George`s slides
... CMBR, absence of monopoles, the right type of density fluctua5on spectrum - it all supports the idea that infla5on did happen, but does not say a lot about its detailed physics • Cosmological observa5ons can indicate or constrain physics well outside the reach of laboratory experiments ...
... CMBR, absence of monopoles, the right type of density fluctua5on spectrum - it all supports the idea that infla5on did happen, but does not say a lot about its detailed physics • Cosmological observa5ons can indicate or constrain physics well outside the reach of laboratory experiments ...
THE BIG BANG - Santa Cruz Institute for Particle Physics
... •1905: special relativity, photoelectric effect, Brownian Motion ...
... •1905: special relativity, photoelectric effect, Brownian Motion ...
Origins of the Universe
... us the more it is red shifted • The only explanation for that is if everything is moving away from us. • This means the universe is expanding ...
... us the more it is red shifted • The only explanation for that is if everything is moving away from us. • This means the universe is expanding ...
HST04-Cosmology - Indico
... expansion, so one needs to introduce another form of energy, called dark energy, which does not cluster, one example being a cosmological constant Cosmic Microwave Background anisotropies: Geometry of the universe is flat! This implies that the total density equals the critical density and is consis ...
... expansion, so one needs to introduce another form of energy, called dark energy, which does not cluster, one example being a cosmological constant Cosmic Microwave Background anisotropies: Geometry of the universe is flat! This implies that the total density equals the critical density and is consis ...
Our Picture of The Universe
... Did the universe have a beginning, and if so what happened before then? What is the nature of time? Will it ever come to an end? ...
... Did the universe have a beginning, and if so what happened before then? What is the nature of time? Will it ever come to an end? ...
Historical overview
... After recombination, matter and radiation evolve independently. The radiation left over from this epoch follows a black-body distribution whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached ...
... After recombination, matter and radiation evolve independently. The radiation left over from this epoch follows a black-body distribution whose effective temperature drops as the universe expands. George Gamow predicted in 1953 that at present this radiation that fills the whole Universe has reached ...
August 29 - Astronomy
... they are, the faster they are moving 2. The Cosmic microwave background radiation – things that are hot emit light and the universe today is filled with this light emitted when it was much hotter ...
... they are, the faster they are moving 2. The Cosmic microwave background radiation – things that are hot emit light and the universe today is filled with this light emitted when it was much hotter ...
E.S. 14: The Universe Universe Formation: The Big Bang Theory
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
... B. Spiral galaxies have spiral arms that start close to the center. i. Ex: The Milky Way ...
Solutions - UC Berkeley Astronomy w
... The brightness of car headlights is instinctively thought to follow the inverse-square law. In this way you can judge the brightness of an oncoming car. In the fog, the apparent brightness can be decreased, making a car look further away than you would guess from instinct. In the same way, stars in ...
... The brightness of car headlights is instinctively thought to follow the inverse-square law. In this way you can judge the brightness of an oncoming car. In the fog, the apparent brightness can be decreased, making a car look further away than you would guess from instinct. In the same way, stars in ...
Space Science Review Vocabulary: Nebula Proto Star Main
... Characteristics of the phases in the Life Cycle of a Star The EM Spectrum The HR Diagram – know how to relate temperature to luminosity or absolute magnitude on the diagram ...
... Characteristics of the phases in the Life Cycle of a Star The EM Spectrum The HR Diagram – know how to relate temperature to luminosity or absolute magnitude on the diagram ...
The Modern Origins Story: From the Big Bang to Habitable Planets
... on an unexceptional galaxy which is one of about 100 billion galaxies. That is the fundamental fact of the universe we inhabit, and it is very good for us to understand that. Carl Sagan ...
... on an unexceptional galaxy which is one of about 100 billion galaxies. That is the fundamental fact of the universe we inhabit, and it is very good for us to understand that. Carl Sagan ...
