Export To Word
... This is an effective tool to help learners gain knowledge about all the aspects of ideal gas law. An ideal gas law is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and there are no inter- molecular attractive forces. An ideal gas can be characterized by thre ...
... This is an effective tool to help learners gain knowledge about all the aspects of ideal gas law. An ideal gas law is defined as one in which all collisions between atoms or molecules are perfectly elastic and there are no inter- molecular attractive forces. An ideal gas can be characterized by thre ...
Purification of TMEDA: 1. In a 4L Beaker, add, 2L MeOH and 500 ml
... 6. Add 450-500 ml of water to dissolve the solid. 7. Allow the mixture to come to rt. Put the solution in the freezer overnight. 8. Repeat 4-7 again (This time, add 300-350 ml of water to dissolve the solid) 9. Filter the solid and allow it to dry overnight (open to air). 10. Add approximately 400 g ...
... 6. Add 450-500 ml of water to dissolve the solid. 7. Allow the mixture to come to rt. Put the solution in the freezer overnight. 8. Repeat 4-7 again (This time, add 300-350 ml of water to dissolve the solid) 9. Filter the solid and allow it to dry overnight (open to air). 10. Add approximately 400 g ...
vertical component - H2 Physics Tuition
... Liquid flows through the horizontal tube T. By maintaining a constant liquid level in the reservoir, liquid flows through T at a constant rate. The rate of flow of the liquid is measured for different tubes T with the same length but of different radii r. The same liquid level is used in each experi ...
... Liquid flows through the horizontal tube T. By maintaining a constant liquid level in the reservoir, liquid flows through T at a constant rate. The rate of flow of the liquid is measured for different tubes T with the same length but of different radii r. The same liquid level is used in each experi ...
Physics and Chemistry 3º ESO Techniques to separate the
... apply the heat to the wine. After boiling begins, reduce the heat so the wine boils at a moderate rate. 5. Watch the temperature closely while distilling and collect the distillate coming from the condenser while the temperature is in the range 80-85ºC. The temperature should remain nearly constant ...
... apply the heat to the wine. After boiling begins, reduce the heat so the wine boils at a moderate rate. 5. Watch the temperature closely while distilling and collect the distillate coming from the condenser while the temperature is in the range 80-85ºC. The temperature should remain nearly constant ...
Document
... Volatile liquid is a liquid that can easily evaporate at one atmospheric pressure and room temperature ...
... Volatile liquid is a liquid that can easily evaporate at one atmospheric pressure and room temperature ...
A Liquid Nitrogen Immersion Cryostat for Optical
... vacuum, Cleartran10 (Janos Technology), broad-band anti-reflection coated Cleartran (Spectral Systems), and fused silica windows (CVI Laser Company) have all been used successfully, whereas calcium fluoride windows (Janos) tended to crack upon repeated cooling. The windows were installed in a unifor ...
... vacuum, Cleartran10 (Janos Technology), broad-band anti-reflection coated Cleartran (Spectral Systems), and fused silica windows (CVI Laser Company) have all been used successfully, whereas calcium fluoride windows (Janos) tended to crack upon repeated cooling. The windows were installed in a unifor ...
Lectures 5
... This is called Henderson Hasselbach equation [HA]T = unionized + ionized [HA]T = [HA] + [A-] in case of saturated solution [HA] = [HA]ss [HA]T = [HA]ss + [A-] [A-] = [HA]T - [HA]ss pHp = Pka + log ([HA]T - [HA]ss) / [HA]ss) ...
... This is called Henderson Hasselbach equation [HA]T = unionized + ionized [HA]T = [HA] + [A-] in case of saturated solution [HA] = [HA]ss [HA]T = [HA]ss + [A-] [A-] = [HA]T - [HA]ss pHp = Pka + log ([HA]T - [HA]ss) / [HA]ss) ...
Matter: properties and characteristics COPY
... 33. Which of the following are considered physical properties of a substance? a. color and odor b. melting and boiling points c. malleability and hardness d. all of the above 34. Which of the following substances is a mixture? a. table salt b. the air you breathe c. purified water d. sucr ...
