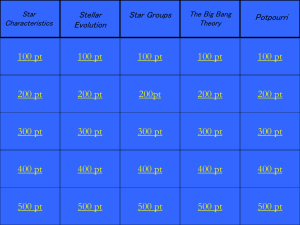
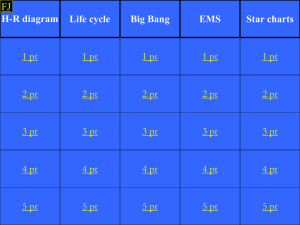
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
tire
... 4. The bending of light from a distance star or galaxy by the gravity of a closer star, galaxy or galaxy cluster. 5. Large black holes found at the center of most galaxies. 6. The oscillations of space caused the rapid movement of matter, such as a supernova or orbiting black holes. 7. An object who ...
... 4. The bending of light from a distance star or galaxy by the gravity of a closer star, galaxy or galaxy cluster. 5. Large black holes found at the center of most galaxies. 6. The oscillations of space caused the rapid movement of matter, such as a supernova or orbiting black holes. 7. An object who ...
Astronomy
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
... Something that is achieved when the inward force of gravity is balanced by the outward pressure from fusion and radiation inside a star ...
Name____________________________________________
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
... __3__ Our Solar System __2___ The Milky Way __1__ The Universe 3. What is a galaxy? A huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 4. What does an elliptical galaxy look like? Round or flattened ball; smashed circle 5. The Milky Way Galaxy is just ...
Structure of the Universe
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
... by combining smaller elements to form a larger one, specifically two hydrogen atoms form a helium atom, ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
Ch 28 Vocab cnp
... A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of measurement used to describe dist ...
... A halo of gases that is formed by the expelled layers of a star’s atmosphere The brightness of a star The measure of how bright a star would be if it were located 10 parsecs from Earth A group of millions, or even billions of stars held together by gravity A unit of measurement used to describe dist ...
Document
... object at the center of some galaxies that produces energy at a high rate- Quasar a neutron star that emits radio waves- Pulsar large celestial body that emits lights; Sun- Star the apparent shift in wavelength of light as the source moves away from or toward observer; Red and blue shifts- Doppler E ...
... object at the center of some galaxies that produces energy at a high rate- Quasar a neutron star that emits radio waves- Pulsar large celestial body that emits lights; Sun- Star the apparent shift in wavelength of light as the source moves away from or toward observer; Red and blue shifts- Doppler E ...
Components of Universe
... Galaxies contain more than just stars. The irregular-looking blobs are either hot (pink) or cold (dark) interstellar clouds ...
... Galaxies contain more than just stars. The irregular-looking blobs are either hot (pink) or cold (dark) interstellar clouds ...
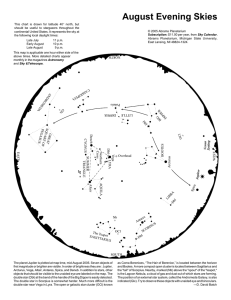
August Evening Skies
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
Chapter 28 Vocabulary
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
... Main sequence star - A star that is at the point in its life cycle in which it is actively fusing hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei; also the band of the Hertzsprun-Russell diagram depicting such stars. ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
... 6. What does the lifetime of a star depend on? IT’S MASS. 7. What is a supernova? EXPLOSION OF A HIGH MASS STAR. 8. What is a star system? A GROUP OF TWO OR MORE STARS. 9. What are eclipsing binary stars? A STAR SYSTEM WHERE ONE STAR BLOCKS THE LIGHT OF THE OTHER STAR AT REGULAR INTERVALS. 10. What ...
Astronomy Tour
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
... dust that is a “tail” Scientists believe that these originate from a large region filled with comet cores called the Oort cloud. ...
Blank Jeopardy
... What stage in a star’s life cycle is the longest? (Have the most hydrogen and most energy?) ...
... What stage in a star’s life cycle is the longest? (Have the most hydrogen and most energy?) ...
Slide 1
... TEKS 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to the Earth than any other star ...
... TEKS 8.8B recognize that the Sun is a medium-sized star near the edge of a disc-shaped galaxy of stars and that the Sun is many thousands of times closer to the Earth than any other star ...
New Directions in Star Cluster Research
... Astrophysics (physics of stars) Is not an experimental science - we cannot devise and conduct experiments in order to test theories Theory is validated by observations Evidence often derived from past events Information we can gather is very restricted - apparent brightness (depends on distance), l ...
... Astrophysics (physics of stars) Is not an experimental science - we cannot devise and conduct experiments in order to test theories Theory is validated by observations Evidence often derived from past events Information we can gather is very restricted - apparent brightness (depends on distance), l ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... 30 light years. • Atmosphere, weather, ruined. • Major extinction. • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbor stars peaceful. • Bad news: when one does show signs of blowing, time to migrate. ...
... 30 light years. • Atmosphere, weather, ruined. • Major extinction. • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbor stars peaceful. • Bad news: when one does show signs of blowing, time to migrate. ...
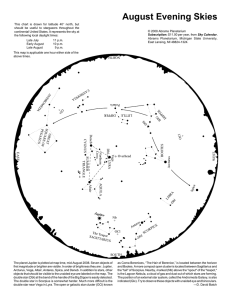
August Evening Skies
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
... is the Lagoon Nebula, a cloud of gas and dust out of which stars are forming. The position of an external star system, called the Andromeda Galaxy, is also indicated (Glx). Try to observe these objects with unaided eye and binoculars. ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light... limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
... 1. Compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of the Sun. Also compute the deflection angle of a star whose light just grazes the limb of a 1.4M neutron star, if the neutron star was at the same distance from the Earth as the Sun. State assumptions. 2. Use the Plummer p ...
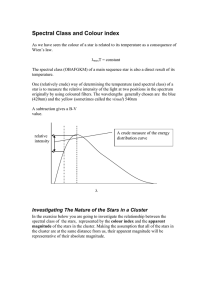
Spectral Class and Colour index
... originally by using coloured filters. The wavelengths generally chosen are the blue (420nm) and the yellow (sometimes called the visual) 540nm A subtraction gives a B-V value. ...
... originally by using coloured filters. The wavelengths generally chosen are the blue (420nm) and the yellow (sometimes called the visual) 540nm A subtraction gives a B-V value. ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.