Cosmology Prof. Yves Gaspar COURSE CONTENT Cosmology
... usually taught separately, are used in a unified framework. The course also contains a part dedicated to theoretical astrophysics, which studies the stars and their evolution, the general aim being the study of the problems inherent to black hole physics. The content of the course can be divided in ...
... usually taught separately, are used in a unified framework. The course also contains a part dedicated to theoretical astrophysics, which studies the stars and their evolution, the general aim being the study of the problems inherent to black hole physics. The content of the course can be divided in ...
Astronomy Quiz #1 Answers
... 8. Some galaxies are thought to produce many more new stars than others. What characteristics do galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have in common? (2 – MC) -they have large amounts of dust and gas 9. Explain why looking at a star in the night sky is like looking back in time. (2 – COM ...
... 8. Some galaxies are thought to produce many more new stars than others. What characteristics do galaxies with a high rate of production of stars have in common? (2 – MC) -they have large amounts of dust and gas 9. Explain why looking at a star in the night sky is like looking back in time. (2 – COM ...
Goodbye Big Bang, hello black hole? A new theory of the
... that the universe is expanding (and indeed is getting faster as it expands, possibly due to the mysterious dark energy). The new theory says that "The study could help to show how inflation is triggered by the motion of the universe through a the expansion comes from this 3-D brane's higher-dimensio ...
... that the universe is expanding (and indeed is getting faster as it expands, possibly due to the mysterious dark energy). The new theory says that "The study could help to show how inflation is triggered by the motion of the universe through a the expansion comes from this 3-D brane's higher-dimensio ...
Announcements
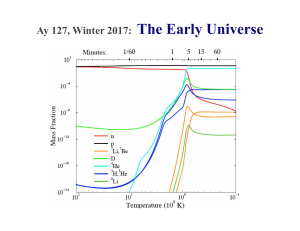
... this isotope in the universe gives us fundamental information about this period of time ...
... this isotope in the universe gives us fundamental information about this period of time ...
The Universe: “Beyond the Big Bang” Video Questions
... 48. Where did the sounds that Penzias and Wilson heard originate? everywhere 49. What was the “smoking gun” that Penzias and Wilson discovered? cosmic background ...
... 48. Where did the sounds that Penzias and Wilson heard originate? everywhere 49. What was the “smoking gun” that Penzias and Wilson discovered? cosmic background ...
Cosmology
... What is the principal observational evidence that the age of the Universe is about 14 billion years? A. The oldest rocks (carbonaceous chondrites) in the solar system indicate an age of 14 billion years; B. Radioactive decay of heavy elements created in the Big Bang indicates an age of 14 billion y ...
... What is the principal observational evidence that the age of the Universe is about 14 billion years? A. The oldest rocks (carbonaceous chondrites) in the solar system indicate an age of 14 billion years; B. Radioactive decay of heavy elements created in the Big Bang indicates an age of 14 billion y ...
New Directions
... But perfect symmetry is as likely as “an infinite number of needles standing on their tips on a mirror” ...
... But perfect symmetry is as likely as “an infinite number of needles standing on their tips on a mirror” ...
Ch 17n18 AGN Cosmology
... obvious, but it has a profound answer: the universe is finite in size and age! 2. The universe is expanding! The redshifts that we measure do NOT result from galaxies flying through space (so NOT Doppler shifts!), but space-time itself expanding and carrying the galaxies with it—as if on an expandin ...
... obvious, but it has a profound answer: the universe is finite in size and age! 2. The universe is expanding! The redshifts that we measure do NOT result from galaxies flying through space (so NOT Doppler shifts!), but space-time itself expanding and carrying the galaxies with it—as if on an expandin ...
The Big Bang
... away from the earth appears to be shifted toward the red end. • This is called the red shift. • The more the spectrum of light is shifted toward the blue or red end of the spectrum, the faster the star is moving toward or away from the earth. ...
... away from the earth appears to be shifted toward the red end. • This is called the red shift. • The more the spectrum of light is shifted toward the blue or red end of the spectrum, the faster the star is moving toward or away from the earth. ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.