Advanced Endocrinology
... Compounding part 1 – Sex Hormones: Learn about compounded estrogen and progesterone, key considerations when ordering bio-identicals and what makes a quality compounded hormone. Infertility, HPA-axis & Genetic Optimization: In this lecture you will learn how chronic stress disrupts normal production ...
... Compounding part 1 – Sex Hormones: Learn about compounded estrogen and progesterone, key considerations when ordering bio-identicals and what makes a quality compounded hormone. Infertility, HPA-axis & Genetic Optimization: In this lecture you will learn how chronic stress disrupts normal production ...
Endocrine Anatomy and Physiology
... will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissues” or cells. These hormones regulate particular body functions. Hormones are usually regulated by a negative feedback mechanism, an increased presence of the hormone, resulting in a decrease ...
... will not be covered in this article. Endocrine organs secrete hormones that act on specific “target tissues” or cells. These hormones regulate particular body functions. Hormones are usually regulated by a negative feedback mechanism, an increased presence of the hormone, resulting in a decrease ...
Chapter 18 Endocrine system
... the nervous system can undergo extreme conditions and override all other systems controlling hormone release example: blood glucose is normally at 80 120 mg per 100 mls glucose but under high sympathetic tone, glucose levels can rise much higher the nervous system is the over-all controller of the e ...
... the nervous system can undergo extreme conditions and override all other systems controlling hormone release example: blood glucose is normally at 80 120 mg per 100 mls glucose but under high sympathetic tone, glucose levels can rise much higher the nervous system is the over-all controller of the e ...
BOX 30.8 THE ROLE OF THE SUBTHALAMIC NUCLEUS IN
... initiated action. Recent studies suggest that rapid stopping of this kind is implemented by a “hyperdirect” pathway between the frontal cortex and the subthalamic nucleus. The broader sequence of events that engages this pathway is as follows. Sensory information about the stop signal (in this case, ...
... initiated action. Recent studies suggest that rapid stopping of this kind is implemented by a “hyperdirect” pathway between the frontal cortex and the subthalamic nucleus. The broader sequence of events that engages this pathway is as follows. Sensory information about the stop signal (in this case, ...
…By the way, where is the fornix???
... VENTRAL = towards the belly (=‘ventrum’ in latin) DORSAL = towards the back (=‘dorsum’ in latin) ROSTRAL = towards the snout (‘rostrum’=beak in latin) CAUDAL = towards the tail (=‘cauda’ in latin) ...
... VENTRAL = towards the belly (=‘ventrum’ in latin) DORSAL = towards the back (=‘dorsum’ in latin) ROSTRAL = towards the snout (‘rostrum’=beak in latin) CAUDAL = towards the tail (=‘cauda’ in latin) ...
Put your name here -> BIOL 415 Nerve cell
... 65. In addition to the 5 primary taste receptors that input via nerves VII, IX and X, say something about either the chemical ("tastant") or the receptor type, or the nerve input mediating appreciation of food at the level of watery stimulation in the mouth. capsacin, polymodal niciceptive fibers, V ...
... 65. In addition to the 5 primary taste receptors that input via nerves VII, IX and X, say something about either the chemical ("tastant") or the receptor type, or the nerve input mediating appreciation of food at the level of watery stimulation in the mouth. capsacin, polymodal niciceptive fibers, V ...
4.a. the trigeminal system
... continuous with the dorsal horn. This means it is several cm long and can be involved in lesions of caudal pons and medulla. C. ...
... continuous with the dorsal horn. This means it is several cm long and can be involved in lesions of caudal pons and medulla. C. ...
cranial nerves
... pons - negligible tectum; pontine nuclei and corticospinal/corticobulbar axons anterior to tegmentum midbrain - thick tectum (inferior and superior colliculi); cerebral peducles (crus cerebri) anterior to tegmentum ...
