SYNOPSIS for the anatomy exam – second year medical students I
... 38. Muscles of the forearm -- anterior and lateral group. 39. Muscles of the forearm -- posterior group. Forearm fascia. 40. Muscles of the hand. 41. Muscles around the hip joint. 42. Muscles of the thigh. Thigh fascia. 43. Muscles of the leg - anterior and lateral group. 44. Muscles of the leg - po ...
... 38. Muscles of the forearm -- anterior and lateral group. 39. Muscles of the forearm -- posterior group. Forearm fascia. 40. Muscles of the hand. 41. Muscles around the hip joint. 42. Muscles of the thigh. Thigh fascia. 43. Muscles of the leg - anterior and lateral group. 44. Muscles of the leg - po ...
Bile Formation: a Concerted Action of Membrane
... After their functional characterization, some of these mechanisms’ individual transport molecules are now identified, allowing better understanding of inherited and acquired disorders of bile formation. ile formation is a vital process. Bile acid secretion serves the intestinal digestion of lipids a ...
... After their functional characterization, some of these mechanisms’ individual transport molecules are now identified, allowing better understanding of inherited and acquired disorders of bile formation. ile formation is a vital process. Bile acid secretion serves the intestinal digestion of lipids a ...
BBA IInd SEMESTER EXAMINATION 2008-09
... c) Which nerve is not a branch of mandibular nerve: i) Inferior alveolar nerve ii) Lingual nerve iii) Auriculotemporal nerve iv) Lesser petrosal nerve d) Which structure open into inferior meatus of nose: i) Maxillary air sinus ii) Frontal air sinus iii) Sphenoidal air sinus iv) Nasolacrimal duct e) ...
... c) Which nerve is not a branch of mandibular nerve: i) Inferior alveolar nerve ii) Lingual nerve iii) Auriculotemporal nerve iv) Lesser petrosal nerve d) Which structure open into inferior meatus of nose: i) Maxillary air sinus ii) Frontal air sinus iii) Sphenoidal air sinus iv) Nasolacrimal duct e) ...
842-2843-1-SM
... members may be affected. Some are born with other congenital anomalies, including biliary atresia and cardiovascular or other gastrointestinal malformations. They often die in infancy. Others are asymptomatic throughout life. Slightly more than half have symptoms suggestive of biliary tract disease; ...
... members may be affected. Some are born with other congenital anomalies, including biliary atresia and cardiovascular or other gastrointestinal malformations. They often die in infancy. Others are asymptomatic throughout life. Slightly more than half have symptoms suggestive of biliary tract disease; ...
L2-THE MUSCLES INVOLVED IN RESPIRATION 2014
... The 3 muscles form a tendinous sheath in which a fourth muscles lies (rectus abdominis) Muscles are attached to: sternum, costal cartilages and ribs + hip bones The aponeurosis of the 3 muscles on both sides fuse in the midline to form linea alba Action (during forced expiration): Compressio ...
... The 3 muscles form a tendinous sheath in which a fourth muscles lies (rectus abdominis) Muscles are attached to: sternum, costal cartilages and ribs + hip bones The aponeurosis of the 3 muscles on both sides fuse in the midline to form linea alba Action (during forced expiration): Compressio ...
CH18 Gasto Uro emergency
... • Digestive juices from pancreas and liver mix • Pancreas releases amylase, bicarbonate, and insulin – Jejunum • Absorbs digestive products • Does most of the work ...
... • Digestive juices from pancreas and liver mix • Pancreas releases amylase, bicarbonate, and insulin – Jejunum • Absorbs digestive products • Does most of the work ...
Anatomy_Deathmatch_2010
... What is the sensory innervation of the larynx (the regions supplied by each nerve/nerves)? a. ...
... What is the sensory innervation of the larynx (the regions supplied by each nerve/nerves)? a. ...
PowerPoint
... 2.contraction of the cecum, this is seen with a diseased terminal ileum 3.dilatation of the bowel may be seen proximal to narrowed areas 4.ulcers :are quite deep. Fine ulceration + mucosal edema=cobblestone appearance 5.thickening,distortion and effacement of mucosal folds 6.separation of loops of b ...
... 2.contraction of the cecum, this is seen with a diseased terminal ileum 3.dilatation of the bowel may be seen proximal to narrowed areas 4.ulcers :are quite deep. Fine ulceration + mucosal edema=cobblestone appearance 5.thickening,distortion and effacement of mucosal folds 6.separation of loops of b ...
