Document
... Example 28-1 (continued). The strong nuclear force has a range of about 1.5x10-15 m. In 1935 Hideki Yukawa predicted the existence of a particle named the pion (π) that somehow “carried” the strong nuclear force. Assume this particle can be created because the uncertainty principle allows non-conse ...
... Example 28-1 (continued). The strong nuclear force has a range of about 1.5x10-15 m. In 1935 Hideki Yukawa predicted the existence of a particle named the pion (π) that somehow “carried” the strong nuclear force. Assume this particle can be created because the uncertainty principle allows non-conse ...
RAD 107 HOMEWORK 4
... 5. How much kinetic energy must an electron have in order to knock a Tungsten K-shell electron out a Tungsten atom? How much to knock out a Tungsten N-shell electron? [Hint: read the first table in Problem 4.] 6. Suppose that a K-shell electron has been knocked out of a Tungsten atom due to a collis ...
... 5. How much kinetic energy must an electron have in order to knock a Tungsten K-shell electron out a Tungsten atom? How much to knock out a Tungsten N-shell electron? [Hint: read the first table in Problem 4.] 6. Suppose that a K-shell electron has been knocked out of a Tungsten atom due to a collis ...
Science 8: Unit C: Light and Optical Systems
... • Most UV radiation produced by the sun is reflected by the Ozone layer in the atmosphere. • This is a good thing because UV radiation has a high enough frequency and energy to penetrate and mutate skin cells, tanning our skin, burning our skin, and if given ...
... • Most UV radiation produced by the sun is reflected by the Ozone layer in the atmosphere. • This is a good thing because UV radiation has a high enough frequency and energy to penetrate and mutate skin cells, tanning our skin, burning our skin, and if given ...
AP B - Unit 11 - 2013
... - typical x-ray wavelengths are about 0.1 nm, which is on the order of the atomic spacing in a solid - x-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum →frequencies higher than those of ultraviolet radiation →can penetrate most materials with relative ease - x-rays are produced when high-speed electr ...
... - typical x-ray wavelengths are about 0.1 nm, which is on the order of the atomic spacing in a solid - x-rays are part of the electromagnetic spectrum →frequencies higher than those of ultraviolet radiation →can penetrate most materials with relative ease - x-rays are produced when high-speed electr ...
Double-Slit Experiment
... 1. Studies in which the frequency of the light is varied show that NO electrons are emitted by a given metal below a specific threshold frequency, v0 . 2. For light with frequency lower than the threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with f ...
... 1. Studies in which the frequency of the light is varied show that NO electrons are emitted by a given metal below a specific threshold frequency, v0 . 2. For light with frequency lower than the threshold frequency, no electrons are emitted regardless of the intensity (amplitude) 3. For light with f ...
Quantum physics
... produced, we first discuss the electron. Quantum theory of the atom describes the behavior of electrons. Electrons can described to follow the rules of standing waves. (Show standing waves with long spring.) Notice the number of loop/nodes/humps are quantized. This means the wavelength and frequenci ...
... produced, we first discuss the electron. Quantum theory of the atom describes the behavior of electrons. Electrons can described to follow the rules of standing waves. (Show standing waves with long spring.) Notice the number of loop/nodes/humps are quantized. This means the wavelength and frequenci ...
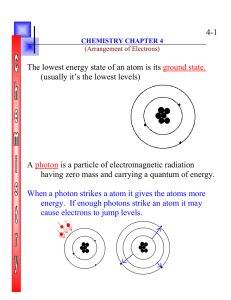
4-1 The lowest energy state of an atom is its ground state. (usually
... having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
... having zero mass and carrying a quantum of energy. When a photon strikes a atom it gives the atoms more energy. If enough photons strike an atom it may cause electrons to jump levels. ...
Atomic Structure Zumdahl Chemistry Chapter 7
... Electromagnetic radiation, which at the turn of the twentieth century was thought to be a pure waveform, was found to possess particulate properties. Conversely, electrons, which were thought to be particles, were found to have a wavelength associated with them. The significance of these results is ...
