Honors Chemistry Unit 1 Outline – 2012-2013
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...
... Chm 1.1.3 Chapter 4 a. Understand that energy exists in discrete units called quanta b. Describe the concepts of excited and ground state electrons in the atom c. Articulate that electromagnetic radiation is made up of photons d. Understand the relationship between wavelength and frequency e. Use th ...
Particle Interactions - NIU - Northern Illinois University
... • Part of the radon decay chain includes a 7.69 MeV alpha particle. What is the range of this particle in soft tissue? • Use proton mass and charge equal to 1. – Ma = 4, Z2 = 4 ...
... • Part of the radon decay chain includes a 7.69 MeV alpha particle. What is the range of this particle in soft tissue? • Use proton mass and charge equal to 1. – Ma = 4, Z2 = 4 ...
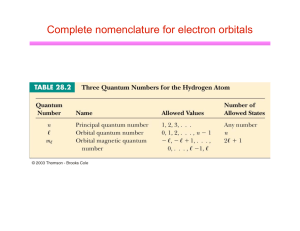
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
... l Can think of the electron as spinning on its axis u ...
... l Can think of the electron as spinning on its axis u ...
Chapter-29 Particles and Waves
... One of the most incredible discoveries of twentiethcentury physics is that particles can also behave like waves and exhibit interference effects. (a) If electrons behaved as discrete particles with no wave properties, they would pass through one or the other of the two slits and strike the screen, c ...
... One of the most incredible discoveries of twentiethcentury physics is that particles can also behave like waves and exhibit interference effects. (a) If electrons behaved as discrete particles with no wave properties, they would pass through one or the other of the two slits and strike the screen, c ...
Chapter 27
... They followed this with extensive diffraction measurements from various materials The wavelength of the electrons calculated from the diffraction data agreed with the expected de Broglie wavelength This confirmed the wave nature of electrons Other experimenters have confirmed the wave nature of othe ...
... They followed this with extensive diffraction measurements from various materials The wavelength of the electrons calculated from the diffraction data agreed with the expected de Broglie wavelength This confirmed the wave nature of electrons Other experimenters have confirmed the wave nature of othe ...
PPT
... goes through a prism, it is decomposed into many colors (white light is the sum of many frequencies). ...
... goes through a prism, it is decomposed into many colors (white light is the sum of many frequencies). ...
Quiz 1 - sample quiz
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
... 9. Which one of the following statements is false? a) An electron jumps from a high energy orbital to a lower energy orbital when a photon of energy is emitted by an atom. b) The energy of light is directly proportional to its wavelength. c) The atomic emission spectrum consists of a series of discr ...
Quantum Mechanical Derivation of the Wallis Formula for $\ pi$
... It is the purpose of this paper to show that this formula can in fact be derived from a variational computation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom. The existence of such a derivation indicates that there are striking connections between well-established physics and pure mathematics [9] that are re ...
... It is the purpose of this paper to show that this formula can in fact be derived from a variational computation of the spectrum of the hydrogen atom. The existence of such a derivation indicates that there are striking connections between well-established physics and pure mathematics [9] that are re ...
Prelab: Empirical Formulas
... n = molecular formula molar mass ÷ empirical formula molar mass If n = 1, then the empirical formula = molecular formula For example, glucose has the Molecular Formula: C6H12O6, but the simplest whole number ratio between C, H and O in glucose is CH2O, which is the Empirical Formula. The value of n ...
... n = molecular formula molar mass ÷ empirical formula molar mass If n = 1, then the empirical formula = molecular formula For example, glucose has the Molecular Formula: C6H12O6, but the simplest whole number ratio between C, H and O in glucose is CH2O, which is the Empirical Formula. The value of n ...
Trends of the Periodic Table - Laureate International College
... electrons will experience a greater electrostatic attraction for the nucleus. • As electrons are positioned in energy shells further from the nucleus, they will experience less electrostatic attraction from the positive nucleus. ...
... electrons will experience a greater electrostatic attraction for the nucleus. • As electrons are positioned in energy shells further from the nucleus, they will experience less electrostatic attraction from the positive nucleus. ...
AtomLightEmissQuantum
... The energy of the emitted photon is related to the frequency, given by the equation E = hf (proposed by Max Planck) ...
... The energy of the emitted photon is related to the frequency, given by the equation E = hf (proposed by Max Planck) ...
Quantization of Energy
... Einstein (1905) successfully resolved this paradox by employing Planck’s idea of quantization of energy and proposed that the incident light consisted of individual quanta, called photons, that interacted with the electrons in the metal like discrete particles, rather than as continuous waves. hν = ...
... Einstein (1905) successfully resolved this paradox by employing Planck’s idea of quantization of energy and proposed that the incident light consisted of individual quanta, called photons, that interacted with the electrons in the metal like discrete particles, rather than as continuous waves. hν = ...
Flame Tests!!
... The Visible Portion of the Electromagnetic Spectrum: • Table A lists the wavelengths associated with each of the colors in the visible spectrum. The representative wavelengths are used as benchmarks for each color. A color of yellow-orange may be estimated at 585 depending on the degree of yellow o ...
... The Visible Portion of the Electromagnetic Spectrum: • Table A lists the wavelengths associated with each of the colors in the visible spectrum. The representative wavelengths are used as benchmarks for each color. A color of yellow-orange may be estimated at 585 depending on the degree of yellow o ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Practice Exam (2).
... a. anything that has mass associated with it is excluded from the possibility of producing a wave, since only photons produce wave. b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of e ...
... a. anything that has mass associated with it is excluded from the possibility of producing a wave, since only photons produce wave. b. any electron present in an atom can have the same quantum state, since all electrons in an atom have the same mass and charge. c. there can be infinitely amount of e ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.