Cell Organelle Notes worksheet
... 3-1 The Cell Theory A cell is defined as ______________________________________________________________ ________________________. Cells contain structures called ___________________________. This terms means tiny _________________________. Cells were first described by the English scientist ________ ...
... 3-1 The Cell Theory A cell is defined as ______________________________________________________________ ________________________. Cells contain structures called ___________________________. This terms means tiny _________________________. Cells were first described by the English scientist ________ ...
Cell Structure Guided Notes
... 5. What did Rudolph Virchow observe under the microscope in 1858? 6. What conclusion did Virchow make from this observation? 7. State the 3 parts of the CELL THEORY. a. b. c. ...
... 5. What did Rudolph Virchow observe under the microscope in 1858? 6. What conclusion did Virchow make from this observation? 7. State the 3 parts of the CELL THEORY. a. b. c. ...
Project Title: Functional characterisation of centrosome proteins in
... polarity axis. The centrosome plays a critical role in this process. As the major microtubuleorganising centre of animal cells, centrosomes contribute to mitotic spindle formation and positioning. In addition, centrosomes are required for the biogenesis of the primary cilium, which is a chemosensory ...
... polarity axis. The centrosome plays a critical role in this process. As the major microtubuleorganising centre of animal cells, centrosomes contribute to mitotic spindle formation and positioning. In addition, centrosomes are required for the biogenesis of the primary cilium, which is a chemosensory ...
We`sproutly` present
... The functionally immortalized human umbilical vein endothelial cell line CI-huVEC has just been published in the peer reviewed 'FASEB Journal'. The article describes a sophisticated three-dimensional cell culture model enabling angiogenesis studies and functional screening. The C ...
... The functionally immortalized human umbilical vein endothelial cell line CI-huVEC has just been published in the peer reviewed 'FASEB Journal'. The article describes a sophisticated three-dimensional cell culture model enabling angiogenesis studies and functional screening. The C ...
Cell Membrane Animal Cell Controls what enters and leaves the cell
... Animal Cell Controls activity within the cell (“brain” of the cell) ...
... Animal Cell Controls activity within the cell (“brain” of the cell) ...
Cells and Batteries
... Cells and Batteries A cell is a unit which includes two electrodes and one electrolyte. ...
... Cells and Batteries A cell is a unit which includes two electrodes and one electrolyte. ...
Notes Outline: How Cells Divide (4
... Notes Outline: Mitosis and Cell Division (6.2) “ As cells busily carry out the functions of life, they grow and develop. When most cells reach a certain size, they either stop growing or divide into two cells. Cell division is essential for the growth and development or an organism.” I. ...
... Notes Outline: Mitosis and Cell Division (6.2) “ As cells busily carry out the functions of life, they grow and develop. When most cells reach a certain size, they either stop growing or divide into two cells. Cell division is essential for the growth and development or an organism.” I. ...
Assessment
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
... _____ 7. Which of these includes the main parts of an organ system? a. leaves on a tree c. heart and blood vessels b. stem of a flower d. large mass of amoebas _____ 8. In which of these does true multicellularity occur? a. eukaryotes c. colonial organisms b. prokaryotes d. All of the above _____ 9. ...
Chapter 1 Eukaryotic Cells Section 1
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
... Nucleus – largest organelle in a eukaryotic cell, contains DNA that directs all cell activity Ribosomes – organelles that make protein Endoplasmic reticulum – folded membrane where cell materials are made (proteins, lipids) and moved to different places in the cell Mitochondria – power source of a c ...
Stem Cell Therapy - Logan County Animal Clinic
... We proudly offer regenerative stem cell therapy. Stem cell therapy is a leading edge medical solution for the treatment of osteoarthritis in pets. VetStem regenerative stem cells use your own animal’s natural healing cells from their fat tissue. This method has been proven and documented in publishe ...
... We proudly offer regenerative stem cell therapy. Stem cell therapy is a leading edge medical solution for the treatment of osteoarthritis in pets. VetStem regenerative stem cells use your own animal’s natural healing cells from their fat tissue. This method has been proven and documented in publishe ...
What are stem cells
... a. A cell taken from an embryo that can become any kind of cell type in the body b. A cell taken from your intestines that can become any kind of tissue in the body c. A kind of cell that can only become other kinds of similar cells d. Any kind of cell that is undifferentiated and can divide to make ...
... a. A cell taken from an embryo that can become any kind of cell type in the body b. A cell taken from your intestines that can become any kind of tissue in the body c. A kind of cell that can only become other kinds of similar cells d. Any kind of cell that is undifferentiated and can divide to make ...
MBD3-deficient embryonic stem cell line
... generated a pluripotent (murine) embryonic stem cell line and have shown that these MBD3‐deficient stem cells are maintained in the absence of any exogenous factors (e.g. serum or LIF). A central goal of stem cell research is to maintain and grow pluripotent stem cells to study the signals that ...
... generated a pluripotent (murine) embryonic stem cell line and have shown that these MBD3‐deficient stem cells are maintained in the absence of any exogenous factors (e.g. serum or LIF). A central goal of stem cell research is to maintain and grow pluripotent stem cells to study the signals that ...
File
... This worksheet relates the structure of the cell surface membrane to its role in cell signalling. Making your own diagram is an excellent way of checking your knowledge of a structure. Part d asks you to apply your knowledge to a new situation. ...
... This worksheet relates the structure of the cell surface membrane to its role in cell signalling. Making your own diagram is an excellent way of checking your knowledge of a structure. Part d asks you to apply your knowledge to a new situation. ...
Morphogenesis – the process of cell development.
... 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by genes b. Information to program and guide growth is controlled by chromosomes c. Shape ...
... 2. A horse grows and develops into an adult with millions of cells through: a. Cell growth b. Mitosis c. Cell division 3. Many different types of cells in full grown horses. a. Differences in cell is controlled by genes b. Information to program and guide growth is controlled by chromosomes c. Shape ...
logcsscibap_2_1_2_d_..
... Animal cells have some of the same structures and organelles that plant cells have, but not all of them. a ...
... Animal cells have some of the same structures and organelles that plant cells have, but not all of them. a ...
Biology EOC Review 6 Cell Cycle, Transport and Differentiation
... 13. What is the term for programmed cell death? A. kinase B. cyclin C. apoptosis D. mutate 14. The most common form of reproduction among prokaryotes is A. mitosis. B. budding. C. binary fission. D. fragmentation. 15. Which of the following is a direct result of a normal cell’s ability to express on ...
... 13. What is the term for programmed cell death? A. kinase B. cyclin C. apoptosis D. mutate 14. The most common form of reproduction among prokaryotes is A. mitosis. B. budding. C. binary fission. D. fragmentation. 15. Which of the following is a direct result of a normal cell’s ability to express on ...
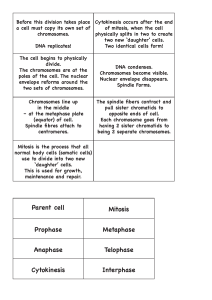
Parent cell Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
... DNA replicates! Two identical cells form! The cell begins to physically divide. The chromosomes are at the poles of the cell. The nuclear envelope reforms around the two sets of chromosomes. Chromosomes line up in the middle – at the metaphase plate (equator) of cell. centromeres. ...
cell organelle webquest
... Name_______________________________ Period _____________ Date ____________ ...
... Name_______________________________ Period _____________ Date ____________ ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.