Puberty and the teen years powerpoint
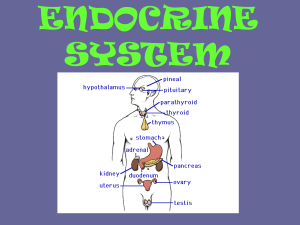
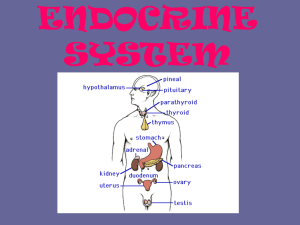
... produced by your endocrine system. The endocrine system produces hormones that go directly into your bloodstream. The hormones are then carried to different parts of the body to control various functions. ...
... produced by your endocrine system. The endocrine system produces hormones that go directly into your bloodstream. The hormones are then carried to different parts of the body to control various functions. ...
pancreas, in beta-cells of islets of Langerhans general, non
... body repairs cells, fats broken down to help conserve glucose, glucose absorption inhibited ...
... body repairs cells, fats broken down to help conserve glucose, glucose absorption inhibited ...
Lecture:
... stimulation of adrenal medulla to secrete hormones norepinephrine and epinephrine stimulates sweat glands to secrete arrector pili hair to stand up on arm/neck blood vessels - causes to constrict thermoregulation - vasodilation of capillaries in skin and sweat gland stimulation release of renin from ...
... stimulation of adrenal medulla to secrete hormones norepinephrine and epinephrine stimulates sweat glands to secrete arrector pili hair to stand up on arm/neck blood vessels - causes to constrict thermoregulation - vasodilation of capillaries in skin and sweat gland stimulation release of renin from ...
Does adderall affect thyroid stimulating hormone
... individuals how to box, and to give back to the sport that has helped change my life. Optimal Levels of Cortisol, Insulin and Thyroid are Essential to Vibrant Health. Tuesday, January 06, 2009 by: Barbara L. Minton Tags: cortisol, health news, Natural News See all 141 heart attack feature articles. ...
... individuals how to box, and to give back to the sport that has helped change my life. Optimal Levels of Cortisol, Insulin and Thyroid are Essential to Vibrant Health. Tuesday, January 06, 2009 by: Barbara L. Minton Tags: cortisol, health news, Natural News See all 141 heart attack feature articles. ...
Hormonal - Hartland High School
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... Copyright © 2006 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
review - PV9McConeghyHealth
... 1. What is an endocrine gland? Glands and ducts that make and secrete hormones into the blood ...
... 1. What is an endocrine gland? Glands and ducts that make and secrete hormones into the blood ...
The Hypothalamic pituitary axis part 1
... The posterior pituitary secretes 2 peptide hormones which are synthesised respectively in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus: 1) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) 2) Oxytocin These hormones are then transported to the posterior pituitary from where they are released into the circ ...
... The posterior pituitary secretes 2 peptide hormones which are synthesised respectively in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of the hypothalamus: 1) Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) 2) Oxytocin These hormones are then transported to the posterior pituitary from where they are released into the circ ...
Shelley A. Tischkau, Stacey L. Krager
... contains the primary oscillator, which drives oscillations in the shell. VIP, GABA, and others are projected as neurotransmitters that provide coupling between core and shell. The core also receives the primary input, especially from the RHT, via glutamate and PACAP release. Core neurons express VIP ...
... contains the primary oscillator, which drives oscillations in the shell. VIP, GABA, and others are projected as neurotransmitters that provide coupling between core and shell. The core also receives the primary input, especially from the RHT, via glutamate and PACAP release. Core neurons express VIP ...
Chapter 28 - RadTherapy
... Produces hormones under complex feedback control mechanisms that affect various functions to meet ongoing metabolic needs and stresses of the organism o Critical for maintaining metabolic homeostasis o Provides the organism with the ability to respond to various stresses Pituitary- master regula ...
... Produces hormones under complex feedback control mechanisms that affect various functions to meet ongoing metabolic needs and stresses of the organism o Critical for maintaining metabolic homeostasis o Provides the organism with the ability to respond to various stresses Pituitary- master regula ...
endocrine system - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
Hormone
... Acts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate the activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones transported in the blood Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, parathy ...
... Acts with the nervous system to coordinate and integrate the activity of body cells Influences metabolic activities by means of hormones transported in the blood Responses occur more slowly but tend to last longer than those of the nervous system Endocrine glands: pituitary, thyroid, parathy ...
Endocrine and Reproductive System Web Quest Vanessa Cooper
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
... hypothalamus is located in the brain and is the main connection between the endocrine and nervous system It controls the pituitary gland by telling it when to make more or to stop producing hormones. • The pituitary gland is very important because it makes hormones that controls other endocrine glan ...
Name
... c. Each motorneuron that is recruited by the stretch reflex will activate only some of the muscle fibers that it synapses on. d. All of the above are true. 3. Considering the situation in the above question, which of the following is a true statement? a. according to the principle of negative feedba ...
