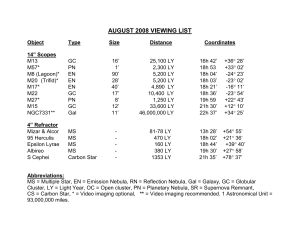
Notes 1 - cloudfront.net
... almost nothing blocks radio waves barred spiral galaxy: ~ a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars ~ bars are found in approximately half of all spiral galaxies ...
... almost nothing blocks radio waves barred spiral galaxy: ~ a spiral galaxy with a central bar-shaped structure composed of stars ~ bars are found in approximately half of all spiral galaxies ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
... • Absolute Magnitude: the “Real” brightness of the star. How much light it really gives off.(Need to know the distance to the Star) • Apparent Magnitude: How bright the star appears to be. ...
August
... However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, the pair is about 500 astronomical units apart & takes at least 5000 years to orbit about each ot ...
... However, Mizar takes its place in the celestial hall of fame as the first known Binary Star, one that consists of a pair of gravitationally bound stars that orbit each other. Found to be double in 1650, the pair is about 500 astronomical units apart & takes at least 5000 years to orbit about each ot ...
Current Study Guide - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? What is the water hole? If our radio telescopes detected signals from a distant planet what kind of extra-terrestrials would you expect to find? The Miller expe ...
... LAWKI? What are it's properties? What would best be the best means of communication between other intelligent species in the galaxy and us? What is the water hole? If our radio telescopes detected signals from a distant planet what kind of extra-terrestrials would you expect to find? The Miller expe ...
School Supplies - Rowan County Schools
... Large & Small Magellanic Clouds Can only be seen by astronomers in the ________________ Hemisphere The two ______________ galaxies to the Milky Way (Less than 200,000 light years away) Visible to the naked eye Relatively small and _____________ in shape Only five percent of the _________ o ...
... Large & Small Magellanic Clouds Can only be seen by astronomers in the ________________ Hemisphere The two ______________ galaxies to the Milky Way (Less than 200,000 light years away) Visible to the naked eye Relatively small and _____________ in shape Only five percent of the _________ o ...
Chapter 1 Vocabulary – The Puzzled of Matter
... Neutron Star – the dense core left after a high-mass star has exploded as a supernova Pulsar – a spinning neutron star that appears to give off strong pulses of radio waves Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – ...
... Neutron Star – the dense core left after a high-mass star has exploded as a supernova Pulsar – a spinning neutron star that appears to give off strong pulses of radio waves Black Hole – an object whose surface gravity is so great that no even electromagnetic waves can escape from it Constellation – ...
PH109 Exploring the Uiverse, Test #4, Spring, 1999
... a) galactic digestion b) dog eat dog c) galactic feeding d) galactic cannibalism 24. The stars located in the lower left corner of the HR diagram are (a) white dwarfs, (b) main sequence stars, (c) giants, (d) supergiants 25. All the stars in a cluster are usually assumed to have the same (a) age, (b ...
... a) galactic digestion b) dog eat dog c) galactic feeding d) galactic cannibalism 24. The stars located in the lower left corner of the HR diagram are (a) white dwarfs, (b) main sequence stars, (c) giants, (d) supergiants 25. All the stars in a cluster are usually assumed to have the same (a) age, (b ...
Name
... Explain the life cycle of a massive star staring with its formation to its death. Be sure to use the following terms and give all possible endings: nebula, black hole, supernova, red supergiant, main sequence, interstellar medium, pulsar ...
... Explain the life cycle of a massive star staring with its formation to its death. Be sure to use the following terms and give all possible endings: nebula, black hole, supernova, red supergiant, main sequence, interstellar medium, pulsar ...
CONSTELLATION CANES VENATICI the two hunting dogs Canes
... voids. It was discovered in 1988 in a deep-sky survey. • Canes Venatici contains five Messier objects, including four galaxies. The more significant are • the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51, NGC 5194) and NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy that is seen face on. This was the first galaxy recognised as hav ...
... voids. It was discovered in 1988 in a deep-sky survey. • Canes Venatici contains five Messier objects, including four galaxies. The more significant are • the Whirlpool Galaxy (M51, NGC 5194) and NGC 5195, a small barred spiral galaxy that is seen face on. This was the first galaxy recognised as hav ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
... collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from inner section; some have barred spirals with stars and gas in a central bar ...
Barred Spiral Galaxy
... Our suns will expand out into a red giant and then collapse into a white dwarf. ...
