Forces - Hicksville Public Schools
... 38. A force of 50 Newtons is used to drag a 10 kg box across a horizontal table. If a frictional force of 15 Newtons is present on the box, a. calculate the unbalanced (net) force on the box. b. Calculate the acceleration of the box c. Calculate the force of gravity acting on the box ...
... 38. A force of 50 Newtons is used to drag a 10 kg box across a horizontal table. If a frictional force of 15 Newtons is present on the box, a. calculate the unbalanced (net) force on the box. b. Calculate the acceleration of the box c. Calculate the force of gravity acting on the box ...
Rigid Bodies, Translations, and Rotations TERMS
... 104. What is the angular momentum of a 2.0-g particle moving counterclockwise (as viewed from above) with an angular speed of 5 rad s in a horizontal circle of radius 15 cm? (Give the magnitude and direction.) 7.1104 kg m2 s toward you 105. A 10-kg rotating disk of radius 0.25 m has an angu ...
... 104. What is the angular momentum of a 2.0-g particle moving counterclockwise (as viewed from above) with an angular speed of 5 rad s in a horizontal circle of radius 15 cm? (Give the magnitude and direction.) 7.1104 kg m2 s toward you 105. A 10-kg rotating disk of radius 0.25 m has an angu ...
F mg - cloudfront.net
... the two tensions. Next realize that the stoplight is at rest in equilibrium, so what does this tell you about the net force? Now, use Newton’s second law to calculate the mass, m. Remember that though mass is not a vector, weight or mg is a vector. Which ...
... the two tensions. Next realize that the stoplight is at rest in equilibrium, so what does this tell you about the net force? Now, use Newton’s second law to calculate the mass, m. Remember that though mass is not a vector, weight or mg is a vector. Which ...
Solutions #5
... wall of the tube, so that there can be a centripetal force to move the objects in a circle. See the free-body diagram for an object on the inside of the outer wall, and a portion of the tube. The normal force of contact between the object and the wall must be maintaining the circular motion. Write N ...
... wall of the tube, so that there can be a centripetal force to move the objects in a circle. See the free-body diagram for an object on the inside of the outer wall, and a portion of the tube. The normal force of contact between the object and the wall must be maintaining the circular motion. Write N ...
The Complete Group 1 Laboratory Manual
... 5. If a mistake is made in recording a datum item, cancel the wrong value by drawing a fine line through it and record the correct value legibly. 6. Get your data sheet signed by the instructor before you leave the laboratory. This will be the only valid proof that you actually did the experiment. 7 ...
... 5. If a mistake is made in recording a datum item, cancel the wrong value by drawing a fine line through it and record the correct value legibly. 6. Get your data sheet signed by the instructor before you leave the laboratory. This will be the only valid proof that you actually did the experiment. 7 ...
Oscillations
... Questions 29-30. A block on a horizontal frictionless plane is attached to a spring, as shown above. The block oscillates along the x-axis with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. 29. Which of the following statements about the block is correct? (A) At x = 0, its velocity is zero. (B) At x = 0, i ...
... Questions 29-30. A block on a horizontal frictionless plane is attached to a spring, as shown above. The block oscillates along the x-axis with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. 29. Which of the following statements about the block is correct? (A) At x = 0, its velocity is zero. (B) At x = 0, i ...
Gravity and Motion
... Do you know of a place where gravity does not exist? If so, where? Why or why not? ...
... Do you know of a place where gravity does not exist? If so, where? Why or why not? ...
additional assignments
... the magnitude of its linear momentum. (b) Find its angular momentum vector about the center of the circle. (c) If the string breaks and the ball flies off through the air, explain the effect on its angular momentum, if any. 39. A mass of 3.00 kg is moving with velocity 2.00 m/s, 30.0° when it is at ...
... the magnitude of its linear momentum. (b) Find its angular momentum vector about the center of the circle. (c) If the string breaks and the ball flies off through the air, explain the effect on its angular momentum, if any. 39. A mass of 3.00 kg is moving with velocity 2.00 m/s, 30.0° when it is at ...
PHYSICS HOMEWORK #31 NEWTON`S LAWS SECOND LAW ΣF=ma
... 19. An automobile, which has a mass of 1140 kg, is moving with a velocity of 22.0 m/s around a curve in the highway which has a radius of R = 85.0 meters and which has a coefficient of static friction of µ = 0.720. a. Draw a freebody diagram showing each of the forces acting on this car. b. What wil ...
... 19. An automobile, which has a mass of 1140 kg, is moving with a velocity of 22.0 m/s around a curve in the highway which has a radius of R = 85.0 meters and which has a coefficient of static friction of µ = 0.720. a. Draw a freebody diagram showing each of the forces acting on this car. b. What wil ...
p250c09
... Example: In a hammer throw, a 7.25 kg shot is swung in a circle 5 times and then released. The shot moves with an average radius of 2.1 m and an average angular acceleration of 2.3 rad/s2. What is the average tangential force and what is the maximum centripetal force on the ...
... Example: In a hammer throw, a 7.25 kg shot is swung in a circle 5 times and then released. The shot moves with an average radius of 2.1 m and an average angular acceleration of 2.3 rad/s2. What is the average tangential force and what is the maximum centripetal force on the ...
Teaching the Kepler Laws for Freshmen
... write, ‘‘In Feynman’s lecture, this is the point at which he finds himself unable to follow Newton’s line of argument any further, and so sets out to invent one of his own’’. ...
... write, ‘‘In Feynman’s lecture, this is the point at which he finds himself unable to follow Newton’s line of argument any further, and so sets out to invent one of his own’’. ...
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
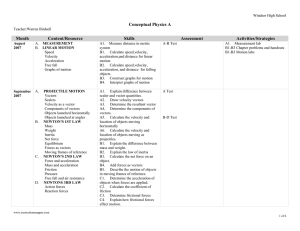
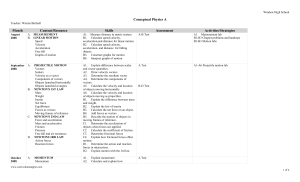
... B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. Describe the motion of objects in moving frames of reference. C1. Determine the acceleration of objects when forces are applied. C2. Calculate the coefficient of friction C3. Determine frictional f ...
... B2. Explain the law of inertia B3. Calculate the net force on an object. B4. Add forces as vectors B5. Describe the motion of objects in moving frames of reference. C1. Determine the acceleration of objects when forces are applied. C2. Calculate the coefficient of friction C3. Determine frictional f ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.