Fast Network Oscillations in the Hippocampal CA1
... events correlated with the relative increase in firing frequency of neurons (Fig. 3B,C). The correlation with pyramidal cell discharges was linear, except for the lowest-amplitude events (,4 SD). Interneurons also increased their firing rate as a f unction of the field amplitude, but rate of the inc ...
... events correlated with the relative increase in firing frequency of neurons (Fig. 3B,C). The correlation with pyramidal cell discharges was linear, except for the lowest-amplitude events (,4 SD). Interneurons also increased their firing rate as a f unction of the field amplitude, but rate of the inc ...
Full-Text PDF
... evolutionary advantage. The regulation of fear and fear memories consists of motor/autonomic components (changes in blood pressure and heart rate, dilation of pupils), endocrine, behavioral responses (freezing behavior, potentiated startle reflex) [90], and the affective component. It has been propo ...
... evolutionary advantage. The regulation of fear and fear memories consists of motor/autonomic components (changes in blood pressure and heart rate, dilation of pupils), endocrine, behavioral responses (freezing behavior, potentiated startle reflex) [90], and the affective component. It has been propo ...
Reinforcement Learning and the Basal Ganglia
... GPi (the entopeduncular nucleus in rodents). Although these two structures are separated by the fibres of the cerebral pedunculus in most mammals, they contain cytologically similar neurons, and are thus commonly regarded as one functional structure (GPi/SNr). In the absence of striatal inhibition, ...
... GPi (the entopeduncular nucleus in rodents). Although these two structures are separated by the fibres of the cerebral pedunculus in most mammals, they contain cytologically similar neurons, and are thus commonly regarded as one functional structure (GPi/SNr). In the absence of striatal inhibition, ...
Primate amygdala neurons evaluate the progress of self
... Abstract The amygdala is a prime valuation structure yet its functions in advanced behaviors are poorly understood. We tested whether individual amygdala neurons encode a critical requirement for goal-directed behavior: the evaluation of progress during sequential choices. As monkeys progressed thro ...
... Abstract The amygdala is a prime valuation structure yet its functions in advanced behaviors are poorly understood. We tested whether individual amygdala neurons encode a critical requirement for goal-directed behavior: the evaluation of progress during sequential choices. As monkeys progressed thro ...
Projections of the median raphe nucleus in the rat
... superior colliculus SC, intermediate and superficial layers septofimbrial nucleus septohippocampal nucleus ...
... superior colliculus SC, intermediate and superficial layers septofimbrial nucleus septohippocampal nucleus ...
Molecular and morphological analyses of basal forebrain
... The axis of patterning in the rostrobasal telencephalon gives rise to subpallial proliferative zones of the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE), lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE) and the preoptic area (POA) which contribute to nearly all forebrain structures such as the cortex, striatum, hippocampus, ...
... The axis of patterning in the rostrobasal telencephalon gives rise to subpallial proliferative zones of the medial ganglionic eminence (MGE), lateral ganglionic eminence (LGE) and the preoptic area (POA) which contribute to nearly all forebrain structures such as the cortex, striatum, hippocampus, ...
CCNBook/Neuron
... biological cells, not just neurons). But often it comes down to a judgment call about what phenomena you regard as being important, which will vary depending on the scientific questions being addressed with the model. The approach taken for the models in this book is to find some kind of happy (or u ...
... biological cells, not just neurons). But often it comes down to a judgment call about what phenomena you regard as being important, which will vary depending on the scientific questions being addressed with the model. The approach taken for the models in this book is to find some kind of happy (or u ...
Hippocampus : Neurotransmission and Plasticity in the Nervous
... sensation [1]. It is part of the grey matter, composed of unmyelinated nerve cells. The neocortex is the outer region of the cerebral cortex. It is folded in lobes or cortical structures; the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes [2]. The hippocampus is a bilateral structure, located benea ...
... sensation [1]. It is part of the grey matter, composed of unmyelinated nerve cells. The neocortex is the outer region of the cerebral cortex. It is folded in lobes or cortical structures; the frontal, parietal, occipital and temporal lobes [2]. The hippocampus is a bilateral structure, located benea ...
Developing Standardized Behavioral Tests for
... given to the animals? The type and amount of food provided to the animals may alter their behavior; for example, dietary restriction alters motor behavior (Duan and Mattson 1999) and levels of constituents such as lineolate in the diet influence activity, emotionality, and cognitive performance (Ume ...
