Examination methods of endocrine disorders
... Together with nervous system, it is specialized in signalling, control and regulation of body processes. Mostly concerned in slower regulation (Time is needed to reach the target cells by blood) Regulates: • Body energy levels, speed and type of metabolism (including responses to stress) • Internal ...
... Together with nervous system, it is specialized in signalling, control and regulation of body processes. Mostly concerned in slower regulation (Time is needed to reach the target cells by blood) Regulates: • Body energy levels, speed and type of metabolism (including responses to stress) • Internal ...
Nerve activates contraction
... D. Effects Caused by Hormones 1. Changes in plasma membrane permeability or electrical state 2. Synthesis of proteins, such as enzymes 3. Activation or inactivation of enzymes 4. Stimulation of mitosis ...
... D. Effects Caused by Hormones 1. Changes in plasma membrane permeability or electrical state 2. Synthesis of proteins, such as enzymes 3. Activation or inactivation of enzymes 4. Stimulation of mitosis ...
File - Dr. Jerry Cronin
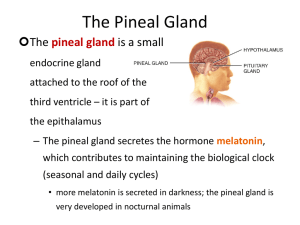
... (seasonal and daily cycles) • more melatonin is secreted in darkness; the pineal gland is very developed in nocturnal animals ...
... (seasonal and daily cycles) • more melatonin is secreted in darkness; the pineal gland is very developed in nocturnal animals ...
Assessment and Management of Patients with Endocrine Disorders
... sc and interstitial tissues. Is the extreme form of hypothyroidism. Can progress to shock. S/S—fatigue, hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails, numbness and tingling of the fingers, amenorrhea, weight gain, decreased heart rate and temperature, lassitude, cognitive changes, elevated cholesterol levels ...
... sc and interstitial tissues. Is the extreme form of hypothyroidism. Can progress to shock. S/S—fatigue, hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails, numbness and tingling of the fingers, amenorrhea, weight gain, decreased heart rate and temperature, lassitude, cognitive changes, elevated cholesterol levels ...
Assessment and Management of Patients with Endocrine Disorders
... sc and interstitial tissues. Is the extreme form of hypothyroidism. Can progress to shock. S/S—fatigue, hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails, numbness and tingling of the fingers, amenorrhea, weight gain, decreased heart rate and temperature, lassitude, cognitive changes, elevated cholesterol levels ...
... sc and interstitial tissues. Is the extreme form of hypothyroidism. Can progress to shock. S/S—fatigue, hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails, numbness and tingling of the fingers, amenorrhea, weight gain, decreased heart rate and temperature, lassitude, cognitive changes, elevated cholesterol levels ...
ENDOCRINE PATHOLOGY: PITUITARY AND THYROID
... hormone production by a cell which is then released into the circulation and acts on a distant target cell. 2. Other mechanisms are paracrine whereby chemical modulators do not enter the circulation but travel a short distance between the secretory cell and the target cell. 3. Neuroendocrine functio ...
... hormone production by a cell which is then released into the circulation and acts on a distant target cell. 2. Other mechanisms are paracrine whereby chemical modulators do not enter the circulation but travel a short distance between the secretory cell and the target cell. 3. Neuroendocrine functio ...
Chapter 18: The Endocrine System
... 1. Alpha cells glucagon increase blood glucose 2. Beta cells insulin decrease blood glucose ...
... 1. Alpha cells glucagon increase blood glucose 2. Beta cells insulin decrease blood glucose ...
Slide 1
... action, as well as cells throughout the lamina terminalis and MnPO. In response to hyperosmolality or AII, projections from the SFO and OVLT to the MnPO activate excitatory and inhibitory interneurons that project to the supraoptic nucleus (SON) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) to modulate direct i ...
... action, as well as cells throughout the lamina terminalis and MnPO. In response to hyperosmolality or AII, projections from the SFO and OVLT to the MnPO activate excitatory and inhibitory interneurons that project to the supraoptic nucleus (SON) and paraventricular nucleus (PVN) to modulate direct i ...
Chapter 17 - Dr. Wilson`s Site
... – norepinephrine, cholecystokinin, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, dopamine and antidiuretic hormone ...
... – norepinephrine, cholecystokinin, thyrotropin-releasing hormone, dopamine and antidiuretic hormone ...
4 pit &adrenal326
... biochemistry and physiology of almost all cells, and which are crucial to the understanding of the actions of many endocrine, anti-inflammatory and other drugs ...
... biochemistry and physiology of almost all cells, and which are crucial to the understanding of the actions of many endocrine, anti-inflammatory and other drugs ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... In males, FSH stimulates the maturation of sperm in the testes; b. A gonadotropin, which targets primary sex organs (ovary & testis). ...
... In males, FSH stimulates the maturation of sperm in the testes; b. A gonadotropin, which targets primary sex organs (ovary & testis). ...
The Autonomic Nervous System
... • Indeed, it was soon realised that ANS is under the control of centers in the brain 1. A variety of brainstem structures/nuclei are involved in visceral control. - Nucles Tractus Solitarius (NTS), ventrolaterla medulla, medullary raphe, reticular formation, locus coerules, parabrachial nucleus, n ...
