Central mechanisms regulating coordinated cardiovascular and
... Sympathetic premotor neurons within the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), many of which are epinephrine-synthesizing neurons of the C1 group, are known to have a critical role in the tonic and reflex control of sympathetic vasomotor activity and blood pressure (41, 70). It is often assumed that ...
... Sympathetic premotor neurons within the rostral ventrolateral medulla (RVLM), many of which are epinephrine-synthesizing neurons of the C1 group, are known to have a critical role in the tonic and reflex control of sympathetic vasomotor activity and blood pressure (41, 70). It is often assumed that ...
ORGANIZATION OF CORTICAL AFFERENTS TO THE FRONTAL
... known to be precisely and topographically connected with this cortex (65). Since MD afferents were determined, it seems justifiable to distinguish within FAC two principal regions, namely the dorsolateral and medioventral. The dorsolateral FAC region is via the lateral MD segment predominantly relat ...
... known to be precisely and topographically connected with this cortex (65). Since MD afferents were determined, it seems justifiable to distinguish within FAC two principal regions, namely the dorsolateral and medioventral. The dorsolateral FAC region is via the lateral MD segment predominantly relat ...
- Journal of Vestibular Research
... time-course of their vestibular compensation. The results show that the monoaminergic changes are different in the two rat strains. In the MVN of albino rats, there was a bilateral increase of MHPG and an ipsilateral increase of dopamine suggesting activation of norepinephrine synthesis and metaboli ...
... time-course of their vestibular compensation. The results show that the monoaminergic changes are different in the two rat strains. In the MVN of albino rats, there was a bilateral increase of MHPG and an ipsilateral increase of dopamine suggesting activation of norepinephrine synthesis and metaboli ...
Neurotoxic Lesions of Basolateral, But Not Central, Amygdala
... mal rats fail to affect the behavior of rats with CN lesions (Holland and Gallagher, 1993a,b). At the same time, evidence from those studies suggests that these attentional functions are regulated by the CN independently of other processes involved in appetitive conditioning. First, rats with CN les ...
... mal rats fail to affect the behavior of rats with CN lesions (Holland and Gallagher, 1993a,b). At the same time, evidence from those studies suggests that these attentional functions are regulated by the CN independently of other processes involved in appetitive conditioning. First, rats with CN les ...
Hindbrain noradrenergic A2 neurons: diverse roles in autonomic
... medullary, pontine, diencephalic, and telencephalic brain regions that underlie these diverse processes. Direct projections from the cortex, limbic forebrain, and hypothalamus to the region of the A2 cell group provide a route through which emotional and cognitive events can modulate visceral respon ...
... medullary, pontine, diencephalic, and telencephalic brain regions that underlie these diverse processes. Direct projections from the cortex, limbic forebrain, and hypothalamus to the region of the A2 cell group provide a route through which emotional and cognitive events can modulate visceral respon ...
PDE5 Exists in Human Neurons and is a Viable Therapeutic Target
... for a variety of neurologic diseases. Although many of these studies have focused on Alzheimer’s disease, the PDE5 literature suggests that PDE5 inhibition may be therapeutic in a variety of neurological disorders (see Discussion). Despite the successes in the animal literature, PDE5 inhibitors have ...
... for a variety of neurologic diseases. Although many of these studies have focused on Alzheimer’s disease, the PDE5 literature suggests that PDE5 inhibition may be therapeutic in a variety of neurological disorders (see Discussion). Despite the successes in the animal literature, PDE5 inhibitors have ...
Here - Institute of Cognitive Neuroscience
... Lesions, Neuropsychology, and Functional Neuroimaging The medial temporal lobes, and hippocampus in particular, have long been known to be crucial for long-term memory (Eichenbaum & Cohen, 1988; Scoville & Milner, 1957; Squire, 1986), together with other elements of Papez’s circuit (Aggleton & Brown ...