Chapter 30 HEIN
... Figure 30.7 Enzyme-substrate interaction illustrating both the lock-and-key hypothesis and the induced-fit model. The correct substrate (orange square-blue circle) fits the active site (lock-andkey hypothesis). This substrate also causes an enzyme conformation change that positions a catalytic grou ...
... Figure 30.7 Enzyme-substrate interaction illustrating both the lock-and-key hypothesis and the induced-fit model. The correct substrate (orange square-blue circle) fits the active site (lock-andkey hypothesis). This substrate also causes an enzyme conformation change that positions a catalytic grou ...
L1: Organisation of ANS L2: Thoracic walls and breast
... - Synapse go up (innervate head), run out to thorax, not synapse and wait till visceral/prevertebral ganglia Parasympathetic (cranio-saccral) o Longer preganglionic neurons synapses with shorter postganglionic neuron in ganglia closer to the organ o Vagus nerve(10th cranial nerve): most preganglio ...
... - Synapse go up (innervate head), run out to thorax, not synapse and wait till visceral/prevertebral ganglia Parasympathetic (cranio-saccral) o Longer preganglionic neurons synapses with shorter postganglionic neuron in ganglia closer to the organ o Vagus nerve(10th cranial nerve): most preganglio ...
29-Posterior Abdomin..
... Nerve Supply: femoral nerve and the ventral rami of L 1, 2, 3 ( lumbar plexus ). Action : it flexes the thigh at the hip joint on the trunk. If the thigh is fixed, it flexes the trunk on the thigh, as in sitting up from a lying position. ...
... Nerve Supply: femoral nerve and the ventral rami of L 1, 2, 3 ( lumbar plexus ). Action : it flexes the thigh at the hip joint on the trunk. If the thigh is fixed, it flexes the trunk on the thigh, as in sitting up from a lying position. ...
SSN Anatomy #2
... Omental herniation: If loop passes through, none of the boundaries can be incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity fluid will collect her ...
... Omental herniation: If loop passes through, none of the boundaries can be incised, bowel must be deflected and withdrawn Second most frequently infected abdominal space, pulmonary abscess may erode across diaphragm When supine it is the lowest portion of the abdominal cavity fluid will collect her ...
Physiology 8 Endocrine and Gastroenterology
... The action of gastrin includes all EXCEPT: a) stimulation of insulin secretion after a carbohydrate meal b) stimulation of gastric acid secretion c) stimulation of gastric motility d) contraction of gastro-oesophageal junction musculature e) stimulation of growth of large intestine mucosa ...
... The action of gastrin includes all EXCEPT: a) stimulation of insulin secretion after a carbohydrate meal b) stimulation of gastric acid secretion c) stimulation of gastric motility d) contraction of gastro-oesophageal junction musculature e) stimulation of growth of large intestine mucosa ...
term 2 answers to questions - Hatzalah of Miami-Dade
... 14. If the lesion is proximal to where chorda tympani leaves the facial nerve in the middle ear, taste on the anterior two thirds of the tongue would be lost. 15. If the lesion is proximal to where the nerve to stapedius leaves the facial nerve in the middle ear, there could be hyperacusis - an incr ...
... 14. If the lesion is proximal to where chorda tympani leaves the facial nerve in the middle ear, taste on the anterior two thirds of the tongue would be lost. 15. If the lesion is proximal to where the nerve to stapedius leaves the facial nerve in the middle ear, there could be hyperacusis - an incr ...
Human Anatomy
... plays a vital role in the respiratory tract by allowing air to pass through it while keeping food and drink from blocking the airway. The larynx is also the body’s “voice box” as it contains the vocal folds that produce the sounds of speech and singing. It opens above into the laryngeal part of the ...
... plays a vital role in the respiratory tract by allowing air to pass through it while keeping food and drink from blocking the airway. The larynx is also the body’s “voice box” as it contains the vocal folds that produce the sounds of speech and singing. It opens above into the laryngeal part of the ...
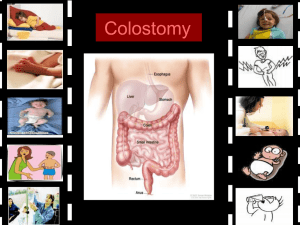
الشريحة 1
... -Monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respirations, and temperature. -The patient is instructed how to support the operative site during deep breathing and coughing, and given pain medication as necessary. -Fluid intake and output is measured, and the operative site is observed for color and amount ...
