a description of planets and stars you may see
... same face. Its cycle of phases have been an important influence on world cultures. The Moon's gravity produces the ocean tides. The Moon appears almost the same size in the sky as the Sun, allowing it to cover the Sun in total solar eclipses. The Moon is the only celestial body on which humans have ...
... same face. Its cycle of phases have been an important influence on world cultures. The Moon's gravity produces the ocean tides. The Moon appears almost the same size in the sky as the Sun, allowing it to cover the Sun in total solar eclipses. The Moon is the only celestial body on which humans have ...
RFS_multiple_choice_Dec8_Key
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
... B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (t ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... Zodiac Constellations • Form a ring that the Sun seems to pass through each year as the Earth orbits around it. • perhaps the most famous of all constellations because of their use in astrology • There are 13 in total ...
... Zodiac Constellations • Form a ring that the Sun seems to pass through each year as the Earth orbits around it. • perhaps the most famous of all constellations because of their use in astrology • There are 13 in total ...
Variable and Binary Stars
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
... – 75% of O-type stars seem to have a companion – If Jupiter had been ~100 times more massive, the Sun would have a companion star ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #20 Key
... Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared the absolute magnitudes of these Cepheids with his observed apparent magnitudes, yielding a distance for ...
... Hubble was able to detect Cepheid variable stars within that “Nebula.” Then by observing their light curves and using the known period- luminosity relation for Cepheids, he obtained and compared the absolute magnitudes of these Cepheids with his observed apparent magnitudes, yielding a distance for ...
Astronomy I Ex.2
... What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) Approximate distance from the earth to the next nearest star - Alpha Centauri: 3.97 × 1018 cm c) Approximate distanc ...
... What is the (approximate) age of the universe in Gyr? 3. Convert the following distances in cm to distances in AU: a) Approximate distance from the earth to the sun: 1.44 × 1013 cm b) Approximate distance from the earth to the next nearest star - Alpha Centauri: 3.97 × 1018 cm c) Approximate distanc ...
2014 Joseph E. Pesce, Ph.D. 1 Astro 113 Final Exam Review 1. What
... 27. Why does the region of the sky called the “Milky Way” have a larger concentration of stars than other regions? 28. What is an effect of a large fraction of dark matter in the Universe? ...
... 27. Why does the region of the sky called the “Milky Way” have a larger concentration of stars than other regions? 28. What is an effect of a large fraction of dark matter in the Universe? ...
Groups of Stars
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
... • Many stars exist in groups of two or more stars that are held close together because of gravity • More than half of all stars are members of star systems • Is our Sun part of a star system? ...
WK10revisedoneweek
... sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic Law) ...
... sweeps out equal areas in equal times. 3. The ratio of the cube of the average radius of a planets orbit to the square of its orbital period of revolution is the same for each planet. (Harmonic Law) ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
Astronomy - Shelbyville Central Schools
... White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons can exist in the dense core Black hole – gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light ...
... White dwarf – outer layer contracts (about size of Earth) Neutron star – only neutrons can exist in the dense core Black hole – gravity is so strong that nothing can escape, not even light ...
Study Guide Astronomy
... Chapter 4 Section 4 Star Systems and Galaxies (pages 141-147) 20. What is the major difference between elliptical galaxies and spiral galaxies? ...
... Chapter 4 Section 4 Star Systems and Galaxies (pages 141-147) 20. What is the major difference between elliptical galaxies and spiral galaxies? ...
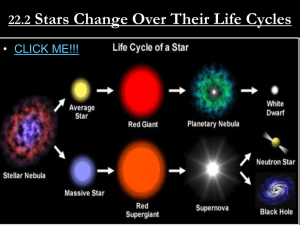
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowing, it is time to migrate. ...
... • Not much harm if further. • SN material in sediments. • 1 SN/100 years in our galaxy • Close 1 per 100million years. • Good news: our neighbors are peaceful. • Bad news: when one shows signs of blowing, it is time to migrate. ...
new_qwk11
... Week 11 (11/27) – Quiz #32 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The constancy of the speed of light is a basic principle of the Special Theory of Relativity B. The General Theory of Relativity was designed to explain situations where the speeds of objects are close to the speed of light C. ...
... Week 11 (11/27) – Quiz #32 Which of the following statements is TRUE? A. The constancy of the speed of light is a basic principle of the Special Theory of Relativity B. The General Theory of Relativity was designed to explain situations where the speeds of objects are close to the speed of light C. ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
... Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast the apparent and actual motion of stars. How can scientists know if a star or galaxy is moving toward ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as a Luminous Blue Variable like Eta Carinae, as an extremely large star that are now often regarded as the ...
... 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 Solarmasses, extremely high luminosity, a variable spectra, and surrounding ejecta, it is classified as a Luminous Blue Variable like Eta Carinae, as an extremely large star that are now often regarded as the ...
Homework 7
... Which star is the brightest in apparent magnitude? Which star is most luminous? Which star is the largest star? Which star is furthest away? For each choice, state the information from the table that was most useful in making the choice. ...
... Which star is the brightest in apparent magnitude? Which star is most luminous? Which star is the largest star? Which star is furthest away? For each choice, state the information from the table that was most useful in making the choice. ...
15.4 Star Systems and Galaxies
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
... I. Star Systems and Planets A. Star system-groups of two or more stars 1. Binary stars - two stars or double stars a. Eclipsing binary-a system in which one star blocks the light from another II. Planets Around Other Stars A. Astronomers study gravitational effects on stars to see if there is a pla ...
Chapter 21 power point - Laconia School District
... White Dwarf • The remaining hot core of a star after its outer layers have expanded and drifted out into space. ...
... White Dwarf • The remaining hot core of a star after its outer layers have expanded and drifted out into space. ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Fixed patterns of stars are called constellations. Astronomers label stars within each constellation according to apparent magnitude using greek letters. The brightest is labeled alpha, then beta and so on. ...
... Fixed patterns of stars are called constellations. Astronomers label stars within each constellation according to apparent magnitude using greek letters. The brightest is labeled alpha, then beta and so on. ...
Serpens

Serpens (""the Serpent"", Greek Ὄφις) is a constellation of the northern hemisphere. One of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, it remains one of the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union. It is unique among the modern constellations in being split into two non-contiguous parts, Serpens Caput (Serpent's Head) to the west and Serpens Cauda (Serpent's Tail) to the east. Between these two halves lies the constellation of Ophiuchus, the ""Serpent-Bearer"". In figurative representations, the body of the serpent is represented as passing behind Ophiuchus between Mu Serpentis in Serpens Caput and Nu Serpentis in Serpens Cauda.The brightest star in Serpens is the red giant star Alpha Serpentis, or Unukalhai, in Serpens Caput, with an apparent magnitude of 2.63. Also located in Serpens Caput are the naked-eye globular cluster Messier 5 and the naked-eye variables R Serpentis and Tau4 Serpentis. Notable extragalactic objects include Seyfert's Sextet, one of the densest galaxy clusters known; Arp 220, the prototypical ultraluminous infrared galaxy; and Hoag's Object, the most famous of the very rare class of galaxies known as ring galaxies.Part of the Milky Way's galactic plane passes through Serpens Cauda, which is therefore rich in galactic deep-sky objects, such as the Eagle Nebula (IC 4703) and its associated star cluster Messier 16. The nebula measures 70 light-years by 50 light-years and contains the Pillars of Creation, three dust clouds that became famous for the image taken by the Hubble Space Telescope. Other striking objects include the Red Square Nebula, one of the few objects in astronomy to take on a square shape; and Westerhout 40, a massive nearby star-forming region consisting of a molecular cloud and an H II region.