... Lesions, Neuropsychology, and Functional Neuroimaging The medial temporal lobes, and hippocampus in particular, have long been known to be crucial for long-term memory (Eichenbaum & Cohen, 1988; Scoville & Milner, 1957; Squire, 1986), together with other elements of Papez’s circuit (Aggleton & Brown ...
Fear Models in Animals and Humans
... nucleus of the amygdala (BA), which in turn projects to the CE. Following CS presentation, the prelimbic cortex might transform phasic signals from the LA into sustained prelimbic firing that directly influences fear expression via its CE projections. Discrimination conditioning paradigms are often ...
... nucleus of the amygdala (BA), which in turn projects to the CE. Following CS presentation, the prelimbic cortex might transform phasic signals from the LA into sustained prelimbic firing that directly influences fear expression via its CE projections. Discrimination conditioning paradigms are often ...
Enhanced intrinsic excitability and EPSP
... alone or if intrinsic plasticity, such as strengthening of E-S coupling, also plays a role. ...
... alone or if intrinsic plasticity, such as strengthening of E-S coupling, also plays a role. ...
Update on models of basal ganglia function and dysfunction
... receive inputs from distinct groups of cortical neurons [18], but these results are difficult to reconcile with primate studies in which cortical neurons, activated by antidromic stimulation of the putamen, were identified as slowly-responding non-pyramidal cells of low activity [19,20]. Finally, anat ...
... receive inputs from distinct groups of cortical neurons [18], but these results are difficult to reconcile with primate studies in which cortical neurons, activated by antidromic stimulation of the putamen, were identified as slowly-responding non-pyramidal cells of low activity [19,20]. Finally, anat ...
Insular cortex – review
... the human taste cortex11 which shows us an evolutionary aspect of eliciting responses in the taste cortex by substances important for modifying behavior and survival. As mentioned earlier, the primary gustatory cortex doesn’t just respond to basic stimuli which accompanies our experience of ingestin ...
... the human taste cortex11 which shows us an evolutionary aspect of eliciting responses in the taste cortex by substances important for modifying behavior and survival. As mentioned earlier, the primary gustatory cortex doesn’t just respond to basic stimuli which accompanies our experience of ingestin ...
On the computational architecture of the neocortex
... R E nucleus, the nuclei in the thalamus are not directly connected to each other. Where does the thalamus get its input? Some nuclei in the thalamus are the principal route for sensory signals and 'relay' these up to the primary sensory areas of the cortex, e.g. L G N to V1. And the nucleus VLp tran ...
... R E nucleus, the nuclei in the thalamus are not directly connected to each other. Where does the thalamus get its input? Some nuclei in the thalamus are the principal route for sensory signals and 'relay' these up to the primary sensory areas of the cortex, e.g. L G N to V1. And the nucleus VLp tran ...
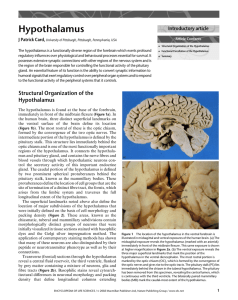
Hypothalamus
... regulatory influences over physiological and behavioural processes essential for survival. It possesses extensive synaptic connections with other regions of the nervous system and is the region of the brain responsible for controlling the functional activity of the pituitary gland. An essential feat ...
... regulatory influences over physiological and behavioural processes essential for survival. It possesses extensive synaptic connections with other regions of the nervous system and is the region of the brain responsible for controlling the functional activity of the pituitary gland. An essential feat ...
The medial geniculate, not the amygdala, as the root of auditory fear
... the lateral nucleus of the amygdala.] 3.3. Experimental support for the AMYG model The AMYG model has been presented in numerous reviews (e.g., Fanselow and LeDoux, 1999; LeDoux, 1990, 1992, 1993a, 1994, 1995, 2000; LeDoux and Muller, 1997; Maren, 2001; Maren and Quirk, 2004; Phelps and LeDoux, 2005 ...