... 33. Which of the following are considered physical properties of a substance? a. color and odor b. melting and boiling points c. malleability and hardness d. all of the above 34. Which of the following substances is a mixture? a. table salt b. the air you breathe c. purified water d. sucr ...
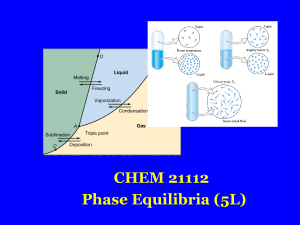
Solid - Liquid Phase Diagram of a Binary Mixture: The Question of
... When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the temperature rises quickly to the melting point and remains constant. The heat (enthalpy) released ...
... When a pure liquid is cooled, the temperature may drop below the melting point without the formation of crystals - a phenomenon known as “supercooling”. As soon as the first crystals form, however, the temperature rises quickly to the melting point and remains constant. The heat (enthalpy) released ...
Expt. 5: Binary Phase Diagram CHEM 366 V-1 Binary Solid
... may behave more or less independent of each other but merely diluted, i.e., an ideal solution or mixture, or there may be substantial chemical interaction or complex formation between the constituents. The study of such mixtures can lead to an understanding of the most fundamental intermolecular int ...
... may behave more or less independent of each other but merely diluted, i.e., an ideal solution or mixture, or there may be substantial chemical interaction or complex formation between the constituents. The study of such mixtures can lead to an understanding of the most fundamental intermolecular int ...
CLASSIFICATION OF MATTER
... Separation of the components of homogeneous mixtures (III) Chromatography Chromatography is a separation method based on the distribution of the components of a mixture between two phases: a medium or support (stationary phase), and a solvent or eluant (mobile phase) that passes through the stationa ...
... Separation of the components of homogeneous mixtures (III) Chromatography Chromatography is a separation method based on the distribution of the components of a mixture between two phases: a medium or support (stationary phase), and a solvent or eluant (mobile phase) that passes through the stationa ...
2. Electrical forces in the bulk: Injection, Conduction and Induction
... from the thickness of the heterocharge layer as compared to the Debye length. If the conductivity is high, both layers (diffuse and heterocharge layers) can have similar thicknesses. In this case, the diffusion processes are not negligible and the approximations are not applicable. For conductivitie ...
... from the thickness of the heterocharge layer as compared to the Debye length. If the conductivity is high, both layers (diffuse and heterocharge layers) can have similar thicknesses. In this case, the diffusion processes are not negligible and the approximations are not applicable. For conductivitie ...
Experiment 4 Separation of a Mixture
... techniques and the above table, after which time you will be asked to design a flow chart that will be used to separate the different components of an unknown mixture. Your flow chart will be rather general to begin with since the detailed steps of the separation techniques are, as of yet, unknown t ...
... techniques and the above table, after which time you will be asked to design a flow chart that will be used to separate the different components of an unknown mixture. Your flow chart will be rather general to begin with since the detailed steps of the separation techniques are, as of yet, unknown t ...
Chemistry Learning Goals Chap 14 Solutions Minniear
... hydration, diffusion). SWBAT discuss the factors that determine the rate of solution for a solid solute and a liquid solvent (agitation, temperature and surface area). SWBAT explain the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas. SWBAT explain the processes involved when a solution has reached ...
... hydration, diffusion). SWBAT discuss the factors that determine the rate of solution for a solid solute and a liquid solvent (agitation, temperature and surface area). SWBAT explain the effect of temperature on the solubility of a gas. SWBAT explain the processes involved when a solution has reached ...
World of matter - Kindle Education
... There is very little empty space between particles in a solid. ...
... There is very little empty space between particles in a solid. ...
