Cell Review Worksheet
... 8. What are the levels of organization from atom to organism? What happens as you move up the levels? ...
... 8. What are the levels of organization from atom to organism? What happens as you move up the levels? ...
Cell organelles
... • Has enzymes that break down food, old materials, etc. • Garbage disposal of cell ...
... • Has enzymes that break down food, old materials, etc. • Garbage disposal of cell ...
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... B = Both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells __E__1. Has a definite, well-defined nucleus _E___2. Type of cells in your body _B___3. Have DNA _P___4. Bacteria cells _E___5. Multicellular _B____6. Has ribosomes _B___7. Can live as unicellular organisms _E___8. Type of cells found in plants _E___9. Type ...
... B = Both Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells __E__1. Has a definite, well-defined nucleus _E___2. Type of cells in your body _B___3. Have DNA _P___4. Bacteria cells _E___5. Multicellular _B____6. Has ribosomes _B___7. Can live as unicellular organisms _E___8. Type of cells found in plants _E___9. Type ...
Cell Cycle Control System - Santa Susana High School
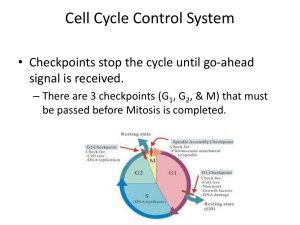
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
... • Checkpoints stop the cycle until go-ahead signal is received. – There are 3 checkpoints (G1, G2, & M) that must be passed before Mitosis is completed. ...
GCSE activity labelling plant and animal cells
... www.thescienceteacher.co.uk | resources for science teachers who like to think ...
... www.thescienceteacher.co.uk | resources for science teachers who like to think ...
Topic - the science teacher
... www.thescienceteacher.co.uk | resources for science teachers who like to think ...
... www.thescienceteacher.co.uk | resources for science teachers who like to think ...
Unit 2 Review: Cells
... 10) What are stem cells? 11) Compare embryonic stem cells and adult stems cells. In other words, how are they similar and how are they different? ...
... 10) What are stem cells? 11) Compare embryonic stem cells and adult stems cells. In other words, how are they similar and how are they different? ...
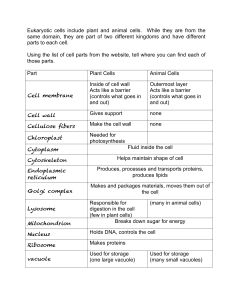
Cell membrane Cell wall Cellulose fibers Chloroplast Cytoplasm
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
... Eukaryotic cells include plant and animal cells. While they are from the same domain, they are part of two different kingdoms and have different parts to each cell. Using the list of cell parts from the website, tell where you can find each of those parts. Part ...
Cell Power Point Questions
... 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) The 3 parts of cell theory: 1) All living t ...
... 3) ___________ was the first to record observations of what we know as bacteria from the plaque of teeth and he called these ____________. 4) The three scientists that contributed to cell theory are: - _______________ - _______________ - _______________ 5) The 3 parts of cell theory: 1) All living t ...
01A004 - Proliferated Cell Lines and Uses Thereof
... of neurological, muscular, cartilage, cardiovascular, liver, pancreatic, eyesight, and autoimmune disorders. Used to supplement progress in such advanced cellular research, this newly developed technology promises to make many currently envisioned cellular therapies a reality. ...
... of neurological, muscular, cartilage, cardiovascular, liver, pancreatic, eyesight, and autoimmune disorders. Used to supplement progress in such advanced cellular research, this newly developed technology promises to make many currently envisioned cellular therapies a reality. ...
Learning Checkpoint ANSWERS TO QUESTIONS p. 16
... apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as solar collectors, collecting light energy from the Sun. This energy is used during photosynthesis to produce sugars. 5. Plant cells c ...
... apparatus receives proteins from the ER and modifies, sorts, and packages these proteins for delivery throughout the cell or out of the cell. 4. The thylakoids act as solar collectors, collecting light energy from the Sun. This energy is used during photosynthesis to produce sugars. 5. Plant cells c ...
sgCh1Cell
... Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control ...
... Introduction to Cells Complete the following Questions. 1.______________basic units of structure and __________in living things. 2. Hooke observed _________________ 3. What did Leeuwenhoek observe? 4. The function of the cell wall is _____________________________________. 5. Organelles that control ...
Cell Theory Timeline
... He is the first to call the spaces in the cork “cells” which means little rooms. ...
... He is the first to call the spaces in the cork “cells” which means little rooms. ...
AP Biology - Mitosis and Meiosis Experiments
... 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each ...
... 2. Observe at least 200 different cells in the apical meristem region. 3. Catagorize each cell as to the cell cycle phase (Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase, Cytokinesis). 4. Calculate the percentage of cells in each phase and the time (in minutes) that the onion cells are in each ...
Diffusion with Eggs Lab
... Learning Targets “I Can. . .” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using eggs with a dissolved shell. -Predict the results of an experiment that involves the movement of water through a membrane. -Recognize cells that are in a hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solution. ...
... Learning Targets “I Can. . .” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using eggs with a dissolved shell. -Predict the results of an experiment that involves the movement of water through a membrane. -Recognize cells that are in a hypotonic, hypertonic, and isotonic solution. ...
Print Preview - D:\Temp\e3temp_3492\.aptcache\aea03492/tfa03492
... to perform similar or related functions ...
... to perform similar or related functions ...
Structures found in Eukaryotes Continued 4. • Formed by • Vesicles
... Cell respiration takes place ...
... Cell respiration takes place ...
I`m a real “powerhouse.” That`s plain to see. I break down food to
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
... Or so they say. I regulate activities from day to day. ...
β1 Integrin Participates in Endoglin-Dependent Inhibition of Prostate
... Using these cells, we determined that endoglin phosphorylation by the TGF-β receptors ALK2 and ALK5 is a mechanism involved in TGF-β1-dependent regulation of cell migration. Our current objective is to analyze the signaling pathways downstream of endoglin that lead to the inhibition of prostate canc ...
... Using these cells, we determined that endoglin phosphorylation by the TGF-β receptors ALK2 and ALK5 is a mechanism involved in TGF-β1-dependent regulation of cell migration. Our current objective is to analyze the signaling pathways downstream of endoglin that lead to the inhibition of prostate canc ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.