... Our suns will expand out into a red giant and then collapse into a white dwarf. ...
Document
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
... • If you know how luminous a star REALLY is and how bright it looks from Earth, you can determine how far away it must be to look that faint. • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are ...
Milky Way
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
... • For any star in the sky, we KNOW: – Apparent Magnitude (m) – Spectral Type (O, B, A, F, G, K, M) – Luminosity Class (Main Sequence, Giant, etc…). These are denoted by a roman numeral (V, III, I,…). ...
Microsoft Word 97
... 3. What do we see when we look in the sky? _____________________________________________ 4. What does our galaxy look like from the top down? ______________________________________ 5. Where is Earth in the Milky Way? ____________________________________________________ 6. How long does it take for u ...
... 3. What do we see when we look in the sky? _____________________________________________ 4. What does our galaxy look like from the top down? ______________________________________ 5. Where is Earth in the Milky Way? ____________________________________________________ 6. How long does it take for u ...
NAME:______ANSWER KEY_______________________Period
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
... 1. What is the universe made up of? matter, energy, and space 2. What does light year measure? distance 3. Why do we use light year instead of kilometers? Kilometers would be way to big of a number 4. Change the following number 78,000,000 to scientific notation. 7.8 x 107 5. Write 1.90 x 108 in sta ...
Star Vocabulary
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
... 1. Apparent Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star appears to an observer. 2. Absolute Magnitude- a measure of how bright a star would be if all stars were at the same distance. 3. Luminosity- the actual brightness of a star. Depends only on the size and temperature of the star. 4.Doppler Effect- ...
The Evolutionary Cycle of Stars
... The star eventually converts into a Red Giant & expands to up to 100 times the diameter of the original star. Red Giants develop as the hydrogen in the core is depleted. White Dwarf The final evolutionary state whose mass is not too high. This is the last stage of stellar evolution. ...
... The star eventually converts into a Red Giant & expands to up to 100 times the diameter of the original star. Red Giants develop as the hydrogen in the core is depleted. White Dwarf The final evolutionary state whose mass is not too high. This is the last stage of stellar evolution. ...
Slide 1
... Neutron Stars • If a star is seven times the size of the sun, it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
... Neutron Stars • If a star is seven times the size of the sun, it will become a red giant fairly quickly. • When its fusion stops, a central iron core remains. • The temperature heats up dramatically and causes a supernova. • A neutron star is the mass that remains. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... Color the hottest stars on the left to the coolest stars on the right. b. Label the spectral classes appropriately under each star (G, B, F, A, O, K, M) ...
... Color the hottest stars on the left to the coolest stars on the right. b. Label the spectral classes appropriately under each star (G, B, F, A, O, K, M) ...
Review Day
... burning at about 15 million degrees F Radiation Zone: Heat travels outward through the zone to the next layer. Convection Zone: Area where currents of heated materials transfer heat to the exterior and carry cooler area in. ...
... burning at about 15 million degrees F Radiation Zone: Heat travels outward through the zone to the next layer. Convection Zone: Area where currents of heated materials transfer heat to the exterior and carry cooler area in. ...
Early Spring Observing – Millstone News Night Sky
... Messier Object M3 - Globular Cluster in Canes Venatici. 1/2 million stars in a sphere 200 light years in diameter Distance: 33000 light Years-image courtesy P. Browne, Spring 2014 Note: Globular clusters are distributed in a halo around our galaxy: Globular clusters are normally associated with a h ...
... Messier Object M3 - Globular Cluster in Canes Venatici. 1/2 million stars in a sphere 200 light years in diameter Distance: 33000 light Years-image courtesy P. Browne, Spring 2014 Note: Globular clusters are distributed in a halo around our galaxy: Globular clusters are normally associated with a h ...
Sample final
... axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with current astronomical ideas) or not surprising (consistent). In either case, state clea ...
... axis? How would you classify (composition or type) this object? In other words, what is it? Essay section part one Choose two of the following discoveries, and determine if they are surprising (not consistent with current astronomical ideas) or not surprising (consistent). In either case, state clea ...
1” “Sky-Notes” of the Open University Astronomy Club. September
... Located further west than Uranus. Opposition was reached on 8th August. At magnitude 7.8 (diameter 2”.5) it may be located in binoculars using a suitable star ...
... Located further west than Uranus. Opposition was reached on 8th August. At magnitude 7.8 (diameter 2”.5) it may be located in binoculars using a suitable star ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.