TEACHER NOTES AND ANSWERS Section 5.1
... 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of ga ...
... 6. additional growth and carrying out of normal functions 7. mitosis 8. cell division 9. prophase 10. metaphase 11. anaphase 12. telophase 13. cytokinesis 14. mitosis 15. interphase Cells divide at different rates Rates of cell division vary widely and are linked to the body’s need. The length of ga ...
Plant and Animal Cells
... Using a red pen correct this piece of pupil work about animal and plant cells using the information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
... Using a red pen correct this piece of pupil work about animal and plant cells using the information you have learned. You may use the other side if you need more space. Cheek cell ...
Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
Scientists, Cell Theory and Prokaryote vs. Eukaryote
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
... Light Microscope – magnifies tiny organisms up to 1,000 times. -Uses light and lenses. -We use these. ...
Cell Test: Study Guide - Peoria Public Schools
... 1. What are all living things made of? describe cells know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. W ...
... 1. What are all living things made of? describe cells know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. W ...
Cell Test: Study Guide - Peoria Public Schools
... 1. What are all living things made of? describe cells know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. What are th ...
... 1. What are all living things made of? describe cells know and explain the Cell Theory name and describe the two types of cells 2. What are the building blocks of organisms? describe the relationship between atoms and molecules identify types of molecules are needed for life processes 3. What are th ...
Cell Structure and Function Study Guide
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
... What are the contributions of Robert Hooke, Anton van Leuwenhoek, Matthias Schleiden, Theodor Schwann, and Rudolph Virchow to our understanding of cells? What are the three parts of the cell theory? How are molecules, organelles, cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and organisms related? Be ...
Cells Test What do I need to know???? Know the parts of a plant
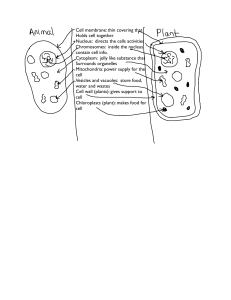
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
... Know the parts of a plant and animal cell and their functions or jobs in the cell. Study flash cards and reading. Animal Cell ...
Chapter 7 The Cell
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
... Nucleus-Brain of cell/controls all cell activities. Cell division. Chromatin-DNA spread out in nucleus Nucleolus-Dark spot. Makes ribosomes. ...
Cells Test Review
... 7. Give 3 examples of things that are not made up of cells. 8. What are cells? 9. What are tissues? 10. What are organs? 11. What is an organ system? 12. Define organism. 13. What are the levels of organization of organisms from simple to complex? ...
... 7. Give 3 examples of things that are not made up of cells. 8. What are cells? 9. What are tissues? 10. What are organs? 11. What is an organ system? 12. Define organism. 13. What are the levels of organization of organisms from simple to complex? ...
Print here - Ecosystemforkids.com
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
... Identify an organism below that has cells that have a cell wall. a. ...
Name - St. Rose of Lima School
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
... Which organelles are common to both plant and animal cells? Why is the vacuole larger in the plant cell? _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________ ...
Chapter 21: The Genetic Basis of Development
... Animals: movement of cells & tissues establishes form Plants: morphogenesis & growth occurs throughout the life of the plant (apical meristems) ...
... Animals: movement of cells & tissues establishes form Plants: morphogenesis & growth occurs throughout the life of the plant (apical meristems) ...
Cell Study Guide
... to do. These are called life processes: 1. They all grow. 2. They all get food. 3. They all respond to the environment. 4. They all reproduce. 2. You need to know where cells come from. ...
... to do. These are called life processes: 1. They all grow. 2. They all get food. 3. They all respond to the environment. 4. They all reproduce. 2. You need to know where cells come from. ...
cells cells - Springwater River Otters
... Cells, cells they're made of organelles Try to pull a fast one, the cytoplasm gels The nucleus takes over controllin' everything The party don't stop 'till the membrane blocks the scene Inside the vacuole we can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, c ...
... Cells, cells they're made of organelles Try to pull a fast one, the cytoplasm gels The nucleus takes over controllin' everything The party don't stop 'till the membrane blocks the scene Inside the vacuole we can float around for hours Running round with chloroplasts, lovin' sunlight showers Cells, c ...
Cell Organelles
... • Burns sugar (glucose) for fuel in the process of cellular respiration. Often referred to as the “engine” or “powerhouse” of the cell. • Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells, usually several or many per cell. ...
... • Burns sugar (glucose) for fuel in the process of cellular respiration. Often referred to as the “engine” or “powerhouse” of the cell. • Found in nearly all eukaryotic cells, usually several or many per cell. ...
Viewing Cells
... larger but not always clear. Modern microscopes that use lenses to bend light. A simple microscope has one lens while a compound microscope has two sets of lenses. ...
... larger but not always clear. Modern microscopes that use lenses to bend light. A simple microscope has one lens while a compound microscope has two sets of lenses. ...
Organelle Notes #2
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
... Cornell Notes Lecture, reading/chapter/novel/article during class, power point, movies (if need to collect info.) ...
Slide ()
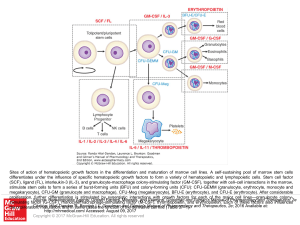
... (SCF), ligand (FL), interleukin-3 (IL-3), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), together with cell–cell interactions in the marrow, stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte ...
... (SCF), ligand (FL), interleukin-3 (IL-3), and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), together with cell–cell interactions in the marrow, stimulate stem cells to form a series of burst-forming units (BFU) and colony-forming units (CFU): CFU-GEMM (granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte ...
lesson_10
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
... Unit Description: When a living thing grows, what happens to its cells? Does an animal get larger because each cell increases in size or because it produces more of them? In most cases, living things grow by producing more cells. Students will begin to explore how cells grow and are produced. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.