... pons - negligible tectum; pontine nuclei and corticospinal/corticobulbar axons anterior to tegmentum midbrain - thick tectum (inferior and superior colliculi); cerebral peducles (crus cerebri) anterior to tegmentum ...
Biological Aspects of Psychology
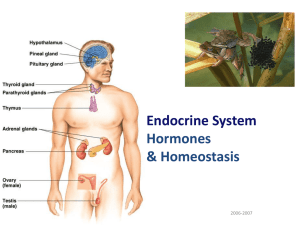
... system’s partner in controlling & coordinating the body’s functions. ◦ Nervous system – neurotransmitters ◦ Endocrine system - hormones Includes Pituitary Gland, Hypothalamus, Thyroid, Pineal gland, Pancreas, Adrenal Glands, Kidneys, Ovaries, Testes. Some glands respond to nervous system message ...
... system’s partner in controlling & coordinating the body’s functions. ◦ Nervous system – neurotransmitters ◦ Endocrine system - hormones Includes Pituitary Gland, Hypothalamus, Thyroid, Pineal gland, Pancreas, Adrenal Glands, Kidneys, Ovaries, Testes. Some glands respond to nervous system message ...
Localization of immunoreactive lamprey gonadotropin
... and lateral POA, with nerve fibers projecting caudally and ventrally to terminate in the external layer of the median eminence. Other fibers apparently projected caudally and circumventrically to terminate around the cerebral aqueduct in the mid-brain central gray. By using a highly specific antiser ...
... and lateral POA, with nerve fibers projecting caudally and ventrally to terminate in the external layer of the median eminence. Other fibers apparently projected caudally and circumventrically to terminate around the cerebral aqueduct in the mid-brain central gray. By using a highly specific antiser ...
( ! ) Notice: Undefined index
... biochemical findings were compatible with isolated central hypothyroidism. Repeated thyroid hormone and TSH measurements showed pattern of central hypothyroidism again and T4 levels appropriately increased after thyroxine replacement, which together made the interference in the assays unlikely to be ...
... biochemical findings were compatible with isolated central hypothyroidism. Repeated thyroid hormone and TSH measurements showed pattern of central hypothyroidism again and T4 levels appropriately increased after thyroxine replacement, which together made the interference in the assays unlikely to be ...
45.1-45.2 - Wild about Bio
... • The endocrine system secretes hormones that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses including reproduction, development, energy metabolism, growth, and behavior • The nervous system conveys high-speed electrical signals along specialized cells called neurons; these signals regulate other cel ...
... • The endocrine system secretes hormones that coordinate slower but longer-acting responses including reproduction, development, energy metabolism, growth, and behavior • The nervous system conveys high-speed electrical signals along specialized cells called neurons; these signals regulate other cel ...
Brainstem
... (4) has expansion area of reticular formation which contains many important nuclear groups of vital centers in medulla, such as center of heart beat, blood pressure and respiratory. ...
... (4) has expansion area of reticular formation which contains many important nuclear groups of vital centers in medulla, such as center of heart beat, blood pressure and respiratory. ...
Endocrine System Homeostatic Imbalances
... Hypo- vs. Hyper• Hypo – – Less than normal; deficient – Hyposecretion • Deficient hormone secretion ...
... Hypo- vs. Hyper• Hypo – – Less than normal; deficient – Hyposecretion • Deficient hormone secretion ...
Thyroid hormones
... • Negative feedback is most common: for example, LH from pituitary stimulates the testis to produce testosterone which in turn feeds back and inhibits LH secretion. The hormone (or one of its products) has a negative feedback effect to prevent oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the targ ...
... • Negative feedback is most common: for example, LH from pituitary stimulates the testis to produce testosterone which in turn feeds back and inhibits LH secretion. The hormone (or one of its products) has a negative feedback effect to prevent oversecretion of the hormone or overactivity at the targ ...
Chapter 26
... 26.1 Coordination in Multicellular Animals 1. Describe how insulin, the liver, and the level of glucose in the blood demonstrate negative feedback. Elevated levels of glucose in the blood stimulate the production of insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that stimulates the liver to ...