... Electromagnetic radiation, which at the turn of the twentieth century was thought to be a pure waveform, was found to possess particulate properties. Conversely, electrons, which were thought to be particles, were found to have a wavelength associated with them. The significance of these results is ...
Chapter 5 practice assessment
... ________ 7. A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy ...
... ________ 7. A particle of electromagnetic radiation with no mass that carries a quantum of energy ...
Frank-Hertz Experiment with Argon
... elegantly supported Niels Bohr's model of the atom, with electrons orbiting the nucleus with specific, discrete energies. Franck and Hertz were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1925 for this work. In the early 20th century, experiments by Ernest Rutherford established that atoms consisted of a ...
... elegantly supported Niels Bohr's model of the atom, with electrons orbiting the nucleus with specific, discrete energies. Franck and Hertz were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1925 for this work. In the early 20th century, experiments by Ernest Rutherford established that atoms consisted of a ...
Document
... A non-relativistic electron and a non-relativistic proton are moving and have the same de Broglie wavelength. Which of the following are also the same for the two particles: (a) speed, (b) kinetic energy, (c) momentum, (d) frequency? ...
... A non-relativistic electron and a non-relativistic proton are moving and have the same de Broglie wavelength. Which of the following are also the same for the two particles: (a) speed, (b) kinetic energy, (c) momentum, (d) frequency? ...
Atoms and Spectra Chapter 7 Guidepost
... The light from a star is usually concentrated in a rather narrow range of wavelengths. The spectrum of a star’s light is approximately a thermal spectrum called a black body spectrum. A perfect black body emitter ...
... The light from a star is usually concentrated in a rather narrow range of wavelengths. The spectrum of a star’s light is approximately a thermal spectrum called a black body spectrum. A perfect black body emitter ...
Properties of photons with similarities to waves and or particles
... Planck attempted to use classical theory to explain the strange behaviour of this distribution curve. Classical theory predicted that the amount of energy emitted by a hot body should increase continuously as the frequency increases. Planck could not explain the observed energy distribution using cl ...
... Planck attempted to use classical theory to explain the strange behaviour of this distribution curve. Classical theory predicted that the amount of energy emitted by a hot body should increase continuously as the frequency increases. Planck could not explain the observed energy distribution using cl ...
Modern Physics 2-Quantum Optics
... • If we raise the temperature of the box and again measure the spectrum of the EM radiation being emitted from the hole, we find that: • The total power output from the hole is now greater. • The spectral curve rises at all wavelengths. • The peak of the power per small wavelength interval shifts to ...
... • If we raise the temperature of the box and again measure the spectrum of the EM radiation being emitted from the hole, we find that: • The total power output from the hole is now greater. • The spectral curve rises at all wavelengths. • The peak of the power per small wavelength interval shifts to ...
Document
... power, you can do more work in the same time or do the same amount of work in less time. For example, if you use a snowblower instead of a shovel, you can move more snow in the same amount of time, or you can move the same amount of snow in a shorter time. This is because the snowblower has more pow ...
... power, you can do more work in the same time or do the same amount of work in less time. For example, if you use a snowblower instead of a shovel, you can move more snow in the same amount of time, or you can move the same amount of snow in a shorter time. This is because the snowblower has more pow ...
pdf format
... – This only happens when a high enough frequency (i.e. short enough wavelength) light is used, because a certain amount of energy is needed to free each electron from the metal and that energy must come from a single photon of high enough energy. Lots of low energy photons don’t work. ...
... – This only happens when a high enough frequency (i.e. short enough wavelength) light is used, because a certain amount of energy is needed to free each electron from the metal and that energy must come from a single photon of high enough energy. Lots of low energy photons don’t work. ...
GAMMA-RAY EMISSION IN PLANETARY ATMOSPHERES DUE TO
... includes all the major relevant physics for the interaction and propagation of photons and energetic electrons in air. Ionization cross sections, atomic excitation, and Møller scattering are included. Elastic scattering is fully modeled using a shielded Coulomb potential, and the code includes brems ...
