Physical and Chemical Properties
... the liquid form. • Basically the range at which the solid changes its state •The melting point of into a liquid. water is 0 degrees ...
... the liquid form. • Basically the range at which the solid changes its state •The melting point of into a liquid. water is 0 degrees ...
Change of state - Mrs. Coyle`s College Chemistry
... Molar heats of fusion are generally much smaller than molar heats of vaporization (liquid molecules are packed closer together and more energy need to rearrange from a solid to liquid) ...
... Molar heats of fusion are generally much smaller than molar heats of vaporization (liquid molecules are packed closer together and more energy need to rearrange from a solid to liquid) ...
11/16/2016- Matter Notes
... Matter is either a pure substance or a mixture of substances Substance -matter with a fixed composition Heterogeneous Mixture -where different materials remain distinct in a mixture EX. Like a salad, each part is itself but as a whole it is a salad Homogeneous Mixture - a mixture that remains consta ...
... Matter is either a pure substance or a mixture of substances Substance -matter with a fixed composition Heterogeneous Mixture -where different materials remain distinct in a mixture EX. Like a salad, each part is itself but as a whole it is a salad Homogeneous Mixture - a mixture that remains consta ...
Print Activity - Let`s Talk Science
... they do in a normal solid. This makes the goop feel and act as a solid. When the pressure is released the molecules form the random arrangement of a liquid and the goop suddenly flows. Why does it matter? All fluids have a measurable viscosity. Viscosity is the thickness or resistance to flow of a l ...
... they do in a normal solid. This makes the goop feel and act as a solid. When the pressure is released the molecules form the random arrangement of a liquid and the goop suddenly flows. Why does it matter? All fluids have a measurable viscosity. Viscosity is the thickness or resistance to flow of a l ...
Chapter 3 PowerPoint Notes
... • Liquids take the shape of the container because particles in a liquid can flow to new locations. The volume of a liquid is constant because the force of attraction keep the particles close together. • Solids have a definite volume and shape because particles in a solid vibrate around a fixed point ...
... • Liquids take the shape of the container because particles in a liquid can flow to new locations. The volume of a liquid is constant because the force of attraction keep the particles close together. • Solids have a definite volume and shape because particles in a solid vibrate around a fixed point ...
Science 9
... 2. Provide a discussion for your observations (e.g., why did it occur?) 3. Identify a PHYSICAL or CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Experiment #2 will take a few days. Make sure you observe your cup in two days. ...
... 2. Provide a discussion for your observations (e.g., why did it occur?) 3. Identify a PHYSICAL or CHEMICAL CHANGE NOTE: Experiment #2 will take a few days. Make sure you observe your cup in two days. ...
ln2_storage_pre
... the critical temperature for both fluids, so you will not get a liquid no matter how much pressure you put on it. The gases in the cylinders are supercritical fluids, though when you get that far above the critical temperature their behavior is much like that of a normal gas unless you get to very h ...
... the critical temperature for both fluids, so you will not get a liquid no matter how much pressure you put on it. The gases in the cylinders are supercritical fluids, though when you get that far above the critical temperature their behavior is much like that of a normal gas unless you get to very h ...
Spring Benchmark Exam
... until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best describes what happened? A As the solution cooled, evapor ...
... until no more KCl would dissolve. She then capped the clear solution and set it aside on the lab bench. After several hours she noticed the solution had become cloudy and some solid had settled to the bottom of the flask. Which statement best describes what happened? A As the solution cooled, evapor ...
practice test2(Answers)
... C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
Vapor Pressure of a Pure Liquid
... and enter the gas phase until the pressure of the vapor in the bulb reaches a definite value which is determined by the nature of the liquid and its temperature. This is called the vapor pressure of the liquid. In this experiment, the variation of vapor pressure with temperature will be measured and ...
... and enter the gas phase until the pressure of the vapor in the bulb reaches a definite value which is determined by the nature of the liquid and its temperature. This is called the vapor pressure of the liquid. In this experiment, the variation of vapor pressure with temperature will be measured and ...