... 26.1 Coordination in Multicellular Animals 1. Describe how insulin, the liver, and the level of glucose in the blood demonstrate negative feedback. Elevated levels of glucose in the blood stimulate the production of insulin. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that stimulates the liver to ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Biology Chapter 22
... Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by the pars distalis region of the anterior pituitary. It regulates the development, growth, and reproductive processes of the human body. In the ovary, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicle. As the follicle grows and matures, it ...
... Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) is secreted by the pars distalis region of the anterior pituitary. It regulates the development, growth, and reproductive processes of the human body. In the ovary, FSH stimulates the growth and maturation of ovarian follicle. As the follicle grows and matures, it ...
Name Chapter 18: Alterations of Hormonal Regulation I
... Defective hormone synthesis resulting from autoimmune thyroiditis, endemic iodine deficiency, or antithyroid drugs Loss of thyroid tissue after surgical or radioactive treatment for hyperthyroidism ...
... Defective hormone synthesis resulting from autoimmune thyroiditis, endemic iodine deficiency, or antithyroid drugs Loss of thyroid tissue after surgical or radioactive treatment for hyperthyroidism ...
Document
... • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells have receptors for that hormone • Insect metamorphosis is regulated by hormones ...
... • Hormones reach all parts of the body, but only target cells have receptors for that hormone • Insect metamorphosis is regulated by hormones ...
HORMONE ACTION AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
... • Hormone –receptor complex first undergoes activation reaction. • Activation reaction occurs by at least two mechanisms: • For example: 1. Glucocorticoids diffuse across the plasma membrane and encounter their cognate receptors in the cytoplasm of target cells. ...
... • Hormone –receptor complex first undergoes activation reaction. • Activation reaction occurs by at least two mechanisms: • For example: 1. Glucocorticoids diffuse across the plasma membrane and encounter their cognate receptors in the cytoplasm of target cells. ...
Bio 30 Endocrine Unit Plan Day Outcome Tasks 1 30–A2.1k identify
... 30–A2.2k describe the function of the hormones of the principal endocrine glands, i.e., thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyroxine, calcitonin/parathyroid hormone (PTH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrin ...
... 30–A2.2k describe the function of the hormones of the principal endocrine glands, i.e., thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)/thyroxine, calcitonin/parathyroid hormone (PTH), adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)/cortisol, glucagon/insulin, human growth hormone (hGH), antidiuretic hormone (ADH), epinephrin ...
Name
... The Endocrine System works with the nervous system to regulate all life processes. The endocrine system is made up of a system of glands, which secrete hormones into the blood. Hormones are special proteins, which act as signals. They bind to certain proteins called receptors, on target cells. The t ...
... The Endocrine System works with the nervous system to regulate all life processes. The endocrine system is made up of a system of glands, which secrete hormones into the blood. Hormones are special proteins, which act as signals. They bind to certain proteins called receptors, on target cells. The t ...
to Pituitary Gland ppt
... Physiological Functions of Growth Hormone Growth hormone promotes growth of almost all the body tissues It promotes increase in size of cells, increased mitosis ...
... Physiological Functions of Growth Hormone Growth hormone promotes growth of almost all the body tissues It promotes increase in size of cells, increased mitosis ...
ABNORMALITIES OF THYROID HORMONE
... • Plasma conc. Of TSH: normal level is 0.3- 3 mu/l. - LOW in Hyperthyroidism - Increased in Hypothyroidism of thyroid origin - LOW or normal in pituitary or hypothalamic Hypothyroidism TSH is the Best single test to screen for thyroid disease. ...
... • Plasma conc. Of TSH: normal level is 0.3- 3 mu/l. - LOW in Hyperthyroidism - Increased in Hypothyroidism of thyroid origin - LOW or normal in pituitary or hypothalamic Hypothyroidism TSH is the Best single test to screen for thyroid disease. ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.