Document
... 2. What is the standard SI unit for volume? MASS 3. What is the standard SI unit for mass? GRAM 4. What is the standard SI unit for length? METER ...
... 2. What is the standard SI unit for volume? MASS 3. What is the standard SI unit for mass? GRAM 4. What is the standard SI unit for length? METER ...
Atomic Structure Practice Answers
... 10. An atomic orbital can hold no more than 2 electrons A 11. The reason the 4s orbitals fill before the 3d. B 12. In the ground state, the highest energy electron of a rubidium atom might have which of the following sets of quantum numbers? A. 5,0,1,1/2 B. 5,1,1,1/2 C. 4,0,0,1/2 D. 5,0,0,1/2 E. 6, ...
... 10. An atomic orbital can hold no more than 2 electrons A 11. The reason the 4s orbitals fill before the 3d. B 12. In the ground state, the highest energy electron of a rubidium atom might have which of the following sets of quantum numbers? A. 5,0,1,1/2 B. 5,1,1,1/2 C. 4,0,0,1/2 D. 5,0,0,1/2 E. 6, ...
ParticleDetection2_2012
... Energy Loss of Electrons and Positrons Electrons lose energy through ionization as for heavy charged particles, but due to small mass additional significant loss through bremsstrahlung radiation. Total energy loss: ...
... Energy Loss of Electrons and Positrons Electrons lose energy through ionization as for heavy charged particles, but due to small mass additional significant loss through bremsstrahlung radiation. Total energy loss: ...
Chapter 5 reveiw
... they are more stable than partially-filled energy sublevels. Examples: Cr and Cu 8. The speed of all types of electromagnetic radiation is always the same (3.0 x 108 m/s) in a vacuum. 9. The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to the frequency of electromagnetic. (the e ...
... they are more stable than partially-filled energy sublevels. Examples: Cr and Cu 8. The speed of all types of electromagnetic radiation is always the same (3.0 x 108 m/s) in a vacuum. 9. The wavelength of electromagnetic radiation is inversely proportional to the frequency of electromagnetic. (the e ...
Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
... still a pleasing result which can be obtained without fancy electromagnetic techniques. One of the things which ultimately led physicists to suspect that this picture was completely wrong is the fact that accelerating charges radiate: i.e., they lose energy to electromagnetic radiation. The rate at ...
... still a pleasing result which can be obtained without fancy electromagnetic techniques. One of the things which ultimately led physicists to suspect that this picture was completely wrong is the fact that accelerating charges radiate: i.e., they lose energy to electromagnetic radiation. The rate at ...
Hands-on-training: Introduction to emission spectroscopy
... In ECRIS plasma heating is based on energy transfer from microwaves to electrons via electron cyclotron resonance Electron energies range from cold electrons with 1 eV energies up to hot electrons with energies in the order of ...
... In ECRIS plasma heating is based on energy transfer from microwaves to electrons via electron cyclotron resonance Electron energies range from cold electrons with 1 eV energies up to hot electrons with energies in the order of ...
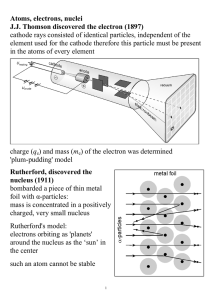
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the nucleus: no radiation atoms radiate if an electron 'jumps' from one such orb ...
... interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a general characteristic of matter Bohr's model (incorrect, but useful) electrons in an atom can only occupy certain distinct orbits around the nucleus: no radiation atoms radiate if an electron 'jumps' from one such orb ...
physics 225, 2nd year lab - University of Toronto Physics
... “Radiation” here refers to ionizing radiation such as α, β, γ nuclear emanations, not low energy electromagnetic (photonic) radiation. Typically arising from spontaneous or stimulated nuclear decay, e.g., neutron, γ or X-ray irradiation of atoms. Kinetic energy (non rest mass component) >> 10 eV , t ...
... “Radiation” here refers to ionizing radiation such as α, β, γ nuclear emanations, not low energy electromagnetic (photonic) radiation. Typically arising from spontaneous or stimulated nuclear decay, e.g., neutron, γ or X-ray irradiation of atoms. Kinetic energy (non rest mass component) >> 10 eV , t ...
Bohr Model Notes - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Electrons are placed in energy levels (orbitals) outside the nucleus. 2 electrons can fit in the first energy level. 8 electrons can fit in the second energy level. 18 electrons can fit in the third energy level. Valence Electrons – electrons found in the outermost energy levels. Magnesium has ...
... Electrons are placed in energy levels (orbitals) outside the nucleus. 2 electrons can fit in the first energy level. 8 electrons can fit in the second energy level. 18 electrons can fit in the third energy level. Valence Electrons – electrons found in the outermost energy levels. Magnesium has ...
Ch 11 WS Orbitals and Electron Arrangement
... is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. 8. Circle the letter of the term that is used to label the energy levels of electrons. a. atomic orbitals c. quantum b. quantum mechanical numbers d. principal quantum numbers (n) 9. Principal energ ...
... is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. 8. Circle the letter of the term that is used to label the energy levels of electrons. a. atomic orbitals c. quantum b. quantum mechanical numbers d. principal quantum numbers (n) 9. Principal energ ...
Ay 122 - Fall 2004 Electromagnetic Radiation And Its Interactions With Matter
... Free-free radiation: Bremsstrahlung Hydrogen is ionized at T ~ 104 K at low density. For the same mixture of chemical elements as the Sun, maximum radiation due to spectral lines occurs at T ~ 105 K. At higher T, radiation due to acceleration of unbound electrons becomes most ...
... Free-free radiation: Bremsstrahlung Hydrogen is ionized at T ~ 104 K at low density. For the same mixture of chemical elements as the Sun, maximum radiation due to spectral lines occurs at T ~ 105 K. At higher T, radiation due to acceleration of unbound electrons becomes most ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
... a. 0.652 dm, b. 2,300 kg, c. 65 mL, d. 50,200 cm 1900 mL 8.7 hours slope = (mass) (volume) = density always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they ...
Nuclear Decay (Radioactivity)
... What would happen to the nuclear make-up as a result of beta radiation? Consider: carbon – 14. ...
... What would happen to the nuclear make-up as a result of beta radiation? Consider: carbon – 14. ...
Accelerated Chemistry
... need to know how to do! Also check out the tables and figures – they help! ...
... need to know how to do! Also check out the tables and figures – they help! ...
Chemistry TEST 4 Review and Answers
... Chapter 5 Electrons in atoms and Chapter 6.3 Periodic Trends ...
... Chapter 5 Electrons in atoms and Chapter 6.3 Periodic Trends ...
Charged Particle Interactions with Matter: R Z M
... γ ≡ 1 / 1 − v 2 / c 2 >> 1 (“fast” = “Born approximation”). The bound electron on the other hand has only a charge, − e , a mass, m , and bound energy such that kinetic energy, T, roughly equals its potential energy. The velocity is v ,(not frequency here). In other words: mv 2 / 2 ~ e 2 / a0 where ...
... γ ≡ 1 / 1 − v 2 / c 2 >> 1 (“fast” = “Born approximation”). The bound electron on the other hand has only a charge, − e , a mass, m , and bound energy such that kinetic energy, T, roughly equals its potential energy. The velocity is v ,(not frequency here). In other words: mv 2 / 2 ~ e 2 / a0 where ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.