Chapter 13 – The Endocrine System ()
... The hypothalamus regulates the production of prolactin. The hypothalamus secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates ne ...
... The hypothalamus regulates the production of prolactin. The hypothalamus secretes a hormone called dopamine which inhibits the production of prolactin. In late pregnancy, an increase in the hormone estrogen will stimulate prolactin production. Also, after a child is born breast feeding stimulates ne ...
21 Endocrine 10a
... blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it to release cortisol to most of the ce ...
... blood protein and glucose levels high enough to support the brain’s activities and affects the metabolic rate. When the brain perceives a stressful situation, the hypothalamus tells the pituitary to secrete ACTH, which travels to the adrenal gland and signals it to release cortisol to most of the ce ...
Example: Angiostatin
... secreting cytokines, which can influence peripheral neuroendo functions ...
... secreting cytokines, which can influence peripheral neuroendo functions ...
presentation source
... THYROID HORMONE SYNTHESIS DEPENDENT ON IODINE (IODINE PUMP CONCENTRATES IODINE IN CELLS) DEPENDENT ON TYROSINE PARTIALLY SYNTHESIZED (THYROGLOBULIN) EXTRACELLULARLY AT LUMINAL SURFACE OF FOLLICULAR CELLS AND STORED IN FOLLICULAR LUMEN ...
... THYROID HORMONE SYNTHESIS DEPENDENT ON IODINE (IODINE PUMP CONCENTRATES IODINE IN CELLS) DEPENDENT ON TYROSINE PARTIALLY SYNTHESIZED (THYROGLOBULIN) EXTRACELLULARLY AT LUMINAL SURFACE OF FOLLICULAR CELLS AND STORED IN FOLLICULAR LUMEN ...
Control of blood glucose
... • High blood pressure, leading to strokes, heart attacks, kidney damage… ...
... • High blood pressure, leading to strokes, heart attacks, kidney damage… ...
Neuroanatomy2
... central hypothermia Posterior region Respond to temperature changes, e.g., sweating; Lesion: hypothermia Midanterior and posterior regions Activate sympathetic nervous system Paraventricular and anterior regions Activate parasympathetic nervous system Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei Regulate w ...
... central hypothermia Posterior region Respond to temperature changes, e.g., sweating; Lesion: hypothermia Midanterior and posterior regions Activate sympathetic nervous system Paraventricular and anterior regions Activate parasympathetic nervous system Supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei Regulate w ...
Control of blood glucose
... • There are many genes which have been associated with obesity • Most are involved with the brain’s regulation of appetite ...
... • There are many genes which have been associated with obesity • Most are involved with the brain’s regulation of appetite ...
the endocrine system - People Server at UNCW
... How does the endocrine system achieve this control? The endocrine system, in contrast, regulates body functions by releasing chemical messengers called hormones (“to urge on” or “to set in motion”) into the bloodstream for delivery throughout the body. Compare the types of effectors the two systems ...
... How does the endocrine system achieve this control? The endocrine system, in contrast, regulates body functions by releasing chemical messengers called hormones (“to urge on” or “to set in motion”) into the bloodstream for delivery throughout the body. Compare the types of effectors the two systems ...
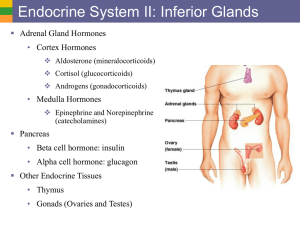
1c Endo Sys II - Inferior Glands
... Adipose tissue: leptin for appetite control Many other areas have scattered endocrine cells ...
... Adipose tissue: leptin for appetite control Many other areas have scattered endocrine cells ...
Visual pathways pathology
... Loss of one side of perception Lesion is post-chiasm and could be anywhere, until the lat. geniculate eg. MCA infarct, tumour, Aneurism postchiasm ...
... Loss of one side of perception Lesion is post-chiasm and could be anywhere, until the lat. geniculate eg. MCA infarct, tumour, Aneurism postchiasm ...
Chapter Summary- Notes
... 1. Describe the process of hormone attachment to its target organ as a lock-and-key mechanism, comparable to that discussed in previous chapters. Key point: In order for the cells of target organs to respond to a particular hormone, the hormone must attach to protein receptors on the target cell’s s ...
... 1. Describe the process of hormone attachment to its target organ as a lock-and-key mechanism, comparable to that discussed in previous chapters. Key point: In order for the cells of target organs to respond to a particular hormone, the hormone must attach to protein receptors on the target cell’s s ...
effect of training on endocrine system
... glands are responsible for the release of cortisol into the bloodstream. Cortisol levels control blood pressure, glucose and acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. The adrenal glands also release aldosterone, a hormone that regulates hydration levels, the speed of the heart and the strength of contract ...
