Physiology Ch 55 p667-678 [4-25
... -special class of neurons called mirror neurons are active when person performs specific motor task or when he/she observes same task performed by others -activity of these neurons mirrors behavior of another person as though observer is performing the movement -mirror neurons are located in premoto ...
... -special class of neurons called mirror neurons are active when person performs specific motor task or when he/she observes same task performed by others -activity of these neurons mirrors behavior of another person as though observer is performing the movement -mirror neurons are located in premoto ...
Notch resolves mixed neural identities in the
... and photoreceptors (Fig. 1B). Thus, to allow us to quantify the total number of projection neurons and photoreceptors, we searched for other markers of these two cell populations. The transgenic line Tg(AANAT2:GFP), in which regulatory elements of the zebrafish serotonin-N-acetyltransferase-2 contro ...
... and photoreceptors (Fig. 1B). Thus, to allow us to quantify the total number of projection neurons and photoreceptors, we searched for other markers of these two cell populations. The transgenic line Tg(AANAT2:GFP), in which regulatory elements of the zebrafish serotonin-N-acetyltransferase-2 contro ...
important ascending tracts
... PAIN AND TEMPERATURE The spinothalamic tract, like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract, uses three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the ...
... PAIN AND TEMPERATURE The spinothalamic tract, like the dorsal column-medial lemniscus tract, uses three neurons to convey sensory information from the periphery to conscious level at the cerebral cortex. Pseudounipolar neurons in the dorsal root ganglion have axons that lead from the skin into the ...
Somatosensory system.
... larger than those of DRG neurons and typically have excitatory centre – inhibitory surround structure • Receptive fields in “higher” cortical areas are larger than those in 3b, and many are much more complex (e.g., sensitive to the orientation of an edge (cf. visual cortex), the direction of movemen ...
... larger than those of DRG neurons and typically have excitatory centre – inhibitory surround structure • Receptive fields in “higher” cortical areas are larger than those in 3b, and many are much more complex (e.g., sensitive to the orientation of an edge (cf. visual cortex), the direction of movemen ...
Neuronal Activity in the Hippocampus During Delayed Non
... performance in an odor-guided continuous delayed non-match to sample task. Although different CAI cells fired in association with each identifiable trial event, these analyses focused on cells that fired selectively during the period of odor cue sampling and response generation. The firing patterns ...
... performance in an odor-guided continuous delayed non-match to sample task. Although different CAI cells fired in association with each identifiable trial event, these analyses focused on cells that fired selectively during the period of odor cue sampling and response generation. The firing patterns ...
Nature template
... efficiently and very fast (5-7). In a brain slice, precise time relations among several neurons have been observed (4). Could this phenomenon be also observed in brains of behaving animals? We use here data-mining techniques and rigorous statistic testing to test how precise are time intervals betwe ...
... efficiently and very fast (5-7). In a brain slice, precise time relations among several neurons have been observed (4). Could this phenomenon be also observed in brains of behaving animals? We use here data-mining techniques and rigorous statistic testing to test how precise are time intervals betwe ...
Neural Coding and Auditory Perception
... higher stimulus levels [20] and fails to account for the upper frequency limit to musical pitch at ~4000 Hz. The failures of traditional rate-place and interval-based representations motivates a search for neural pitch codes that would combine spatial and temporal information. We tested physiologica ...
... higher stimulus levels [20] and fails to account for the upper frequency limit to musical pitch at ~4000 Hz. The failures of traditional rate-place and interval-based representations motivates a search for neural pitch codes that would combine spatial and temporal information. We tested physiologica ...
Rnd family genes are differentially regulated by 3,4 - HAL
... cocaine in this structure. The mRNA level of Rnd3 was affected by the two drugs tested in the three structures at different levels and time post-injection. These results suggest that Rnd3 is a common effector of cocaine and MDMA. This study confirmed the up-regulation of Rnd3 in mice striatum two ho ...
... cocaine in this structure. The mRNA level of Rnd3 was affected by the two drugs tested in the three structures at different levels and time post-injection. These results suggest that Rnd3 is a common effector of cocaine and MDMA. This study confirmed the up-regulation of Rnd3 in mice striatum two ho ...
lec12-dec11
... In n dimensions the relation w • x=q defines a n1 dimensional hyper-plane, which is perpendicular to the weight vector w. On one side of the hyper-plane (w • x > q) all patterns are classified by the TLU as “1”, while those that get classified as “0” lie on the other side of the hyper-plane. If patt ...
... In n dimensions the relation w • x=q defines a n1 dimensional hyper-plane, which is perpendicular to the weight vector w. On one side of the hyper-plane (w • x > q) all patterns are classified by the TLU as “1”, while those that get classified as “0” lie on the other side of the hyper-plane. If patt ...
