Problem 1
... decreased. The force that the scale exerts on the person is less than the person’s weight, and hence the minus sign in Equation (3.1). The positive direction must be upward; scales as a rule do not measure forces tending to move the top part of the scale, where the person is standing, upward. The pl ...
... decreased. The force that the scale exerts on the person is less than the person’s weight, and hence the minus sign in Equation (3.1). The positive direction must be upward; scales as a rule do not measure forces tending to move the top part of the scale, where the person is standing, upward. The pl ...
Chapter 5 DYNAMICS OF UNIFORM CIRCULAR MOTION PREVIEW
... 5.1 – 5.3 Uniform Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force The law of inertia states that if an object is moving it will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity until a net force causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. If a force on an object i ...
... 5.1 – 5.3 Uniform Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force The law of inertia states that if an object is moving it will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity until a net force causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. If a force on an object i ...
Ch. 4 Motion and Forces
... 7. Complete the following table about the different kinds of friction. Kinds of Friction Kind of Friction ...
... 7. Complete the following table about the different kinds of friction. Kinds of Friction Kind of Friction ...
Building` a Galaxy SED
... Fundamental problem: We live in one, and want to understand our origin. Fun problem: galaxy astrophysics spans a wide range of scales: deeply rooted in cosmology, large variation in physics (fluid dynamics, quantum physics) Practical problem: galaxies are biased tracers of underlying mass distributi ...
... Fundamental problem: We live in one, and want to understand our origin. Fun problem: galaxy astrophysics spans a wide range of scales: deeply rooted in cosmology, large variation in physics (fluid dynamics, quantum physics) Practical problem: galaxies are biased tracers of underlying mass distributi ...
Chapter 5
... 5.1 – 5.3 Uniform Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force The law of inertia states that if an object is moving it will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity until a net force causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. If a force on an object i ...
... 5.1 – 5.3 Uniform Circular Motion, Centripetal Acceleration and Centripetal Force The law of inertia states that if an object is moving it will continue moving in a straight line at a constant velocity until a net force causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. If a force on an object i ...
November - LVAstronomy.com
... known as the Milky Way. We know this glow is the plane of our home galaxy and holds a multitude of open star clusters. Dozens of these galactic clusters are found in Cassiopeia. One of the finest, but often overlooked, is NGC-7789. Cassiopeia is one of the most recognized constellations. The constel ...
... known as the Milky Way. We know this glow is the plane of our home galaxy and holds a multitude of open star clusters. Dozens of these galactic clusters are found in Cassiopeia. One of the finest, but often overlooked, is NGC-7789. Cassiopeia is one of the most recognized constellations. The constel ...
1 Conservation of Linear Momentum Purpose: To understand
... to fire at thes same time, to prevent interference, causing a lag between left and right sensors. Since the collision takes place over a very short time, the software incorrectly calculates the total momentum before both sensors are actually read. It is important to note this slight glitch, but it s ...
... to fire at thes same time, to prevent interference, causing a lag between left and right sensors. Since the collision takes place over a very short time, the software incorrectly calculates the total momentum before both sensors are actually read. It is important to note this slight glitch, but it s ...
Our Place in Space
... should print out the cards (preferably in color) and laminate them so that the information on each object appears on the reverse side of the image of that object. ...
... should print out the cards (preferably in color) and laminate them so that the information on each object appears on the reverse side of the image of that object. ...
Example
... He showed that all masses, big or small, gave a gravitational field or force The bigger the object, the bigger the field (force) Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth g = 9.81 m/s2 This number is an average and can change slightly depending on where you are on the earth (dista ...
... He showed that all masses, big or small, gave a gravitational field or force The bigger the object, the bigger the field (force) Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of Earth g = 9.81 m/s2 This number is an average and can change slightly depending on where you are on the earth (dista ...
Dynamics
... 2) What happens as you turn a corner? Your body tries to keep moving in a straight line, while the car turns the corner. You feel as if you are being pushed into the side of your seat. 3) What happens when the car decelerates? Your inertia keeps you moving and you lurch forward. If the car brakes su ...