... glands are responsible for the release of cortisol into the bloodstream. Cortisol levels control blood pressure, glucose and acts as an anti-inflammatory agent. The adrenal glands also release aldosterone, a hormone that regulates hydration levels, the speed of the heart and the strength of contract ...
doc
... Relative amounts of 4 different types of fluids found in the body (Figure 11.3) Isotonic, hypovolemia, thirst (as defined by the text) Osmometric thirst, osmoreceptors Volumetric thirst, role of kidneys (renin and angiotensin I & II, Figure 11.7) and heart (atrial baroreceptors) Brain area ...
... Relative amounts of 4 different types of fluids found in the body (Figure 11.3) Isotonic, hypovolemia, thirst (as defined by the text) Osmometric thirst, osmoreceptors Volumetric thirst, role of kidneys (renin and angiotensin I & II, Figure 11.7) and heart (atrial baroreceptors) Brain area ...
Stimulation of Medial Prefrontal Cortex Decreases the
... responses of neurons in the basolateral amygdala (BLA), which excite neurons in the central nucleus (Ce) of the amygdala. In turn, the Ce projects to the brainstem and hypothalamic areas that mediate fear responses. The present study was undertaken to test the hypothesis that the mPFC inhibits condi ...
... responses of neurons in the basolateral amygdala (BLA), which excite neurons in the central nucleus (Ce) of the amygdala. In turn, the Ce projects to the brainstem and hypothalamic areas that mediate fear responses. The present study was undertaken to test the hypothesis that the mPFC inhibits condi ...
Endocrinology - Hypoadrenocorticism
... from the adrenal glands. These hormones directly or indirectly affect virtually every process in the body, and therefore their deficiency or absence, that is, hypoadrenocorticism, can be lifethreatening. Even in cases requiring hospitalization initially, however, hypoadrenocorticism can usually be t ...
... from the adrenal glands. These hormones directly or indirectly affect virtually every process in the body, and therefore their deficiency or absence, that is, hypoadrenocorticism, can be lifethreatening. Even in cases requiring hospitalization initially, however, hypoadrenocorticism can usually be t ...
CHAPTER 36
... Introduction and scope of course There are two major regulatory systems in the body: the NERVOUS system and the ENDOCRINE system. ...
... Introduction and scope of course There are two major regulatory systems in the body: the NERVOUS system and the ENDOCRINE system. ...
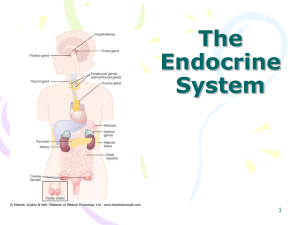
The Endocrine System Pituitary Gland (Hypophysis)
... In sections, each islet consists of lightly stained polygonal or rounded cells, arranged in cords separated by a network of blood capillaries . In 3-dimensional reconstructions, islets of Langerhans are seen as round, compact masses of secretory epithelial cells pervaded by a labyrinthine network of ...
... In sections, each islet consists of lightly stained polygonal or rounded cells, arranged in cords separated by a network of blood capillaries . In 3-dimensional reconstructions, islets of Langerhans are seen as round, compact masses of secretory epithelial cells pervaded by a labyrinthine network of ...
Chapter 13
... – Usually associated with lesions in the sub-thalamic nucleus (which regulates the globus pallidus) – Hemiballism: unilateral ballism (e.g. unilateral stroke) – Can be treated with dopamine blockade or resection of GP. ...
... – Usually associated with lesions in the sub-thalamic nucleus (which regulates the globus pallidus) – Hemiballism: unilateral ballism (e.g. unilateral stroke) – Can be treated with dopamine blockade or resection of GP. ...
Thyroid hormones
... Estradiol acts on ovarian follicles to promote granulosa cell differentiation, on uterus to stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secret ...
... Estradiol acts on ovarian follicles to promote granulosa cell differentiation, on uterus to stimulate its growth and maintain the cyclic change of uterine mucosa, on mammary gland to stimulate ductal growth, on bone to promote linear growth and closure of epiphyseal plates, on HPA to regulate secret ...
Hypothalamic and pituitary disorders Diseases of the adrenal cortex
... -ITT, CRH, ACTH test • 2 positive tests are necessary for diagnosis ...
... -ITT, CRH, ACTH test • 2 positive tests are necessary for diagnosis ...
Patients New to Bio-HRT
... When beginning HRT, Dr Gentry often recommends using a cream or gel. APPLY this to the bend of your arms, the fat at the back of your upper arms, the inner thigh, the back of the knees, the abdomen, the buttocks, or to the vaginal labia. The larger the area of application the better absorption will ...
... When beginning HRT, Dr Gentry often recommends using a cream or gel. APPLY this to the bend of your arms, the fat at the back of your upper arms, the inner thigh, the back of the knees, the abdomen, the buttocks, or to the vaginal labia. The larger the area of application the better absorption will ...
Chapter 11: The Endocrine System (pp
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
... The endocrine system, like the nervous system, controls body activities to maintain a relatively constant internal environment. The methods used by these two systems are different. This chapter describes the location of the endocrine glands and the hormones they secrete. It Explains the nature of ho ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.