Mitosis and Cancer - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
... They are stuck in the mitosis part of the cell cycle; always dividing without replicating and preparing the cells DNA. ...
Neurogenesis (Emília Madarász)
... Migration of neurons: CNS: with the help of radial glia cells PNS: migration of cells of the neural crest (they migrate to different parts of the body depending on what cell type they differentiate into → regulated by many factors) Axon and dendrite formation are regulated by additional factors grow ...
... Migration of neurons: CNS: with the help of radial glia cells PNS: migration of cells of the neural crest (they migrate to different parts of the body depending on what cell type they differentiate into → regulated by many factors) Axon and dendrite formation are regulated by additional factors grow ...
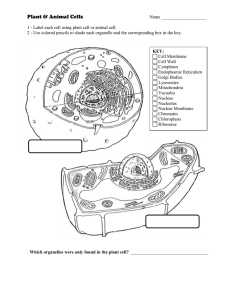
Plant and Animal Cells Notes
... 3) One part found in all cells is the __________________ __________________________. The cell membrane _________________________________ the cell and holds the cell __________________________________. It controls what ____________________________ can enter and leave the cell. 4) Another part found i ...
... 3) One part found in all cells is the __________________ __________________________. The cell membrane _________________________________ the cell and holds the cell __________________________________. It controls what ____________________________ can enter and leave the cell. 4) Another part found i ...
Name______________________________________
... 12) Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 13) The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called: 14) Which term refers to cells having different jobs in an organism? 15) Give an example of an organ? 16) A group of simple carbohydrates can be ...
... 12) Which means of particle transport requires input of energy from the cell? 13) The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane is called: 14) Which term refers to cells having different jobs in an organism? 15) Give an example of an organ? 16) A group of simple carbohydrates can be ...
Plurioptent stem cell translation: basic and
... from the same accomplishment in humans, translational applications of this science are now underway. This includes the use of animal and human pluripotent stem cells in drug screening, to model disease and in humans cellular therapies. However, the transformation of these practices into robust manuf ...
... from the same accomplishment in humans, translational applications of this science are now underway. This includes the use of animal and human pluripotent stem cells in drug screening, to model disease and in humans cellular therapies. However, the transformation of these practices into robust manuf ...
P006 Could Stem Cells be a source for primary cells in HTS scenario?
... than the stable cell lines currently used. The adult stem cells could be the key as they can expand to high number of cells and differentiate into any adult specialized cell type. At the same time, the use of adult stem cells overcomes any ethical consideration. But because the telomeres shortening ...
... than the stable cell lines currently used. The adult stem cells could be the key as they can expand to high number of cells and differentiate into any adult specialized cell type. At the same time, the use of adult stem cells overcomes any ethical consideration. But because the telomeres shortening ...
1. All living things are made of cell
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
... 3. What process creates new cells for growth and repair through cell division that are identical to the parent cell? Mitosis ...
Subcellular Organelles and Structures
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
... Liver Cell (TEM x9,400). This image is copyright Dennis Kunkel ...
Cells - Weebly
... ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
... ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. ...
HW Chapter 4 HB
... Name: ________________________________________________ Homework Chapter 5 Biology of the Cell ...
... Name: ________________________________________________ Homework Chapter 5 Biology of the Cell ...
Cell Review Cell Theory Levels of Organization Organelle
... 9. Mitochondria – Eats protein to make energy (ATP) for the cell. (Powerhouse) 1. Nucleus – Command center of the cell. (Receives and sends messages) 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes ...
... 9. Mitochondria – Eats protein to make energy (ATP) for the cell. (Powerhouse) 1. Nucleus – Command center of the cell. (Receives and sends messages) 6. Cell Membrane – Barrier of protection for the cell (Allows nutrients in and waste out) 8. Vacuole – Stores water and waste. 4. Chloroplasts – Makes ...
answers - Biology Resources
... 6 If a cell develops in such a way that it does one particular job very efficiently, it is said to be specialised. Such a cell is also said to be adapted to its function. A nerve cell is specialised for conducting impulses. It can do this efficiently because of its shape and the chemical reactions i ...
... 6 If a cell develops in such a way that it does one particular job very efficiently, it is said to be specialised. Such a cell is also said to be adapted to its function. A nerve cell is specialised for conducting impulses. It can do this efficiently because of its shape and the chemical reactions i ...
Ch 10 Cell Growth and Division
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
... stage of development most multicellular organisms pass through ...
Section 1 The World of Cells
... All living things are made of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells come from cells that already exist. ...
... All living things are made of cells The cell is the basic unit of life All cells come from cells that already exist. ...
Unit 2 Cells Test Study Guide
... Unit 2 Cells Study Guide Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
... Unit 2 Cells Study Guide Answer the following questions using your textbook and notes. Study each of these questions and topics as all will appear on your test. ...
Chapter 6 Exam – Part II
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
... Mitosis Study Guide - Biology 1. __________ is a process of eukaryotic cell division which results in the production of two daughter cells from a single parent cell. 2. Name the steps of the cell cycle in order. 3. Name the steps of mitosis in order. 4. What kind of cells undergo mitosis? 5. How man ...
Name School Class Date Laboratory Investigation on Cells Observing Plant Cells
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
... microscope slide. The piece of onion should be no bigger than 1cm . Cover this with one drop of iodine solution and place the cover slip over this. Observe the cells using the x10 objective lens. ...
Science Chapter 2 Study Guide – Cells to Systems Parts of a Cell
... ____________ : the part of the cell that gives plant cells support and protection ____________ : the part of the cell that combines oxygen and food to produce energy in the process of cellular respiration Labs: What do yeast cells need to grow? How should you properly carry a microscope? What does a ...
... ____________ : the part of the cell that gives plant cells support and protection ____________ : the part of the cell that combines oxygen and food to produce energy in the process of cellular respiration Labs: What do yeast cells need to grow? How should you properly carry a microscope? What does a ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.