Forces - Cloudfront.net
... Suppose a large rock is dropped straight down from a high cliff while the other is pushed out from the top of the cliff. Which one will land first and WHY? A. The rock that is pushed out from the cliff will hit first because it had an extra force to make it fall faster. B. The rock that’s dropped st ...
... Suppose a large rock is dropped straight down from a high cliff while the other is pushed out from the top of the cliff. Which one will land first and WHY? A. The rock that is pushed out from the cliff will hit first because it had an extra force to make it fall faster. B. The rock that’s dropped st ...
Physical property
... Matter: anything that occupies spaced and has mass Matter can be distinguished by its physical properties Physical property: a property that can be observed/or measured without changing the chemical makeup of the substance What are some physical properties? • color • melting and boiling point • odor ...
... Matter: anything that occupies spaced and has mass Matter can be distinguished by its physical properties Physical property: a property that can be observed/or measured without changing the chemical makeup of the substance What are some physical properties? • color • melting and boiling point • odor ...
In what ways do forces affect an object`s motion?
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
app_A (WP)
... Just for completeness sake, we should also mention Newton's Third Law, which has to do with the forces between bodies: Whenever a body exerts a force on another body, the latter exerts a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction on the former. An example of Newton's Third Law is the situation ...
... Just for completeness sake, we should also mention Newton's Third Law, which has to do with the forces between bodies: Whenever a body exerts a force on another body, the latter exerts a force of equal magnitude and opposite direction on the former. An example of Newton's Third Law is the situation ...
Chapter 9
... The increase in rocket speed is proportional to the speed of the escape gases (ve) So, the exhaust speed should be very high The increase in rocket speed is also proportional to the natural log of the ratio Mi/Mf So, the ratio should be as high as possible, meaning the mass of the rocket should be ...
... The increase in rocket speed is proportional to the speed of the escape gases (ve) So, the exhaust speed should be very high The increase in rocket speed is also proportional to the natural log of the ratio Mi/Mf So, the ratio should be as high as possible, meaning the mass of the rocket should be ...
Ch 2.1 and 2.2 PPT Chap 2.1 and 2.2
... 2. 3.A.1.3: To analyze experimental data describing the motion of an object and to express the result using above representation. ...
... 2. 3.A.1.3: To analyze experimental data describing the motion of an object and to express the result using above representation. ...
Chapter 4 - Ove Tedenstig
... substantial properties of space and matter. We will do that by applying the same basic ideas as we have used before when treating the electric field with its associated phenomena. We start from a very simple arrangement, a straight metallic wire in which an electric current flows. This electric curr ...
... substantial properties of space and matter. We will do that by applying the same basic ideas as we have used before when treating the electric field with its associated phenomena. We start from a very simple arrangement, a straight metallic wire in which an electric current flows. This electric curr ...
How do we describe motion?
... unless an external twisting force (torque) is acting on it. • Earth experiences no twisting force as it orbits the Sun, so its rotation and orbit will continue indefinitely. ...
... unless an external twisting force (torque) is acting on it. • Earth experiences no twisting force as it orbits the Sun, so its rotation and orbit will continue indefinitely. ...
In Chapters 2 and 3 of this course the emphasis is
... • Because they have the same initial velocity, when they leave the table gravity acts on each ball equally, so the two balls hit the floor the same distance away from the table. • The x- and y-components of motion are independent; elaborates on first comment. • The effect of friction is the same for ...
... • Because they have the same initial velocity, when they leave the table gravity acts on each ball equally, so the two balls hit the floor the same distance away from the table. • The x- and y-components of motion are independent; elaborates on first comment. • The effect of friction is the same for ...
free fall motion
... Free falling motion have two important characteristic that: a). Free falling bodies does not encounter air resistance. This characteristic is arise because the free falling bodies are only affected by gravitational force. This characteristic also showing us that the shape, mass, weight and any other ...
... Free falling motion have two important characteristic that: a). Free falling bodies does not encounter air resistance. This characteristic is arise because the free falling bodies are only affected by gravitational force. This characteristic also showing us that the shape, mass, weight and any other ...
Chap.4 Conceptual Modules Fishbane
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
... After the cart is released, there is no longer a force in the x-direction. This does not mean that the cart stops moving!! It simply means that the cart will continue moving with the same velocity it had at the moment of release. The initial push got the cart moving, but that force is not needed to ...
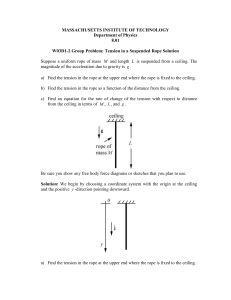
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... We choose the upper piece as our system with mass m ( M / L) y . The forces acting on j ( M / L) ygφ j , the force at y 0 holding the upper rope are the gravitational force mg φ the rope up, (we refer to that force as T ( y 0) , the tension at the upper end), and the tension at the point y ...
... We choose the upper piece as our system with mass m ( M / L) y . The forces acting on j ( M / L) ygφ j , the force at y 0 holding the upper rope are the gravitational force mg φ the rope up, (we refer to that force as T ( y 0) , the tension at the upper end), and the tension at the point y ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.