... given to the animals? The type and amount of food provided to the animals may alter their behavior; for example, dietary restriction alters motor behavior (Duan and Mattson 1999) and levels of constituents such as lineolate in the diet influence activity, emotionality, and cognitive performance (Ume ...
Behavioral consequences of abnormal cortical development
... correlation between cortical synaptogenesis and behavioral development emphasizes the importance of this developmental phase and its relevancy to behavior [47,140,159]. In humans, cortical differentiation extends through the first two decades of life [228], making this phase the most relevant to stu ...
... correlation between cortical synaptogenesis and behavioral development emphasizes the importance of this developmental phase and its relevancy to behavior [47,140,159]. In humans, cortical differentiation extends through the first two decades of life [228], making this phase the most relevant to stu ...
The habenular nuclei - Philosophical Transactions of the Royal
... been reported to reduce substance P levels in the LHb (see Sutherland 1982). (ii) Lateral habenula When compared with the MHb, the LHb shows broader and less evolutionarily conserved connectivity. It is thought to be involved in the motor–limbic interface because it receives significant pallidal inp ...
... been reported to reduce substance P levels in the LHb (see Sutherland 1982). (ii) Lateral habenula When compared with the MHb, the LHb shows broader and less evolutionarily conserved connectivity. It is thought to be involved in the motor–limbic interface because it receives significant pallidal inp ...
Gap Junctions in the Ventral Hippocampal-Medial
... Departments of 1Psychology and 2Molecular Biology and Princeton Neuroscience Institute, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544 ...
... Departments of 1Psychology and 2Molecular Biology and Princeton Neuroscience Institute, Princeton University, Princeton, New Jersey 08544 ...
Psychosocial Stress in Rats: Animal Model of PTSD Based on
... expression, and most important, persistence. That is, only a subset (10–50 %) of traumatized individuals develops PTSD, depending on a multitude of interacting risk factors, including the nature of the trauma, genetics, gender, social support, and early life experiences (Zoladz and Diamond 2013). Th ...
... expression, and most important, persistence. That is, only a subset (10–50 %) of traumatized individuals develops PTSD, depending on a multitude of interacting risk factors, including the nature of the trauma, genetics, gender, social support, and early life experiences (Zoladz and Diamond 2013). Th ...
Central Nervous System (CNS) The Brain Embryonic Development
... • Motor areas – control voluntary movement • Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensation • Association areas – integrate diverse information ...
... • Motor areas – control voluntary movement • Sensory areas – conscious awareness of sensation • Association areas – integrate diverse information ...
The continuous performance test: a window on
... The posterior parietal lobe takes on increased importance with regard to visual and spatial information. As with Mesulam’s model, the limbic system is involved with the motivational state of the individual. Thus, sensory inattention is viewed specifically as a dysfunction of the corticolimbic–reticu ...
... The posterior parietal lobe takes on increased importance with regard to visual and spatial information. As with Mesulam’s model, the limbic system is involved with the motivational state of the individual. Thus, sensory inattention is viewed specifically as a dysfunction of the corticolimbic–reticu ...
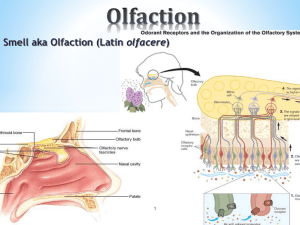
olfaction
... paleocortex) adjacent to lateral olfactory tract in temporal lobe. This is only sense that does not have relay in thalamus on way from receptors to cerebral cortex. From piriform cortex there are projections to hypothalamus, the thalamus, amygdala, entorhinal cortex. From thalamus there is a project ...
... paleocortex) adjacent to lateral olfactory tract in temporal lobe. This is only sense that does not have relay in thalamus on way from receptors to cerebral cortex. From piriform cortex there are projections to hypothalamus, the thalamus, amygdala, entorhinal cortex. From thalamus there is a project ...
Projection patterns from the amygdaloid nuclear complex to
... An example of retrogradely-labeled neurons in the amygdaloid nuclear complex following WG injection into midline (Figs. 3A–C, R119) or lateral wing DR (Figs. 3D–F, R127) is depicted in Fig. 3. As described, the majority of labeled cells were mainly located in the medial amygdaloid nucleus (Figs. 3A– ...