Modelling Cerebellar Function in Saccadic Adaptation
... • Different regions have different inputs and outputs, (microzones) but same basic organisation • Gives rise to idea of cerebellar chip: ~5000, each with its own particular connections. ...
... • Different regions have different inputs and outputs, (microzones) but same basic organisation • Gives rise to idea of cerebellar chip: ~5000, each with its own particular connections. ...
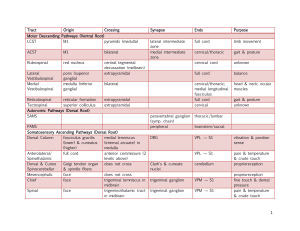
Tract Origin Crossing Synapse Ends Purpose Motor Descending
... pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate other thalamic structures → project to PRF locked-in syndrome: ...
... pons: pontomesencephalic reticular formation (PRF) receives inputs from somatosensory (cord), limbic/cingulate cortex, frontoparietal association cortex, & thalamic reticular nucleus thalamic reticular nucleus: cortical input → modulate other thalamic structures → project to PRF locked-in syndrome: ...
NA EXAM 3 (May 2001)
... There are two pathways for the projections from the basal ganglia output nuclei to the thalamus. The ansa lenticularis is the longer pathway that courses inferior to and around the posterior limb of the internal capsule, on its way to various thalamic targets. It can only been seen in one oblique se ...
... There are two pathways for the projections from the basal ganglia output nuclei to the thalamus. The ansa lenticularis is the longer pathway that courses inferior to and around the posterior limb of the internal capsule, on its way to various thalamic targets. It can only been seen in one oblique se ...
Branched nanostructures represent unique, 3D building blocks for
... investigate extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, where an array of nanoholes precludes or single window allows for direct microbeelectrode contacts. The ability to control and image cell/electrode interactions down to the single-cell level provide a powerful approach for ad ...
... investigate extracellular electron transfer in Shewanella oneidensis MR-1, where an array of nanoholes precludes or single window allows for direct microbeelectrode contacts. The ability to control and image cell/electrode interactions down to the single-cell level provide a powerful approach for ad ...
Cells of the Brain
... learn about the world around them and form memories of events that have taken place. Learning and memory formation alters the structure of the nervous system primarily by affecting the strength of particular synapses. Memories are stored in the brain in stages. Small pieces of new information are pr ...
... learn about the world around them and form memories of events that have taken place. Learning and memory formation alters the structure of the nervous system primarily by affecting the strength of particular synapses. Memories are stored in the brain in stages. Small pieces of new information are pr ...
Multimodal imaging and the neural basis of EEG and fMRI
... diffuse and also have selective pumps (e.g. the sodiumpotassium pump forces 3Na+ out of the cell and picks up 2K+ into the cell on the return trip) causing a concentration gradient. Because ions have electrical charge, the concentration gradient creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) ...
... diffuse and also have selective pumps (e.g. the sodiumpotassium pump forces 3Na+ out of the cell and picks up 2K+ into the cell on the return trip) causing a concentration gradient. Because ions have electrical charge, the concentration gradient creates an electrical potential (about -70 millivolt) ...
make motor neuron posters now
... A. Myelinated axons send messages more quickly than nonmyelinated ones. B. Axons with greater diameter send impulses more quickly. ...
... A. Myelinated axons send messages more quickly than nonmyelinated ones. B. Axons with greater diameter send impulses more quickly. ...
Role of Basal Ganglia in the Regulation of Motor Activities by the
... striatum, subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra. Corpus straitum comprises of the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus (globus pallidus external segment (GPe), globus pallidus internal segment (GPi)). Below is described the role of basal ganglia in the regulation of motor activities by th ...
... striatum, subthalamic nucleus and substantia nigra. Corpus straitum comprises of the caudate nucleus, putamen and globus pallidus (globus pallidus external segment (GPe), globus pallidus internal segment (GPi)). Below is described the role of basal ganglia in the regulation of motor activities by th ...
Stimulus-Dependent Synchronization of Neuronal Responses in the
... selectively and jointly the saliency of all responses that contain episodes of synchronous spiking because synchronous EPSPs summate optimally in target cell populations. If temporal synchronization is exploited by the nervous system to select constellations of responses for further joint processing ...
... selectively and jointly the saliency of all responses that contain episodes of synchronous spiking because synchronous EPSPs summate optimally in target cell populations. If temporal synchronization is exploited by the nervous system to select constellations of responses for further joint processing ...