... 2) What happens as you turn a corner? Your body tries to keep moving in a straight line, while the car turns the corner. You feel as if you are being pushed into the side of your seat. 3) What happens when the car decelerates? Your inertia keeps you moving and you lurch forward. If the car brakes su ...
Circular Motion Lab
... Fc = Fg mv2 = Mg R It is important to note that the masses cannot be cancelled because they are different. The m of the centripetal force Fc side is the mass of the whirling stopper, while the M of the weight Fg side is the mass hanging from the cord that causes the tension in the cord. The velocity ...
... Fc = Fg mv2 = Mg R It is important to note that the masses cannot be cancelled because they are different. The m of the centripetal force Fc side is the mass of the whirling stopper, while the M of the weight Fg side is the mass hanging from the cord that causes the tension in the cord. The velocity ...
Curriculum Map
... 5) Calculate the velocity and position of an object in freefall if given the time falling or being shot upward as well as the initial velocity. 6) Predict the instantaneous velocity of an accelerating object using the slope of the tangent on a d vs t graph. 7) Find the displacement of an acceleratin ...
... 5) Calculate the velocity and position of an object in freefall if given the time falling or being shot upward as well as the initial velocity. 6) Predict the instantaneous velocity of an accelerating object using the slope of the tangent on a d vs t graph. 7) Find the displacement of an acceleratin ...
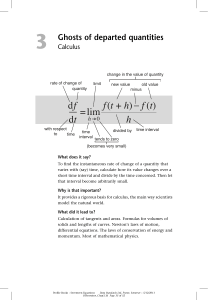
In Pursuit of the Unknown : 17 Equations That Changed
... had worked out the basics of calculus, some of Newton’s friends sparked a largely pointless but heated controversy about priority, accusing Leibniz of plagiarising Newton’s unpublished manuscripts. A few mathematicians from continental Europe responded with counter-claims of plagiarism by Newton. En ...
... had worked out the basics of calculus, some of Newton’s friends sparked a largely pointless but heated controversy about priority, accusing Leibniz of plagiarising Newton’s unpublished manuscripts. A few mathematicians from continental Europe responded with counter-claims of plagiarism by Newton. En ...
Answer Key at Bottom
... Washington. A car released in Boston would fall under the influence of gravity, gaining speed, and then finally coasting back to the surface at Washington. The only expenditure of energy required would be that to overcome friction, and this could be reduced by using an evacuated tunnel or magnetic l ...
... Washington. A car released in Boston would fall under the influence of gravity, gaining speed, and then finally coasting back to the surface at Washington. The only expenditure of energy required would be that to overcome friction, and this could be reduced by using an evacuated tunnel or magnetic l ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... 4.3 Applications Newton’s Laws (Normal Forces) A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
... 4.3 Applications Newton’s Laws (Normal Forces) A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
Forces - Hicksville Public Schools
... 38. A force of 50 Newtons is used to drag a 10 kg box across a horizontal table. If a frictional force of 15 Newtons is present on the box, a. calculate the unbalanced (net) force on the box. b. Calculate the acceleration of the box c. Calculate the force of gravity acting on the box ...
... 38. A force of 50 Newtons is used to drag a 10 kg box across a horizontal table. If a frictional force of 15 Newtons is present on the box, a. calculate the unbalanced (net) force on the box. b. Calculate the acceleration of the box c. Calculate the force of gravity acting on the box ...
fall04-term2-exercise
... Two objects attract each other gravitationally with a force of 2.5 ð 10-10 N when they are 0.25 m apart. 18. In the above problem if the two objects experience no forces other than their mutual gravitational attraction then their resulting accelerations are a. equal b. different Two satellites are i ...
... Two objects attract each other gravitationally with a force of 2.5 ð 10-10 N when they are 0.25 m apart. 18. In the above problem if the two objects experience no forces other than their mutual gravitational attraction then their resulting accelerations are a. equal b. different Two satellites are i ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.