... • Indeed, it was soon realised that ANS is under the control of centers in the brain 1. A variety of brainstem structures/nuclei are involved in visceral control. - Nucles Tractus Solitarius (NTS), ventrolaterla medulla, medullary raphe, reticular formation, locus coerules, parabrachial nucleus, n ...
laboratory exercise using ``virtual rats`
... detects the change and activates the air conditioner to cool the room. The thermostat will turn the air conditioner off once the temperature of the room drops below the set point (67°F). To keep the room at a fairly constant temperature, the thermostat assesses the situation and turns the air condit ...
... detects the change and activates the air conditioner to cool the room. The thermostat will turn the air conditioner off once the temperature of the room drops below the set point (67°F). To keep the room at a fairly constant temperature, the thermostat assesses the situation and turns the air condit ...
lambdinanatomyandphysiology
... •A carrier molecule secreted into the blood moves them through the body •Readily crosses the plasma (cell) membrane. •Many lipid hormones have long term effects on body because they directly control DNA. ...
... •A carrier molecule secreted into the blood moves them through the body •Readily crosses the plasma (cell) membrane. •Many lipid hormones have long term effects on body because they directly control DNA. ...
The Endocrine System
... • The nervous system can override normal endocrine controls – For example, control of blood glucose levels • Normally the endocrine system maintains blood glucose • Under stress, the body needs more glucose • The hypothalamus and the sympathetic nervous system are activated to supply ample glucose ...
... • The nervous system can override normal endocrine controls – For example, control of blood glucose levels • Normally the endocrine system maintains blood glucose • Under stress, the body needs more glucose • The hypothalamus and the sympathetic nervous system are activated to supply ample glucose ...
Slide 1
... • "What is the Rhesus Factor?" Wise Geek. Conjecture Corporation, n.d. Web. 4 Mar. 2013..
...
... • "What is the Rhesus Factor?" Wise Geek. Conjecture Corporation, n.d. Web. 4 Mar. 2013.
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... The endocrine system consists of a number of glands distributed in the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. They secrete hormones which enter the blood to be distributed throughout the body to regulate growth, metabolism, and the function of many other cells, tissues, and organs. The functions of these ...
... The endocrine system consists of a number of glands distributed in the head, neck, thorax, and abdomen. They secrete hormones which enter the blood to be distributed throughout the body to regulate growth, metabolism, and the function of many other cells, tissues, and organs. The functions of these ...
Pituitary anatomy and physiology
... posterior to the buccopharyngeal membrane. This structure contributes to the formation of the hypophysis in lower vertebrates but not in primates. Nonetheless, it sometimes persists in human beings and can be the source of certain tumors [4]. Morphogenesis Rathke’s pouch and the infundibulum are bot ...
... posterior to the buccopharyngeal membrane. This structure contributes to the formation of the hypophysis in lower vertebrates but not in primates. Nonetheless, it sometimes persists in human beings and can be the source of certain tumors [4]. Morphogenesis Rathke’s pouch and the infundibulum are bot ...
JAMA Patient Page | Subclinical Hypothyroidism
... describes a situation in which thyroid function is only mildly Thyroid hormone TSH stimulates provides feedback low, so that the blood level of thyroxine remains within the production of to the brain (pituitary normal range, but the blood level of TSH is elevated, indicating thryoid hormone and hypo ...
... describes a situation in which thyroid function is only mildly Thyroid hormone TSH stimulates provides feedback low, so that the blood level of thyroxine remains within the production of to the brain (pituitary normal range, but the blood level of TSH is elevated, indicating thryoid hormone and hypo ...
UNIT 9 – EXCRETORY SYSTEM
... neuron is at resting potential when the voltage is -70mV and there is a greater concentration of sodium ions outside the neuron and greater concentration of potassium ions inside the neuron. When there is stimulation of the neuron (either due to neurotransmitters or receptors), depolarization begins ...
... neuron is at resting potential when the voltage is -70mV and there is a greater concentration of sodium ions outside the neuron and greater concentration of potassium ions inside the neuron. When there is stimulation of the neuron (either due to neurotransmitters or receptors), depolarization begins ...
Subclinical Hypothyroidism
... describes a situation in which thyroid function is only mildly Thyroid hormone TSH stimulates provides feedback low, so that the blood level of thyroxine remains within the production of to the brain (pituitary normal range, but the blood level of TSH is elevated, indicating thryoid hormone and hypo ...
... describes a situation in which thyroid function is only mildly Thyroid hormone TSH stimulates provides feedback low, so that the blood level of thyroxine remains within the production of to the brain (pituitary normal range, but the blood level of TSH is elevated, indicating thryoid hormone and hypo ...
growth hormone (GH)
... a hormone produced by the pineal gland which helps regulate a persons daily cycle or circadian rhythms; levels are high at night promoting sleepiness and low during the day as we awake. methamphetamine a stimulant sometimes called speed which causes a sensation of a rush similar to cocaine but the e ...
... a hormone produced by the pineal gland which helps regulate a persons daily cycle or circadian rhythms; levels are high at night promoting sleepiness and low during the day as we awake. methamphetamine a stimulant sometimes called speed which causes a sensation of a rush similar to cocaine but the e ...
Document
... • In most systems the maximum biological response is achieved at concentrations of hormone lower than required to occupy all of the receptors on the cell (spare receptors). ...
... • In most systems the maximum biological response is achieved at concentrations of hormone lower than required to occupy all of the receptors on the cell (spare receptors). ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.