Sexual Reproduction Male Sex Cell
... Female Sex Cell= _________Cell -Egg and Sperm have _________the number of chromosomes (genetic information) as the body cells ; fertilization can happen internally or externally -Sperm fertilize eggs creating a new cell that has the genetic information of both the mom and dad Advantages= __________ ...
... Female Sex Cell= _________Cell -Egg and Sperm have _________the number of chromosomes (genetic information) as the body cells ; fertilization can happen internally or externally -Sperm fertilize eggs creating a new cell that has the genetic information of both the mom and dad Advantages= __________ ...
Cells
... Only in plants, they use light to make food (glucose) from water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide(CO₂) during photosynthesis. ...
... Only in plants, they use light to make food (glucose) from water (H₂O) and carbon dioxide(CO₂) during photosynthesis. ...
Sexual Reproduction Guided Notes
... 1. At the end of meiosis, one cell has produced _______________ cells that each have half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. 2. Because the original cell in meiosis has different homologous chromosomes, each of the 4 daughter cells will have one or the other of each homologous chromosom ...
... 1. At the end of meiosis, one cell has produced _______________ cells that each have half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. 2. Because the original cell in meiosis has different homologous chromosomes, each of the 4 daughter cells will have one or the other of each homologous chromosom ...
Tunneling nanotubes meso abstract
... Background: Research efforts to understand communication mechanisms that influence cancer growth and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell co ...
... Background: Research efforts to understand communication mechanisms that influence cancer growth and metastasis have been focused on gap junctions, exosomes and microvesicles, and cytokine signaling interactions between cells. Currently there is limited understanding of how efficient cell-to-cell co ...
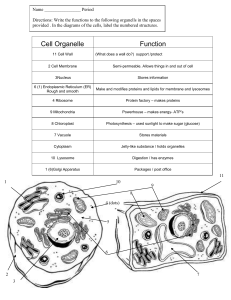
Cell Organelle
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
... Name ________________ Period Directions: Write the functions to the following organells in the spaces provided . In the diagrams of the cells, label the numbered structures. ...
2.2 – Prokaryotic Cells
... and possible harm from other organisms. Plasmid - Aid DNA exchange. These are DNA molecule capable of replicating. ...
... and possible harm from other organisms. Plasmid - Aid DNA exchange. These are DNA molecule capable of replicating. ...
Draw a labelled diagram of a prokaryotic cell as seen in electron
... Explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes (3) ...
... Explain how the surface area to volume ratio influences cell sizes (3) ...
Asexual Reproduction
... 1. Reproduces an entire organism (unicellular organisms like amoeba and paramecium) 2. Cell division is the basis of sperm and egg for sexually reproducing organisms. 3. Cell division also enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from a single cell (fertilized egg, or zygote) into and adult ...
... 1. Reproduces an entire organism (unicellular organisms like amoeba and paramecium) 2. Cell division is the basis of sperm and egg for sexually reproducing organisms. 3. Cell division also enables sexually reproducing organisms to develop from a single cell (fertilized egg, or zygote) into and adult ...
Criterion
... Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is encouraged. Be sure to carefully record the magnification. Label the parts of your cell. Guidelin ...
... Make scientific drawings for 2 different cells. Choose one red blood cell and one respiration cell. The drawing must be done to scale. Draw only a few cells. Use solid lines, no shading but stippling is encouraged. Be sure to carefully record the magnification. Label the parts of your cell. Guidelin ...
Basic Bio 3
... Q. This is a two-part process that ends in the assembly of proteins at the ribosomes within cells. The first part, transcription, begins in the nucleus, when the DNA code is transferred to mRNA. The second part, translation, takes place at the ribosomes, where both mRNA and tRNA work to assemble pro ...
... Q. This is a two-part process that ends in the assembly of proteins at the ribosomes within cells. The first part, transcription, begins in the nucleus, when the DNA code is transferred to mRNA. The second part, translation, takes place at the ribosomes, where both mRNA and tRNA work to assemble pro ...
topic 5 -part 3 guided notes -plant vs animal cells - student
... 9. vacuole (much bigger in plant cells!) 10. lysosomes 11. mitochondria 12. cytoplasm ...
... 9. vacuole (much bigger in plant cells!) 10. lysosomes 11. mitochondria 12. cytoplasm ...
1-2.02 test study guide
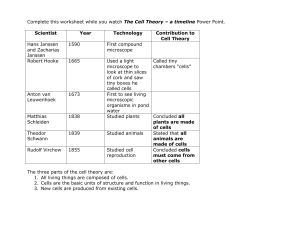
... 13.What is the main source of energy for all living things? 14.What are the functions of proteins? 15.Who was the first person to see the cell? 16.What did schleiden and Schwann tell us? 17.What are the 3 principals of the cell theory 18.What does the cell theory apply to? 19.What is the difference ...
... 13.What is the main source of energy for all living things? 14.What are the functions of proteins? 15.Who was the first person to see the cell? 16.What did schleiden and Schwann tell us? 17.What are the 3 principals of the cell theory 18.What does the cell theory apply to? 19.What is the difference ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... through an object—can only use DEAD cells. (Transmission Electron Microscope 1 MILLION stronger than light microscope and Scanning Electron Microscope can produce REALISTIC images. The Cell Theory A. Mid 1800’s, 3 main ideas 1. All organisms are made of one or more CELLS. 2. A cell is the basic unit ...
... through an object—can only use DEAD cells. (Transmission Electron Microscope 1 MILLION stronger than light microscope and Scanning Electron Microscope can produce REALISTIC images. The Cell Theory A. Mid 1800’s, 3 main ideas 1. All organisms are made of one or more CELLS. 2. A cell is the basic unit ...
Cell Structure and Function Worksheet
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
... Cell Structure and Function Worksheet 1. Construct a Venn diagram of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cells and give at least one example of each type of cell. ...
Cytology
... acids and to define their role in biochemical processes. • To analyze and explain the chemical reactions the provide energy for the body. • To investigate and describe the integration of the chemical and physical properties that contribute to homeostasis in cells. • To compare the structures and fun ...
... acids and to define their role in biochemical processes. • To analyze and explain the chemical reactions the provide energy for the body. • To investigate and describe the integration of the chemical and physical properties that contribute to homeostasis in cells. • To compare the structures and fun ...
Mitosis - Mahopac Voyagers!
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
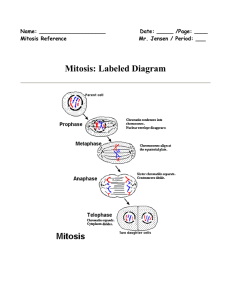
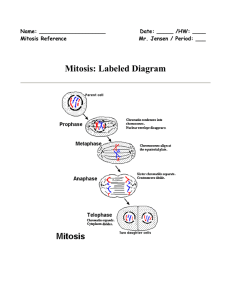
Mitosis: Labeled Diagram
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
... Mitosis is a process of cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. The daughter cells are identical to one another and to the original parent cell. In a typical animal cell, mitosis can be divided into four principals stages: ...
powerpoint jeopardy
... When a group of cells divide uncontrollably, they are said to be these types of cells. ...
... When a group of cells divide uncontrollably, they are said to be these types of cells. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.