chapt17_student - Human Anatomy and Physiology
... (Similarities) • several chemicals function as both hormones and neurotransmitters • some hormones secreted by neuroendocrine cells (neurons) that release their secretion into the bloodstream – oxytocin and catecholamines ...
... (Similarities) • several chemicals function as both hormones and neurotransmitters • some hormones secreted by neuroendocrine cells (neurons) that release their secretion into the bloodstream – oxytocin and catecholamines ...
Methodological Instruction to Practical Lesson № 19
... Functional interrelation between hypothalamus, hypophysis and thyroid gland. ...
... Functional interrelation between hypothalamus, hypophysis and thyroid gland. ...
The Neuron
... (2) into the brain and spinal cord where it binds to oxytocin receptors. Oxytocin acts primarily as a neurotransmitter Oxytocin has been linked to trusting other people. Experimental manipulation of oxytocin levels has shown increase in trust. According to evolutionary psychologists, trust ...
... (2) into the brain and spinal cord where it binds to oxytocin receptors. Oxytocin acts primarily as a neurotransmitter Oxytocin has been linked to trusting other people. Experimental manipulation of oxytocin levels has shown increase in trust. According to evolutionary psychologists, trust ...
File
... endocrine gland. Which gland secretes the substance that was injected? a) adrenal gland b) pancreas ...
... endocrine gland. Which gland secretes the substance that was injected? a) adrenal gland b) pancreas ...
Endocrine System Part 2
... Produced in outer adrenal cortex Regulate mineral content in blood Regulate water and electrolyte balance Target organ is the kidney Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone ...
... Produced in outer adrenal cortex Regulate mineral content in blood Regulate water and electrolyte balance Target organ is the kidney Production stimulated by renin and aldosterone ...
Endocrine System
... • Plays a role in the integration of growth and development • Plays a role in the reproductive process Hormones: • Definition – an organic substance secreted by a cell that effects the function of another cell • Are released into extracellular spaces • The physiological action is restricted to the t ...
... • Plays a role in the integration of growth and development • Plays a role in the reproductive process Hormones: • Definition – an organic substance secreted by a cell that effects the function of another cell • Are released into extracellular spaces • The physiological action is restricted to the t ...
chapter 45 - Biology Junction
... stimulate the anterior pituitary to release its hormones. Others (inhibiting hormones) inhibit hormone secretion. Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are secreted into capillaries at the base of the hypothalamus. The capillaries drain into portal vessels that subdivide into a second c ...
... stimulate the anterior pituitary to release its hormones. Others (inhibiting hormones) inhibit hormone secretion. Hypothalamic releasing and inhibiting hormones are secreted into capillaries at the base of the hypothalamus. The capillaries drain into portal vessels that subdivide into a second c ...
Endocrinology 11
... 16. All of the following statements are correct regarding Endothelin A receptor, except: a. ETA is found on the surface of a smooth muscle cells in the blood vessels wall b. The vasoconstriction that is caused by endothelin-1 is mediated by ETA c. Activation of the ETA causes an increase of the intr ...
... 16. All of the following statements are correct regarding Endothelin A receptor, except: a. ETA is found on the surface of a smooth muscle cells in the blood vessels wall b. The vasoconstriction that is caused by endothelin-1 is mediated by ETA c. Activation of the ETA causes an increase of the intr ...
Hormonal Responses to Exercise Objectives Objectives
... discuss how those changes influence the 4 mechanisms used to maintain the blood glucose concentration: insulin, glucagon, cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine, and norepinephrine ...
... discuss how those changes influence the 4 mechanisms used to maintain the blood glucose concentration: insulin, glucagon, cortisol, growth hormone, epinephrine, and norepinephrine ...
File
... Hormones are chemical messengers produced at one site and have their effect at another site Hormones are proteins that act as chemical messengers Endocrine Gland ...
... Hormones are chemical messengers produced at one site and have their effect at another site Hormones are proteins that act as chemical messengers Endocrine Gland ...
anatomy_lab10_17_4_2011
... 1. Central canal of the spinal cord 2. Left foramen of Luschka 3. Right foramen of luschka These foramens retain the CSF to subarachnoid space * Posterior horn of lateral ventricles descend to emotion area "hippocampus" which exist in the temporal pole **pole means the prominent part of the lobe * C ...
... 1. Central canal of the spinal cord 2. Left foramen of Luschka 3. Right foramen of luschka These foramens retain the CSF to subarachnoid space * Posterior horn of lateral ventricles descend to emotion area "hippocampus" which exist in the temporal pole **pole means the prominent part of the lobe * C ...
The system that consists of group of ductless glands
... 2. Chemical messengers produced & secreted by endocrine glands: ...
... 2. Chemical messengers produced & secreted by endocrine glands: ...
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... homeostasis), in conjunction with the nervous system. Recall that glands are effectors or responsive body parts that are stimulated by motor impulses from the autonomic nervous system. Some of these glands, endocrine glands compose the endocrine system. ...
... homeostasis), in conjunction with the nervous system. Recall that glands are effectors or responsive body parts that are stimulated by motor impulses from the autonomic nervous system. Some of these glands, endocrine glands compose the endocrine system. ...
Understanding Our Environment - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
... Copyright © McGraw-Hill Companies Permission required for reproduction or display ...