Chapter 12 Lecture Outline
... – Name the six types of cells that aid neurons and state their respective functions. – Describe the myelin sheath that is found around certain nerve fibers and explain its importance. – Describe the relationship of unmyelinated nerve fibers to their supportive cells. – Explain how damaged nerve fibe ...
... – Name the six types of cells that aid neurons and state their respective functions. – Describe the myelin sheath that is found around certain nerve fibers and explain its importance. – Describe the relationship of unmyelinated nerve fibers to their supportive cells. – Explain how damaged nerve fibe ...
Visual pathway class..
... • We do not have a descriptive or mechanistic model that predicts response properties of downstream visual areas, or behavior. • A descriptive model would vastly transform technology: the primate visual system is far superior to anything that engineers can build. • A mechanistic model is the ultimat ...
... • We do not have a descriptive or mechanistic model that predicts response properties of downstream visual areas, or behavior. • A descriptive model would vastly transform technology: the primate visual system is far superior to anything that engineers can build. • A mechanistic model is the ultimat ...
Neuronal Activation in the Medulla Oblongata During Selective
... intensity, supramaximal for eliciting just the LAR, to provide a similar stimulus intensity across animals. One approach for studying functional brain stem pathways involves Fos immunocytochemistry. The protein product of the immediate early gene c-fos is regarded as a marker for neuronal activation ...
... intensity, supramaximal for eliciting just the LAR, to provide a similar stimulus intensity across animals. One approach for studying functional brain stem pathways involves Fos immunocytochemistry. The protein product of the immediate early gene c-fos is regarded as a marker for neuronal activation ...
Imaging Cells in the Developing Nervous System with Retrovirus
... developing rat cerebral cortex and avian embryos, to test whether the GFP can be used to image the development of cells in these disparate systems. The GFP marker expresses well in many different cell types in both species and continues to be expressed in mature neurons and glia in adult animals. In ...
... developing rat cerebral cortex and avian embryos, to test whether the GFP can be used to image the development of cells in these disparate systems. The GFP marker expresses well in many different cell types in both species and continues to be expressed in mature neurons and glia in adult animals. In ...
nervous system physiology 7
... rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulated organ. Ex. vasoconstriction/dilation of the vessels background "tone" of the PS in the ga ...
... rates of activity are known, respectively, as sympathetic tone and parasympathetic tone. The value of tone is that it allows a single nervous system both to increase and to decrease the activity of a stimulated organ. Ex. vasoconstriction/dilation of the vessels background "tone" of the PS in the ga ...
Physiology of the Striate Cortex
... • Hierarchy of complex receptive fields • Retinal ganglion cells: Center-surround structure, Sensitive to contrast, and wavelength of light • Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity • Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., ...
... • Hierarchy of complex receptive fields • Retinal ganglion cells: Center-surround structure, Sensitive to contrast, and wavelength of light • Striate cortex: Orientation selectivity, direction selectivity, and binocularity • Extrastriate cortical areas: Selective responsive to complex shapes; e.g., ...
Optogenetics

Optogenetics (from Greek optikós, meaning ""seen, visible"") is a biological technique which involves the use of light to control cells in living tissue, typically neurons, that have been genetically modified to express light-sensitive ion channels. It is a neuromodulation method employed in neuroscience that uses a combination of techniques from optics and genetics to control and monitor the activities of individual neurons in living tissue—even within freely-moving animals—and to precisely measure the effects of those manipulations in real-time. The key reagents used in optogenetics are light-sensitive proteins. Spatially-precise neuronal control is achieved using optogenetic actuators like channelrhodopsin, halorhodopsin, and archaerhodopsin, while temporally-precise recordings can be made with the help of optogenetic sensors for calcium (Aequorin, Cameleon, GCaMP), chloride (Clomeleon) or membrane voltage (Mermaid).The earliest approaches were developed and applied by Boris Zemelman and Gero Miesenböck, at the Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center in New York City, and Dirk Trauner, Richard Kramer and Ehud Isacoff at the University of California, Berkeley; these methods conferred light sensitivity but were never reported to be useful by other laboratories due to the multiple components these approaches required. A distinct single-component approach involving microbial opsin genes introduced in 2005 turned out to be widely applied, as described below. Optogenetics is known for the high spatial and temporal resolution that it provides in altering the activity of specific types of neurons to control a subject's behaviour.In 2010, optogenetics was chosen as the ""Method of the Year"" across all fields of science and engineering by the interdisciplinary research journal Nature Methods. At the same time, optogenetics was highlighted in the article on “Breakthroughs of the Decade” in the academic research journal Science. These journals also referenced recent public-access general-interest video Method of the year video and textual SciAm summaries of optogenetics.