... -Monitoring of blood pressure, pulse, respirations, and temperature. -The patient is instructed how to support the operative site during deep breathing and coughing, and given pain medication as necessary. -Fluid intake and output is measured, and the operative site is observed for color and amount ...
Cranial Nerve Exam
... Exits: jugular foramen Branches Somatic sensory: o Auricular branch – external auditory meatus & auricle o Dura of post cranial fossa Pharyngeal (somatic motor) – mms of swallowing except stylopharnygeus: o Runs between carotids o Levator palate o Salpingopharyngeus o Palatopharyngeus o palato ...
... Exits: jugular foramen Branches Somatic sensory: o Auricular branch – external auditory meatus & auricle o Dura of post cranial fossa Pharyngeal (somatic motor) – mms of swallowing except stylopharnygeus: o Runs between carotids o Levator palate o Salpingopharyngeus o Palatopharyngeus o palato ...
Enzymes - WordPress.com
... Enzymes are biologic polymers that catalyze the chemical reactions by increasing the rate of reactions without being changed in the overall process. Biomedical importance: • Enzymes play an important role in metabolism, digestion and therapeutics. • The presence and maintenance of enzymes is essent ...
... Enzymes are biologic polymers that catalyze the chemical reactions by increasing the rate of reactions without being changed in the overall process. Biomedical importance: • Enzymes play an important role in metabolism, digestion and therapeutics. • The presence and maintenance of enzymes is essent ...
Cranial Nerves
... Swallowing, head, neck and shoulder movement – damage causes impaired head, neck, shoulder movement; head turns towards injured side ...
... Swallowing, head, neck and shoulder movement – damage causes impaired head, neck, shoulder movement; head turns towards injured side ...
Cha. 9 Autonomic Nervous System
... • enteric nervous system – nervous system in wall of digestive tract – does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord – innervates smooth muscle and glands ...
... • enteric nervous system – nervous system in wall of digestive tract – does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord – innervates smooth muscle and glands ...
Practice Lecture Exam
... The hardened arteries are unable to relax and allow surrounding erectile tissues to fill with blood, which would normally lead to an erection. 6. Trace the fertilization pathway from the site of spermatozoa production to site of fertilization, include all structures traveled. Answer: Seminiferous tu ...
... The hardened arteries are unable to relax and allow surrounding erectile tissues to fill with blood, which would normally lead to an erection. 6. Trace the fertilization pathway from the site of spermatozoa production to site of fertilization, include all structures traveled. Answer: Seminiferous tu ...
Oral sensation
... ▫ hedonistic value of food ~ neural activity here ▫ activity also relates to hunger/repletion ▫ cells can be less provocated by taste from the food which overstock but stay sensitive for other taste modalities ...
... ▫ hedonistic value of food ~ neural activity here ▫ activity also relates to hunger/repletion ▫ cells can be less provocated by taste from the food which overstock but stay sensitive for other taste modalities ...
15-LARYNX
... respiratory tract containing the vocal cords • A 2-inch-long, tube-shaped organ, opens into the laryngeal part of the pharynx above and is continuous with the trachea below • The larynx functions in: Deglutition (swallowing) Respiration (breathing) Phonation (voice production) ...
... respiratory tract containing the vocal cords • A 2-inch-long, tube-shaped organ, opens into the laryngeal part of the pharynx above and is continuous with the trachea below • The larynx functions in: Deglutition (swallowing) Respiration (breathing) Phonation (voice production) ...
Human digestive system

In the human digestive system, the process of digestion has many stages, the first of which starts in the mouth (oral cavity). Digestion involves the breakdown of food into smaller and smaller components which can be absorbed and assimilated into the body. The secretion of saliva helps to produce a bolus which can be swallowed to pass down the oesophagus and into the stomach.Saliva also contains a catalytic enzyme called amylase which starts to act on food in the mouth. Another digestive enzyme called lingual lipase is secreted by some of the lingual papillae to enter the saliva. Digestion is helped by the mastication of food by the teeth and also by the muscular contractions of peristalsis. Gastric juice in the stomach is essential for the continuation of digestion as is the production of mucus in the stomach.Peristalsis is the rhythmic contraction of muscles that begins in the oesophagus and continues along the wall of the stomach and the rest of the gastrointestinal tract. This initially results in the production of chyme which when fully broken down in the small intestine is absorbed as chyle into the lymphatic system. Most of the digestion of food takes place in the small intestine. Water and some minerals are reabsorbed back into the blood, in the colon of the large intestine. The waste products of digestion are defecated from the anus via the rectum.