Lecture 3 Figure 1
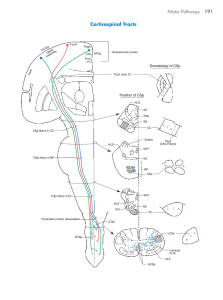
... Corticonuclear (corticobulbar) fibers arise in the frontal eye fields (areas 6 and 8 in caudal portions of the middle frontal gyrus), the precentral gyrus (somatomotor cortex, area 4), and some originate from the postcentral gyrus (areas 3,1, 2). Fibers from area 4 occupy the genu of the internal caps ...
... Corticonuclear (corticobulbar) fibers arise in the frontal eye fields (areas 6 and 8 in caudal portions of the middle frontal gyrus), the precentral gyrus (somatomotor cortex, area 4), and some originate from the postcentral gyrus (areas 3,1, 2). Fibers from area 4 occupy the genu of the internal caps ...
Nervous System Division By Dr. Nand Lal Dhomeja
... Characteristics of the ANS A part of the PNS Actions are involuntary (not under conscious control) Regulated by centers in the hypothalamus and brain stem regions of the CNS The motor part is subdivided into the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division Components of the ANS Autonomic s ...
... Characteristics of the ANS A part of the PNS Actions are involuntary (not under conscious control) Regulated by centers in the hypothalamus and brain stem regions of the CNS The motor part is subdivided into the sympathetic division and the parasympathetic division Components of the ANS Autonomic s ...
Endocrine System Powerpoint
... • Are very potent in small amounts • Are not stored in cells but synthesized just before release • Rapidly inactivate • Regulate cellular responses to hormones • Can activate or inhibit adenylate cyclase • Controls cAMP production • Alters a cells response to hormones • Has a wide variety of effects ...
... • Are very potent in small amounts • Are not stored in cells but synthesized just before release • Rapidly inactivate • Regulate cellular responses to hormones • Can activate or inhibit adenylate cyclase • Controls cAMP production • Alters a cells response to hormones • Has a wide variety of effects ...
13. Name the hormones and their functions that are secreted from
... dwarfs are all a result of too much or too little growth hormone. Which gland secretes this? ...
... dwarfs are all a result of too much or too little growth hormone. Which gland secretes this? ...
Practical Strategies for Management of the Pseudo
... association with TSH levels that are low, normal or slightly elevated. Primary hypothyroidism is most often due to autoimmune lymphocytic thyroiditis, surgery or radiation therapy. Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis physiology is highly complex, involving hypothalamic and pituitary regulation of t ...
... association with TSH levels that are low, normal or slightly elevated. Primary hypothyroidism is most often due to autoimmune lymphocytic thyroiditis, surgery or radiation therapy. Hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis physiology is highly complex, involving hypothalamic and pituitary regulation of t ...
endocrine part 1
... cells of the posterior pituitary The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... cells of the posterior pituitary The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones Copyright © 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Homeostasis
... calcium to that of potassium ion • Parathyroid hormone increases calium ion level while aldosterone descreases potassium ion level, so the major direction of regulation is the opposite • Calcium ion level can be regulated in both direction as not only parathyroid hormone but also calcitonin plays a ...
... calcium to that of potassium ion • Parathyroid hormone increases calium ion level while aldosterone descreases potassium ion level, so the major direction of regulation is the opposite • Calcium ion level can be regulated in both direction as not only parathyroid hormone but also calcitonin plays a ...
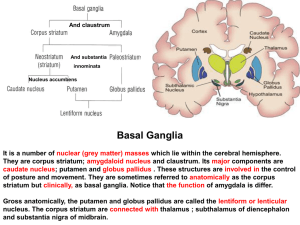
17-Basal ganglion
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
... They are corpus striatum; amygdaloid nucleus and claustrum. Its major components are caudate nucleus; putamen and globus pallidus . These structures are involved in the control of posture and movement. They are sometimes referred to anatomically as the corpus striatum but clinically, as basal gangli ...
Name
... a. a long refractory period prevents tetanus b. the ANS produces the action potentials in cardiac muscle c. slow Ca channels cause a depolarization plateau which prolongs contraction d. autorhythmic fibers spontaneously depolarize, producing action potentials 64) The left ventricular wall is thicker ...
... a. a long refractory period prevents tetanus b. the ANS produces the action potentials in cardiac muscle c. slow Ca channels cause a depolarization plateau which prolongs contraction d. autorhythmic fibers spontaneously depolarize, producing action potentials 64) The left ventricular wall is thicker ...
Hypothalamus

The hypothalamus (from Greek ὑπό, ""under"" and θάλαμος, ""room, chamber"") is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system to the endocrine system via the pituitary gland (hypophysis).The hypothalamus is located below the thalamus, just above the brainstem and is part of the limbic system. In the terminology of neuroanatomy, it forms the ventral part of the diencephalon. All vertebrate brains contain a hypothalamus. In humans, it is the size of an almond.The hypothalamus is responsible for certain metabolic processes and other activities of the autonomic nervous system. It synthesizes and secretes certain neurohormones, often called releasing hormones or hypothalamic hormones, and these in turn stimulate or inhibit the secretion of pituitary hormones.The hypothalamus controls body temperature, hunger, important aspects of parenting and attachment behaviors, thirst, fatigue, sleep, and circadian rhythms.