... An example of retrogradely-labeled neurons in the amygdaloid nuclear complex following WG injection into midline (Figs. 3A–C, R119) or lateral wing DR (Figs. 3D–F, R127) is depicted in Fig. 3. As described, the majority of labeled cells were mainly located in the medial amygdaloid nucleus (Figs. 3A– ...
Gamma Oscillations in the Hippocampus
... oscillations provided the precise temporal synchrony necessary for binding distributed cells involved in coding various aspects of a particular stimulus. Gamma synchronized firing was recorded across neurons in separate columns of primary visual cortex when cells responded to different aspects of th ...
... oscillations provided the precise temporal synchrony necessary for binding distributed cells involved in coding various aspects of a particular stimulus. Gamma synchronized firing was recorded across neurons in separate columns of primary visual cortex when cells responded to different aspects of th ...
Piracetam and other structurally related nootropics
... Almost thirty years have now passed since the discovery of the piracetam-like nootropics. The term nootropiC92794,95 was coined by Giurgea in 1972, from Greek BOOS(~00s) (mind) and Greek tropos (T~OTOS) (turn), to describe the then netily discovered properties of these compounds: (1) enhancement of ...
... Almost thirty years have now passed since the discovery of the piracetam-like nootropics. The term nootropiC92794,95 was coined by Giurgea in 1972, from Greek BOOS(~00s) (mind) and Greek tropos (T~OTOS) (turn), to describe the then netily discovered properties of these compounds: (1) enhancement of ...
Supplementary Information (doc 137K)
... We also analyzed the probe data by examining the time mice spent in each of the four zones, rather than comparing the time spent in the target zone versus the average of the three other zones (as in Figure 2b). During this probe test, WT-GFP, WT-CREB and Tg-CREB mice spent more time in the zone in w ...
... We also analyzed the probe data by examining the time mice spent in each of the four zones, rather than comparing the time spent in the target zone versus the average of the three other zones (as in Figure 2b). During this probe test, WT-GFP, WT-CREB and Tg-CREB mice spent more time in the zone in w ...
Effects of tryptophan andror acute running on extracellular 5
... Among animal models of psychiatric disorders, starvation-induced hyperactivity has received a great deal of attention because it may be endowed with features observed in anorexia nervosa w2,3,19,38x andror obsessivecompulsive disorder w1x. This model is based on the observation that fed rats given a ...
... Among animal models of psychiatric disorders, starvation-induced hyperactivity has received a great deal of attention because it may be endowed with features observed in anorexia nervosa w2,3,19,38x andror obsessivecompulsive disorder w1x. This model is based on the observation that fed rats given a ...
From Neuro-Psychoanalysis to Cognitive and Affective Automation Systems
... evaluate situations, different types of memories, planning (‘acting-as-if’) capabilities, and conflict resolution mechanisms are introduced as important functional elements. All these elements are arranged using the id-ego-superego model of Freud as template. The model helps to determine how to comb ...
... evaluate situations, different types of memories, planning (‘acting-as-if’) capabilities, and conflict resolution mechanisms are introduced as important functional elements. All these elements are arranged using the id-ego-superego model of Freud as template. The model helps to determine how to comb ...
Prefrontal Activation Deficits During Episodic Memory in
... ALE produces convergence maps of brain activation by examining the probability that spatially smoothed activation foci from individual studies occur across multiple studies. This approach tests the null hypothesis that the location of activated foci is equal at every voxel against an alternative hyp ...
... ALE produces convergence maps of brain activation by examining the probability that spatially smoothed activation foci from individual studies occur across multiple studies. This approach tests the null hypothesis that the location of activated foci is equal at every voxel against an alternative hyp ...
Limbic system

The limbic system (or paleomammalian brain) is a complex set of brain structures located on both sides of the thalamus, right under the cerebrum. It is not a separate system but a collection of structures from the telencephalon, diencephalon, and mesencephalon. It includes the olfactory bulbs, hippocampus, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei, fornix, columns of fornix, mammillary body, septum pellucidum, habenular commissure, cingulate gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, limbic cortex, and limbic midbrain areas.The limbic system supports a variety of functions including epinephrine flow, emotion, behavior, motivation, long-term memory, and olfaction. Emotional life is largely housed in the limbic system, and it has a great deal to do with the formation of memories.Although the term only originated in the 1940s, some neuroscientists, including Joseph LeDoux, have suggested that the concept of a functionally unified limbic system should be abandoned as obsolete because it is grounded mainly in historical concepts of brain anatomy that are no longer accepted as accurate.