... the lateral nucleus of the amygdala.] 3.3. Experimental support for the AMYG model The AMYG model has been presented in numerous reviews (e.g., Fanselow and LeDoux, 1999; LeDoux, 1990, 1992, 1993a, 1994, 1995, 2000; LeDoux and Muller, 1997; Maren, 2001; Maren and Quirk, 2004; Phelps and LeDoux, 2005 ...
Cognitive function in young and adult IL (interleukin)
... on the basis of the total number of errors (which corresponded to a re-entry into the arm just visited). At the same time, the pattern of arm entry was examined according to McCann et al. [32], who designed a method to analyse the angle chosen when the mouse entered two consecutive arms. In the eigh ...
... on the basis of the total number of errors (which corresponded to a re-entry into the arm just visited). At the same time, the pattern of arm entry was examined according to McCann et al. [32], who designed a method to analyse the angle chosen when the mouse entered two consecutive arms. In the eigh ...
Neural Correlates of Object-Associated Choice Behavior
... The perirhinal cortex (PRC) is reportedly important for object recognition memory, with supporting physiological evidence obtained largely from primate studies. Whether neurons in the rodent PRC also exhibit similar physiological correlates of object recognition, however, remains to be determined. W ...
... The perirhinal cortex (PRC) is reportedly important for object recognition memory, with supporting physiological evidence obtained largely from primate studies. Whether neurons in the rodent PRC also exhibit similar physiological correlates of object recognition, however, remains to be determined. W ...
FULL TEXT PDF - An International Journal of Experimental and
... of aberrant electrical activity of epileptic seizures.[4] However, it has become clear that neuronal function and by extension neuronal dysfunction, are tightly modulated, in fact controlled, by a number of non-neuronal cells. Many of these are glial cells including astrocytes, microglial cells, and ...
... of aberrant electrical activity of epileptic seizures.[4] However, it has become clear that neuronal function and by extension neuronal dysfunction, are tightly modulated, in fact controlled, by a number of non-neuronal cells. Many of these are glial cells including astrocytes, microglial cells, and ...
Distinct Mechanisms for Processing Spatial Sequences and Pitch
... cortical areas (Griffiths and Warren, 2002). PT is a large region of auditory association cortex, occupying the superior temporal plane posterior to Heschl’s gyrus (HG) (Westbury et al., 1999). PT is involved in processing many different types of sound patterns, including both intrinsic spectrotempo ...
... cortical areas (Griffiths and Warren, 2002). PT is a large region of auditory association cortex, occupying the superior temporal plane posterior to Heschl’s gyrus (HG) (Westbury et al., 1999). PT is involved in processing many different types of sound patterns, including both intrinsic spectrotempo ...
Chapter 12 PowerPoint - Hillsborough Community College
... Clinical – Homeostatic Imbalance 12.1 • Muscle strength or ability to perform discrete individual movements is not impaired; only control over movements is lost – Example: damage to premotor area controlling movement of fingers would still allow fingers to move, but voluntary control needed to type ...
... Clinical – Homeostatic Imbalance 12.1 • Muscle strength or ability to perform discrete individual movements is not impaired; only control over movements is lost – Example: damage to premotor area controlling movement of fingers would still allow fingers to move, but voluntary control needed to type ...
The Prefrontal Cortex and Flexible Behavior
... the specialized connection of the posterior orbitofrontal cortex with the amygdala, which has a key role in emotional processes. Excitatory Prefrontal Pathways In primates, the pathways that link a given cortical area with other cortical or subcortical structures are excitatory glutamatergic pathway ...
... the specialized connection of the posterior orbitofrontal cortex with the amygdala, which has a key role in emotional processes. Excitatory Prefrontal Pathways In primates, the pathways that link a given cortical area with other cortical or subcortical structures are excitatory glutamatergic pathway ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.