Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... Black Holes • Formed when a supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
... Black Holes • Formed when a supernova explodes causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
The Pulsar “Lighthouse”
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
... • Outer layers of star gradually contract onto core which becomes too massive to be held up by degenerate electron pressure • e- + p Î n • Sudden core collapse: 104 km Î 20 km • Then core rebounds • Outer layers fall in, then get hit by rebounding core. ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
... 17. Below sketch out the H-R diagram plotting the main stars and labeling the main sequence. ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
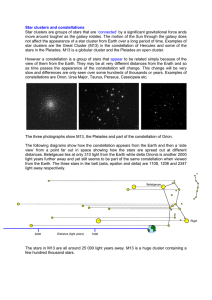
Star clusters and constellations
... as time passes the appearance of the constellation will change. This change will be very slow and differences are only seen over some hundreds of thousands or years. Examples of constellations are Orion, Ursa Major, Taurus, Perseus, Cassiopeia etc. ...
... as time passes the appearance of the constellation will change. This change will be very slow and differences are only seen over some hundreds of thousands or years. Examples of constellations are Orion, Ursa Major, Taurus, Perseus, Cassiopeia etc. ...
Organize Your Space PowerPoint.
... Asteroid Belt – Most asteroids orbit the sun in this area between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter ...
... Asteroid Belt – Most asteroids orbit the sun in this area between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
... What happens to white light as it passes through a prism ? REFRACTS Which color refracts the most and least ? RED What is thought to be at the center of all galaxies ? ____BLACK HOLE______ What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
Badge Day - GBT
... 4. Cosmic Clues 1.Analyze the spectrum for three stars. What are the 2 most prominent differences between the spectra? Which star is hottest? ...
... 4. Cosmic Clues 1.Analyze the spectrum for three stars. What are the 2 most prominent differences between the spectra? Which star is hottest? ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... characteristics of stars. You will also be asked to locate and identify some non-stellar objects. You may begin by trying the website at http://www.stellar-database.com/ ...
... characteristics of stars. You will also be asked to locate and identify some non-stellar objects. You may begin by trying the website at http://www.stellar-database.com/ ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
June 2016 night sky chart
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
Diapositiva 1
... the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that runaway stllar colosion at an earlier age may have formed ...
... the brightest star Theta-1 Orionis C powers the complex star forming region's entire visible glow. About three million years old, the Orion Nebula Cluster was even more compact in its younger years and a recent dinamical study indicates that runaway stllar colosion at an earlier age may have formed ...
Astronomy - The-A-List
... 1431, Cygnus X-1, SXP 1062, M1, V838 Mon, Delta Cep, a Orionis, SN 2010JL, NGC 3582, LHa115N19, Antares/Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex and IC ...
... 1431, Cygnus X-1, SXP 1062, M1, V838 Mon, Delta Cep, a Orionis, SN 2010JL, NGC 3582, LHa115N19, Antares/Rho Ophiuchi cloud complex and IC ...
Stars and Galaxies
... It may take several years for a spacecraft to reach other planets in our solar system. It may take several centuries to reach other stars in our galaxy. ...
... It may take several years for a spacecraft to reach other planets in our solar system. It may take several centuries to reach other stars in our galaxy. ...
Week 5 (10/16) – Quiz #11
... Which of the following statements comparing our Sun to another star X located at the outer edge of the Milky Way galaxy is TRUE: ...
... Which of the following statements comparing our Sun to another star X located at the outer edge of the Milky Way galaxy is TRUE: ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... The point at which the line bends away from the main sequence straight line is the turnoff point. The star’s age is just a tiny bit less than the main sequence lifetime. To get the cluster’s age we therefore measure the age of the star at the turnoff point by calculating its main sequence lifetime f ...
... The point at which the line bends away from the main sequence straight line is the turnoff point. The star’s age is just a tiny bit less than the main sequence lifetime. To get the cluster’s age we therefore measure the age of the star at the turnoff point by calculating its main sequence lifetime f ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... scintillate much more than stars high overhead since you are looking through more air (often the refracted light will display individual colors). In space stars would not twinkle at all- and this is the ...
... scintillate much more than stars high overhead since you are looking through more air (often the refracted light will display individual colors). In space stars would not twinkle at all- and this is the ...
2.7 - 2.9a
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
... include the Milky Way (our galaxy) all have a central nucleus have long curved arms contain a lot of gas and dust ...
Chapter 24 Test:Stars/Galaxies
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
... The positions of the constellations appear to change throughout the year because _____. (a) the sun revolves around the galaxy, (b) Earth revolves around the sun, (c) the constellations revolve around Earth, (d) Earth revolves around the stars. ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... Discovery of the Milky Way as a Galaxy… • Edwin Hubble used the new 100” Mt. Wilson telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nea ...
... Discovery of the Milky Way as a Galaxy… • Edwin Hubble used the new 100” Mt. Wilson telescope in the 1920’s to image The Andromeda Nebula • Could see the brightest individual stars. Among them, variables of the right color and light variation to show them as Cepheids • Therefore, this was not a nea ...
Place in Space
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
... space. Light can travel about seven times around Earth in one second. Astronomers use the speed of light to measure how far away things are in space. They use light years. A light year is the distance that light can travel in one year. In one year light travels about 9,460,000,000,000 kilometres. So ...
Astronomy Quiz #1 Answers
... 7. What are the two important discoveries made by Edwin Hubble? -many galaxies existed beyond the Milky Way -almost all galaxies are moving away from each other ...
... 7. What are the two important discoveries made by Edwin Hubble? -many galaxies existed beyond the Milky Way -almost all galaxies are moving away from each other ...
Earth Science
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
Constellation
... Binary star - A stellar system consisting of two stars orbiting about a common center of mass and often appearing as a single visual or telescopic object. Constellation - An arbitrary formation of stars perceived as a figure or design, especially one of 88 recognized groups named after characters fr ...
... Binary star - A stellar system consisting of two stars orbiting about a common center of mass and often appearing as a single visual or telescopic object. Constellation - An arbitrary formation of stars perceived as a figure or design, especially one of 88 recognized groups named after characters fr ...
stars and galaxies – study guide
... 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellation is Orion. 26. White dwarf stars are hot, faint, Earth-sized stars. 27. A black hole is the densest object in the universe, and ...
... 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellation is Orion. 26. White dwarf stars are hot, faint, Earth-sized stars. 27. A black hole is the densest object in the universe, and ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.