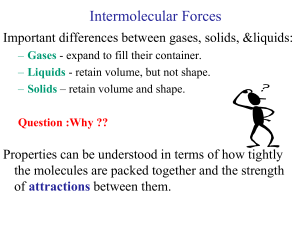
Chapter 12: Intermolecular Attractions and the Properties of Liquids
... Strength of London forces depends on three factors: a. Polarizability is a measure of the ease with which the electron cloud on a particle is distorted. It tends to increase as the electron cloud volume increases. b. Number of atoms in the molecule ...
... Strength of London forces depends on three factors: a. Polarizability is a measure of the ease with which the electron cloud on a particle is distorted. It tends to increase as the electron cloud volume increases. b. Number of atoms in the molecule ...
Latent Heat of Vaporization and Speci c Heat - Physlab
... Liquid nitrogen is a colorless, odorless and tasteless uid which boils at 77 K, and is formed by cooling and increasing pressure on air which is predominantly N2 . On evaporation, it generates enormous pressure and direct contact with liquid nitrogen can cause cold burns or frost bites. Liquid nitr ...
... Liquid nitrogen is a colorless, odorless and tasteless uid which boils at 77 K, and is formed by cooling and increasing pressure on air which is predominantly N2 . On evaporation, it generates enormous pressure and direct contact with liquid nitrogen can cause cold burns or frost bites. Liquid nitr ...
0922085
... 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air ...
... 11% (by volume). What would the properties of a mixture of 0.1% (by volume) of aniline and 99.9% (by volume) of air ...
MP 2 workbook 2016
... Matter typically exists in one of three states: solid , liquid , or gas . The state a given substance exhibits is also a physical property. Some substances exist as gases at room temperature (oxygen and carbon dioxide), while others, like water and mercury metal, exist as liquids. Most metals exist ...
... Matter typically exists in one of three states: solid , liquid , or gas . The state a given substance exhibits is also a physical property. Some substances exist as gases at room temperature (oxygen and carbon dioxide), while others, like water and mercury metal, exist as liquids. Most metals exist ...
chapter 3
... is long (a.c), then this force drives the particles towards the area of maximum stress. If the number of particles is large, they become aligned due to these forces, and thus form a stable chain bridging the electrode gap causing a breakdown between the electrodes. If there is only a single conducti ...
... is long (a.c), then this force drives the particles towards the area of maximum stress. If the number of particles is large, they become aligned due to these forces, and thus form a stable chain bridging the electrode gap causing a breakdown between the electrodes. If there is only a single conducti ...
The Functional Form of the Internal Energy
... is usually much greater than the external pressure (usually around atmospheric). For common liquids Pint is around 3000 atm. Liquids, in effect, are held together by their internal pressure, that is, by their intermolecular attraction." (A Textbook of Physical Chemistry, Arthur W. Adamson) Some typi ...
... is usually much greater than the external pressure (usually around atmospheric). For common liquids Pint is around 3000 atm. Liquids, in effect, are held together by their internal pressure, that is, by their intermolecular attraction." (A Textbook of Physical Chemistry, Arthur W. Adamson) Some typi ...
SOLUBILITY OF GASES AT 25 C AND HIGH PRESSURES: THE
... As we expected, the curvature rises with increasing the reduced temperature, but presents a maximum in the vicinity of Boyle point [11, 12]. Literature data indicate [13, 14] that equation of regular solutions is valid only for nonpolar systems, therefore it can’t be directly used for correlation so ...
... As we expected, the curvature rises with increasing the reduced temperature, but presents a maximum in the vicinity of Boyle point [11, 12]. Literature data indicate [13, 14] that equation of regular solutions is valid only for nonpolar systems, therefore it can’t be directly used for correlation so ...
Liquid

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Water is, by far, the most common liquid on Earth. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena.The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matter. On the other hand, as liquids and gases share the ability to flow, they are both called fluids. Although liquid water is abundant on Earth, this state of matter is actually the least common in the known universe, because liquids require a relatively narrow temperature/pressure range to exist. Most known matter in the universe is in gaseous form (with traces of detectable solid matter) as interstellar clouds or in plasma form within stars.