... includes all the major relevant physics for the interaction and propagation of photons and energetic electrons in air. Ionization cross sections, atomic excitation, and Møller scattering are included. Elastic scattering is fully modeled using a shielded Coulomb potential, and the code includes brems ...
Section 5-1
... The Wave Nature of Light (cont.) • The wavelength (λ) is the shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave. • The frequency (f) is the number of waves that pass a given point per second. The unit for frequency is 1/sec or sec-1, which is known as a Hertz. • The amplitude is the w ...
... The Wave Nature of Light (cont.) • The wavelength (λ) is the shortest distance between equivalent points on a continuous wave. • The frequency (f) is the number of waves that pass a given point per second. The unit for frequency is 1/sec or sec-1, which is known as a Hertz. • The amplitude is the w ...
GROUP V: Summary talk
... Broken powerlaw extends down to 5 keV Thermal component never dominates EM and T are poorly determined Chisquare ~ 1 if EM=0 ...
... Broken powerlaw extends down to 5 keV Thermal component never dominates EM and T are poorly determined Chisquare ~ 1 if EM=0 ...
G482 Electrons , Photons and Waves
... When do particles behave like waves ? Travelling electrons are diffracted by graphite producing a series of diffraction rings. Maximum diffraction occurs when the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons is similar to the gap between layers of carbon atoms. ...
... When do particles behave like waves ? Travelling electrons are diffracted by graphite producing a series of diffraction rings. Maximum diffraction occurs when the de Broglie wavelength of the electrons is similar to the gap between layers of carbon atoms. ...
Bonding homework
... A chemical bond that occurs when atoms share electrons is a(n) ______ bond. a. covalent c. magnetic b. ionic d. polyatomic The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is always ________. a. a negative number c. a positive number b. one d. zero The oxidation number of an atom is shown with ...
... A chemical bond that occurs when atoms share electrons is a(n) ______ bond. a. covalent c. magnetic b. ionic d. polyatomic The sum of the oxidation numbers in a neutral compound is always ________. a. a negative number c. a positive number b. one d. zero The oxidation number of an atom is shown with ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... The system must be in a state of population inversion The excited state of the system must be a metastable state Its lifetime must be long compared to the normal lifetime of an excited state The emitted photons must be confined in the system long enough to allow them to stimulate further emission fr ...
... The system must be in a state of population inversion The excited state of the system must be a metastable state Its lifetime must be long compared to the normal lifetime of an excited state The emitted photons must be confined in the system long enough to allow them to stimulate further emission fr ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... cations, which are named for the sign of the net charge. Anions have gained one or more electrons, giving them more negatively charged electrons than positively charged protons, for an overall negative charge. Cations have lost one or more electrons, so they have more protons than electrons and an o ...
... cations, which are named for the sign of the net charge. Anions have gained one or more electrons, giving them more negatively charged electrons than positively charged protons, for an overall negative charge. Cations have lost one or more electrons, so they have more protons than electrons and an o ...
Bremsstrahlung
Bremsstrahlung (German pronunciation: [ˈbʁɛmsˌʃtʁaːlʊŋ], from bremsen ""to brake"" and Strahlung ""radiation"", i.e. ""braking radiation"" or ""deceleration radiation"") is electromagnetic radiation produced by the deceleration of a charged particle when deflected by another charged particle, typically an electron by an atomic nucleus. The moving particle loses kinetic energy, which is converted into a photon, thus satisfying the law of conservation of energy. The term is also used to refer to the process of producing the radiation. Bremsstrahlung has a continuous spectrum, which becomes more intense and whose peak intensity shifts toward higher frequencies as the change of the energy of the accelerated particles increases.Strictly speaking, braking radiation is any radiation due to the acceleration of a charged particle, which includes synchrotron radiation, cyclotron radiation, and the emission of electrons and positrons during beta decay. However, the term is frequently used in the more narrow sense of radiation from electrons (from whatever source) slowing in matter.Bremsstrahlung emitted from plasma is sometimes referred to as free/free radiation. This refers to the fact that the radiation in this case is created by charged particles that are free both before and after the deflection (acceleration) that caused the emission.