25 Study Guide
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
... • Binary stars can be used to determine stellar mass. • The nearest stars have the largest parallax angles, while those of distant stars are too small to measure. • Three factors control the apparent brightness of a star as seen from Earth: how big it is, how hot it is, and how far away it is. • A H ...
PARTS OF THE UNIVERSE
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
... v Parallax: apparent shift in the position of an object when view from two different locations. v Parallax Example v Can be used to measure the distance of stars from Earth that are relatively close. v Proxima Centauri: closest star to earth v (4.3 light years away – 40 trillion km) ...
8-3-Star_Classification STUDENT
... In the night sky, a band of stars can be seen across the sky as a blurry image. When you see this, you are looking into the part of the galaxy with more stars. ...
... In the night sky, a band of stars can be seen across the sky as a blurry image. When you see this, you are looking into the part of the galaxy with more stars. ...
the life cycle of stars
... the main-sequence. • This is the second and longest stage of its life. • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
... the main-sequence. • This is the second and longest stage of its life. • Energy is generated in the core and causes the star to shine. • The size of the star changes very little as long as its supply of hydrogen nuclei fuse into helium nuclei. ...
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
... 5. A shock wave may be the stimulus that causes a nebula to start condensing to form new ...
life and death of a high mass star 2
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
... AFTER THAT, THEY LOSE THEIR MASS AND HEAT AND BEGIN TO DIE. THIS PROCESS TAKES BILLIONS AND BILLIONS OF YEARS. ...
THE MILKY WAY GALAXY
... The nature and size of the Galaxy, as well as our location within this stellar system were finally appreciated in the early 20th century when: The locations of the globular clusters were mapped out, indicating that the galactic center was located thousands of light years distant, towards the const ...
... The nature and size of the Galaxy, as well as our location within this stellar system were finally appreciated in the early 20th century when: The locations of the globular clusters were mapped out, indicating that the galactic center was located thousands of light years distant, towards the const ...
Study Guide - Universe Exam key 2014-15 v2
... c) How are color and temperature related? Red to blue = cooler to hotter d) How is luminosity and temperature related in the Main Sequence stars? They are equal e) In what two ways are the stars Sirius B and Regulus alike? Similar in temperature ...
... c) How are color and temperature related? Red to blue = cooler to hotter d) How is luminosity and temperature related in the Main Sequence stars? They are equal e) In what two ways are the stars Sirius B and Regulus alike? Similar in temperature ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... Stars vary widely in their surface temperatures' The coolest stars have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how tempera ...
... Stars vary widely in their surface temperatures' The coolest stars have surface temperatures aS low as 3,000oC, while the hottest stars have surface temperatures ten times higher. The temperature of a star determines its color-from cool, red stars to hot, blue ones. The table below Shows how tempera ...
solar system formation and gal
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
SSG Coordinators will be at the Cronan Ranch observing site at 5
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
... scopes in the 4” range under medium to high magnification may glimpse a faint dust lane and some surface mottling. Cassiopeia (S&T Pocket Sky Atlas – pg 1 – 3) This constellation is one of the most recognized in the sky due to its prominent M (or W) asterism. Cassiopeia is also a circumpolar constel ...
A-105 Homework 1
... 18. (2 pts.) If the true distance to the center of our galaxy is found to be 7 kpc (instead of 8.5 kpc) and the orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
... 18. (2 pts.) If the true distance to the center of our galaxy is found to be 7 kpc (instead of 8.5 kpc) and the orbital velocity of the sun is 220 km/s, what is the minimum mass of the galaxy? (Hints: Find the orbital period of the sun at 7 kpc, and then use Kepler’s 3rd law.) ...
COM 2014 January
... The Alpha Persei Cluster, also know as Melotte 20, is a bright stellar association in Perseus constellation. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue stars of spectral type B, along with the most massive member, the yellow supergiant Alpha Persei itself. Brightest members include Alpha ...
... The Alpha Persei Cluster, also know as Melotte 20, is a bright stellar association in Perseus constellation. To the naked eye, the cluster consists of several blue stars of spectral type B, along with the most massive member, the yellow supergiant Alpha Persei itself. Brightest members include Alpha ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnitude of a star tells its mass (c) the gravitational force on a companion star in a double star (d) the mass of a star is determined by its location in the Galaxy 2. “Solar Analog Stars” are stars very, very ...
... (a) measuring the color of the star and using a color-mass relationship (b) the apparent magnitude of a star tells its mass (c) the gravitational force on a companion star in a double star (d) the mass of a star is determined by its location in the Galaxy 2. “Solar Analog Stars” are stars very, very ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
... _________________ 24. Synonym for Cepheid variable _________________ 25. The apparent path that the sun (and planets) appear to move along against the star background _________________26. # of crests passing by a spot in a set amount of time. ________________ 27. List, in order, the steps of the li ...
Slide 1
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Sydney Observatory night sky map June 2014
... (winter solstice; 9 hours and 48 minutes of daylight) when the Sun is at its most northerly position in the sky. Saturn is located towards the east in Libra. Mars can be seen high in the sky towards the north in Virgo. The best time to view the Moon with a small telescope or binoculars is a few days ...
... (winter solstice; 9 hours and 48 minutes of daylight) when the Sun is at its most northerly position in the sky. Saturn is located towards the east in Libra. Mars can be seen high in the sky towards the north in Virgo. The best time to view the Moon with a small telescope or binoculars is a few days ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... What is dark matter? What type of object do scientists believe it helps to hold together? ...
... What is dark matter? What type of object do scientists believe it helps to hold together? ...
September Evening Skies
... objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. Our usual monthly maps are designed for stargazers just beginning to find their way around the sky. This month’s map is useful for serious stargazing f ...
... objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Arcturus, Vega, Capella, Altair, Antares, Fomalhaut, and Deneb. Our usual monthly maps are designed for stargazers just beginning to find their way around the sky. This month’s map is useful for serious stargazing f ...
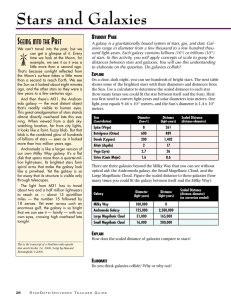
Stars and Galaxies
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
... And then there’s M31, the Andromeda galaxy — the most distant object that’s readily visible to human eyes. This great amalgamation of stars stands almost directly overhead late this evening. When viewed from a dark skywatching location, far from city lights, it looks like a faint, fuzzy blob. But th ...
Jeopardy Questions
... Q: How far away is a star that has a parallax angle of 10 arcseconds? A: 0.1 parsecs ...
... Q: How far away is a star that has a parallax angle of 10 arcseconds? A: 0.1 parsecs ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.