Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... 3) Which property of a star can be determined by its color? Temperature 4) About how many stars are estimated to occur in pairs or multiples? 50% ...
... 3) Which property of a star can be determined by its color? Temperature 4) About how many stars are estimated to occur in pairs or multiples? 50% ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Stars_Galaxies_Introduction - Etiwanda E
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
... What is the source of light in a galaxy? – How is energy produced by the sun? – How are sunspots, prominences, and solar flares related? – Why is our sun considered to be an average star? – How does our sun differ from stars in binary systems? ...
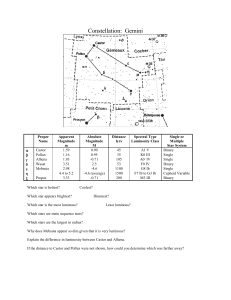
Gemini
... million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by ...
... million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and orange giants of spectral type late G to early K). Its hottest main sequence star is given as of spectral class B3 (Sky Catalogue 2000.0), and its Trumpler classification as III,3,r by ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
Name: ____________________________ Date: _____________ Per. _________ Stars Study Guide (Ch. 21)
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
... 13. What is a graph that shows the relationship between absolute brightness and surface temperature of a star? __________________ ...
The HR Diagram and Stars Worksheet
... b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 626 - Label the following stars: Spica, Vega, Sun, Proxima Cent ...
... b. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to add and label the band that represents Main Sequence stars. c. Page 626 – Use colored pencils to label the following areas: Blue Giants, Red Super Giants, Red Giants, Red Dwarfs, White Dwarfs d. Page 626 - Label the following stars: Spica, Vega, Sun, Proxima Cent ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. October 2005
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 12th, 17th, 22nd and 28th. Mu ( ...
... Delta () Cephei. +3.5 to +4.4, period 5.37 days. The prototype for the Cepheid class of variable stars. Their period-luminosity relationship has lead them to being used as “standard candles” in measuring distances to nearby galaxies. Maximum brightness occurs on 6th, 12th, 17th, 22nd and 28th. Mu ( ...
September Evening Skies
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy after the constellation in which it appears, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
April
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
... above distorted the shape of this irregular galaxy, creating considerable turbulence in its innermost regions. Over 100 globular clusters have been observed orbiting this galaxy. NGC 3079 is an 11th magnitude spiral galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh MAY-jer). This galaxy is seen nearly ...
Name Date ______ Period _____ Earth Science Chapter 25 Study
... What is the name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star? __________________________________________________________________ When is a star said to be born? __________________________________________________________________ What forces are most responsible for the formation of a ...
... What is the name for the interstellar matter that will eventually form a star? __________________________________________________________________ When is a star said to be born? __________________________________________________________________ What forces are most responsible for the formation of a ...
For each statement or question, select the word or expression that
... ____ 9. The constellation that contains the "pointer stars" used to locate Polaris is A. Canis Major B. Cassiopeia C. Orion D. Ursa Major ____ 10. An example of a winter constellation is A. Lyra B. Orion C. Cygnus D. Cassiopeia ____ 11. A light-year measures A. time B. distance C. speed D. energy _ ...
... ____ 9. The constellation that contains the "pointer stars" used to locate Polaris is A. Canis Major B. Cassiopeia C. Orion D. Ursa Major ____ 10. An example of a winter constellation is A. Lyra B. Orion C. Cygnus D. Cassiopeia ____ 11. A light-year measures A. time B. distance C. speed D. energy _ ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
... Both Star D and star B appear equally bright in the night sky; which is farther away from the observer (_18_)? How many times farther (_19_)? Of the two light curves in Section 2, which was produced by a cataclysmic variable star (_20_)? Specifically what type of cataclysmic variable (_21_)? Approxi ...
... Both Star D and star B appear equally bright in the night sky; which is farther away from the observer (_18_)? How many times farther (_19_)? Of the two light curves in Section 2, which was produced by a cataclysmic variable star (_20_)? Specifically what type of cataclysmic variable (_21_)? Approxi ...
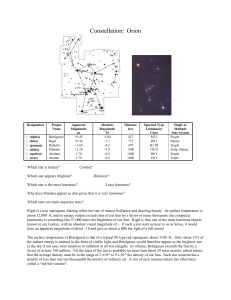
Orion
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
... Why does Mintaka appear so dim given that it is very luminous? Which stars are main sequence stars? Rigel is a true supergiant, blazing white-hot star of intense brilliance and dazzling beauty. Its surface temperature is about 12,000 K and its energy output exceeds that of our Sun by a factor of ma ...
Watch the episode titled “The Milky Way” from the series “The
... dust clouds in our galaxy? Name two of the four wave types that help astronomers see distant galaxies. Why is it important to use different wave types when observing the galaxy? How many main spiral arms does the Milky Way have? ...
... dust clouds in our galaxy? Name two of the four wave types that help astronomers see distant galaxies. Why is it important to use different wave types when observing the galaxy? How many main spiral arms does the Milky Way have? ...
proposed october viewing list
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
... CS = Carbon Star, * = Video imaging optional, ** = Video imaging recommended ...
Stars
... The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the skies year after year. However, stars are actually in rapid motion, but their distances are so great that their relative changes in position become apparent only over the centuries. The nu ...
... The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the skies year after year. However, stars are actually in rapid motion, but their distances are so great that their relative changes in position become apparent only over the centuries. The nu ...
Extra Questions Stellar properties
... 1.A certain type of variable star is known to have an absolute magnitude of 0.0. Such stars are observed in a particular star cluster to have an average magnitude of +16.0 What is the distance to that star cluster. 2 The star Procyon in Canis Major is a prominent star in the winter sky because its a ...
... 1.A certain type of variable star is known to have an absolute magnitude of 0.0. Such stars are observed in a particular star cluster to have an average magnitude of +16.0 What is the distance to that star cluster. 2 The star Procyon in Canis Major is a prominent star in the winter sky because its a ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.