... c. Each motorneuron that is recruited by the stretch reflex will activate only some of the muscle fibers that it synapses on. d. All of the above are true. 3. Considering the situation in the above question, which of the following is a true statement? a. according to the principle of negative feedba ...
endocrine function tests
... Cathecolamines: either epinephrine or norepinephrine is increased and should be assayed separately. Plasma norepinephrine >750pg/ml or Epinephrine >100pg/ml are found in 90-95% of patients ...
... Cathecolamines: either epinephrine or norepinephrine is increased and should be assayed separately. Plasma norepinephrine >750pg/ml or Epinephrine >100pg/ml are found in 90-95% of patients ...
cms/lib/NY01001456/Centricity/Domain/535/Endocrine System
... 1. What is the function of the Pituitary gland? -the master gland - produces and secretes hormones that control that activity of other glands 2. What is the function of the thyroid gland? secretes thyroxine and calcitonin 3. What is the function of the parathyroid gland? produces parathyroid hormone ...
... 1. What is the function of the Pituitary gland? -the master gland - produces and secretes hormones that control that activity of other glands 2. What is the function of the thyroid gland? secretes thyroxine and calcitonin 3. What is the function of the parathyroid gland? produces parathyroid hormone ...
endocrine system - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
... Gonadal hormones ~ estrogen, testosterone Adrenalcorticoids hormones ~ corticosteroids Eicosanoids (eye cos an oids) Increase inflammation & cause swelling NON-CIRCULATING hormones ~ act locally only Released from most cell membranes & have a highly localized response Prostaglandins ~ most common ...
4-Gonads
... • LH stimulates Leydig's cells of testes to secrete testosterone. This hormone is responsible for male secondary sex characteristics, and gives male characters in general. • It inhibits gonadotropin secretion by negative feedback inhibition, similar to that of ovarian hormones in females. • If there ...
... • LH stimulates Leydig's cells of testes to secrete testosterone. This hormone is responsible for male secondary sex characteristics, and gives male characters in general. • It inhibits gonadotropin secretion by negative feedback inhibition, similar to that of ovarian hormones in females. • If there ...
Agents Affecting Thyroid, Parathyroid, and Pituitary Function
... Form the neuroendocrine system Main director is the hypothalamus ...
... Form the neuroendocrine system Main director is the hypothalamus ...
Pituitary Adenoma Diagnosis and Management Anatomical land
... B. Nelson's syndrome: hyperpigmentation (due to melanin stimulating hormone (MSH) cross reactivity with ACTH). Develops in 10·30% of patients who have undergone adrenalectomy for treatment of Cushing's syndrome FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS ...
... B. Nelson's syndrome: hyperpigmentation (due to melanin stimulating hormone (MSH) cross reactivity with ACTH). Develops in 10·30% of patients who have undergone adrenalectomy for treatment of Cushing's syndrome FUNCTIONAL PITUITARY TUMORS ...
Chapter 45
... up glucose and stores it as glycogen. STIMULUS: Rising blood glucose level (for instance, after eating a carbohydraterich meal) ...
... up glucose and stores it as glycogen. STIMULUS: Rising blood glucose level (for instance, after eating a carbohydraterich meal) ...
SD_31_ques
... 1) The relaying of mechanical information from the skin (i.e., your sense of touch) is handled by which major branch of the peripheral nervous system? A. somatic sensory B. somatic motor C. sympathetic branch of the autonomic D. parasympathetic branch of the autonomic DIFFICULTY: 3 ANS_KEY: A EXPL: ...
... 1) The relaying of mechanical information from the skin (i.e., your sense of touch) is handled by which major branch of the peripheral nervous system? A. somatic sensory B. somatic motor C. sympathetic branch of the autonomic D. parasympathetic branch of the autonomic DIFFICULTY: 3 ANS_KEY: A EXPL: ...
Reproduction Study Guide
... 1. What is the purpose of meiosis? 2. Where does it occur? 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Where does it occur? 5. How many cells & chromosomes (in each cell) are present at the end of meiosis? Mitosis? 6. How are twins formed? Explain each type. 7. Draw a sketch of a placenta and umbilical co ...
... 1. What is the purpose of meiosis? 2. Where does it occur? 3. What is the purpose of mitosis? 4. Where does it occur? 5. How many cells & chromosomes (in each cell) are present at the end of meiosis? Mitosis? 6. How are twins formed? Explain each type. 7. Draw a sketch of a placenta and umbilical co ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 19 Martini Lecture Outine
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 19 Martini Lecture Outine
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
... 2. Triggers release of TRH from the 3. TRH targets the adenohypophysis 4. Causes the release of TSH 5. TSH targets the thyroid gland 6. Triggers release of T3 and T4 7. Normal levels of T3 and T4 are restored ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.