopharynx. This cavity ca ...
... 11 Observe the palate on the roof of the mouth. The anterior part of the palate is the hard palate, while the posterior part is the soft palate. 12 Locate the epiglottis, a cone-shaped structure at the back of the mouth. Above the epiglottis, find the round opening of the nasopharynx. This cavity ca ...
Appendicitis Clinical Essay
... Gut irritation is detected by autonomic sensory neurones that travel with the sympathetic nerves in the bowel and the visceral peritoneum. The visceral peritoneum is that layer of peritoneum that covers the organs. Consequently, gastrointestinal pain is felt as an unlocalised general abdominal disco ...
... Gut irritation is detected by autonomic sensory neurones that travel with the sympathetic nerves in the bowel and the visceral peritoneum. The visceral peritoneum is that layer of peritoneum that covers the organs. Consequently, gastrointestinal pain is felt as an unlocalised general abdominal disco ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... B. Innervates organs of the pelvis and lower abdomen 1. contraction of urinary bladder for urination 2. erection of the penis - (S2,3,4) 3. inhibits contraction of uterine smooth muscles 4. vasodilation - clitoris and contraction of smooth m. of vagina ...
... B. Innervates organs of the pelvis and lower abdomen 1. contraction of urinary bladder for urination 2. erection of the penis - (S2,3,4) 3. inhibits contraction of uterine smooth muscles 4. vasodilation - clitoris and contraction of smooth m. of vagina ...
EnzymesLect1 2014
... acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Individual monomers may then combine via non-covalent interactions to form a multimeric protein. Many enzymes can be unfolded or inactivated by heating, which destroys the threedimensional structure of the protein. Ac ...
... acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Individual monomers may then combine via non-covalent interactions to form a multimeric protein. Many enzymes can be unfolded or inactivated by heating, which destroys the threedimensional structure of the protein. Ac ...
Physiology of Swallowing Disorders
... An apneal pause between 1 and 3.5 seconds in duration occurs during the pharyngeal stage. This phase begins when the pharyngeal swallow is triggered and the bolus is moved through the pharynx, and it ends by opening the upper esophageal sphincter (Cricopharyngeal sphincter). The pharyngeal phase of ...
... An apneal pause between 1 and 3.5 seconds in duration occurs during the pharyngeal stage. This phase begins when the pharyngeal swallow is triggered and the bolus is moved through the pharynx, and it ends by opening the upper esophageal sphincter (Cricopharyngeal sphincter). The pharyngeal phase of ...
Face - Lectures - gblnetto
... Trigeminal neuroalgia is a relatively common condition in which the patient experiences excruciating pain in the distribution of the mandibular or maxillary division, with the ophthalmic division usually escaping. A physician should be able to map out accurately on a patient's face the distributiÂon ...
... Trigeminal neuroalgia is a relatively common condition in which the patient experiences excruciating pain in the distribution of the mandibular or maxillary division, with the ophthalmic division usually escaping. A physician should be able to map out accurately on a patient's face the distributiÂon ...
Unit 20: Superficial Face and Parotid Region Dissection Instructions
... 629). Locate as many of the following muscles as possible: the levator labii superioris muscle which has three parts, a medial part called the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, a middle part and a lateral part called the zygomaticus minor; the zygomaticus major muscle which is lateral to the z ...
... 629). Locate as many of the following muscles as possible: the levator labii superioris muscle which has three parts, a medial part called the levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, a middle part and a lateral part called the zygomaticus minor; the zygomaticus major muscle which is lateral to the z ...
Chapter 1 Basic science
... The fimbriae stabilize the abdominal ostium over the ripening follicle in the ovary. ...
... The fimbriae stabilize the abdominal ostium over the ripening follicle in the ovary. ...
By the Name of Allah
... The laryngeal orifice at the beginning is a slit line shaped opening (6th week) after that it changes its shape into T like opining then at the age of 12th week it takes its final shape These changes are due to rapid proliferation of the mesenchyma The rapid proliferation of the lining epitheliu ...
... The laryngeal orifice at the beginning is a slit line shaped opening (6th week) after that it changes its shape into T like opining then at the age of 12th week it takes its final shape These changes are due to rapid proliferation of the mesenchyma The rapid proliferation of the lining epitheliu ...
Slide 1
... Origin: Posterior aspect of pubic bone, fascia of pelvic side wall, ischial spine Insertion: Perineal body, anal sphincter, coccyx Constitute pelvic diaphragm Surfaces covered by fascia ...
... Origin: Posterior aspect of pubic bone, fascia of pelvic side wall, ischial spine Insertion: Perineal body, anal sphincter, coccyx Constitute pelvic diaphragm Surfaces covered by fascia ...
Lophophorata SP
... cilia on the inner edge of the tentacle are the frontal cilia. Their responsibility is to move captured food toward the mouth Food particles are retained inside the cone and then moved to the mouth by the frontal cilia. Digestive System The largest and most obvious organ system is the digestive syst ...
... cilia on the inner edge of the tentacle are the frontal cilia. Their responsibility is to move captured food toward the mouth Food particles are retained inside the cone and then moved to the mouth by the frontal cilia. Digestive System The largest and most obvious organ system is the digestive syst ...
Chronic Liver Diseases
... Cardiac Markers in the Diagnosis of AMI -5 • The cardiac troponins (T or I) are the most efficient markers available today for diagnosis of AMI • The specificity of troponin is also increased over CK-MB or myoglobin • cardiac troponin has been recommended by the NACB as the preferred marker for the ...
... Cardiac Markers in the Diagnosis of AMI -5 • The cardiac troponins (T or I) are the most efficient markers available today for diagnosis of AMI • The specificity of troponin is also increased over CK-MB or myoglobin • cardiac troponin has been recommended by the NACB as the preferred marker for the ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.