Chapter 9 Outline
... Colloidal dispersion – a homogeneous mixture that is not a true solution, contain relatively large solute particles. Colloids – large particles that don’t disperse completely in a solution ...
... Colloidal dispersion – a homogeneous mixture that is not a true solution, contain relatively large solute particles. Colloids – large particles that don’t disperse completely in a solution ...
9/21 properties of matter ppt
... distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost completely evaporated the liquid with the next lowest b ...
... distilled first. This liquid turns into a vapor (gas) and flows out the distillation flask. As it enters the condensing tube, it is cooled and condenses back into a liquid. It is then collected in a graduated cylinder. When the liquid is almost completely evaporated the liquid with the next lowest b ...
GENERAL CONSIDERATIONS TO HYDROTHERAPY
... • Water exerts a perpendicular pressure against the surface of the body. • This hydrostatic pressure is the ratio of the magnitude of the force exerted by the fluid per body surface area. • This pressure is dependent on the depth of the submerged part and the density of the liquid. • Hydrostatic pre ...
... • Water exerts a perpendicular pressure against the surface of the body. • This hydrostatic pressure is the ratio of the magnitude of the force exerted by the fluid per body surface area. • This pressure is dependent on the depth of the submerged part and the density of the liquid. • Hydrostatic pre ...
Lecture 35 (Slides) November 7
... • The normal boiling point of water is 100 oC. At this temperature the vapor pressure of water is exactly 760mm Hg (the normal average atmospheric pressure at sea level). If we heat water in a sealed container all of the steam that is formed is trapped above the liquid water. The additional steam fo ...
... • The normal boiling point of water is 100 oC. At this temperature the vapor pressure of water is exactly 760mm Hg (the normal average atmospheric pressure at sea level). If we heat water in a sealed container all of the steam that is formed is trapped above the liquid water. The additional steam fo ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... d. Not enough information e. Mixture of all three states 17. Which of the following is a physical change? a. Nitrogen gas s cooled until it becomes a liquid b. H2 and O2 combine to form H2O2 c. Grape juice is fermented to produce wine d. Natural gas is burned to produce energy e. Mercuric oxide is h ...
... d. Not enough information e. Mixture of all three states 17. Which of the following is a physical change? a. Nitrogen gas s cooled until it becomes a liquid b. H2 and O2 combine to form H2O2 c. Grape juice is fermented to produce wine d. Natural gas is burned to produce energy e. Mercuric oxide is h ...
practice test2
... C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
... C) The temperature of liquid water increases linearly as it is heated D) The temperature of liquid water remains at 100°C as it boils E) Both liquid water and ice are present at 0°C. ...
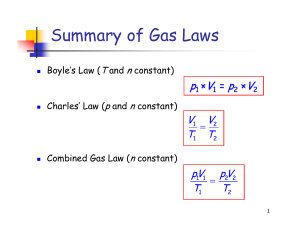
Summary of Gas Laws
... In every sample of liquid there is some fraction of molecules that possess enough kinetic energy to break away into a gas phase This process is called evaporation Therefore, some part of a liquid substance is always present in form of vapor (gas phase) over the surface of the liquid Gas phase molecu ...
... In every sample of liquid there is some fraction of molecules that possess enough kinetic energy to break away into a gas phase This process is called evaporation Therefore, some part of a liquid substance is always present in form of vapor (gas phase) over the surface of the liquid Gas phase molecu ...
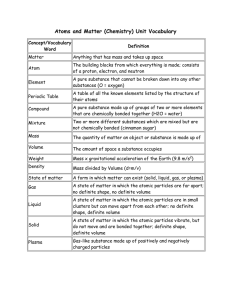
File
... A pure substance made up of groups of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together (H2O = water) ...
... A pure substance made up of groups of two or more elements that are chemically bonded together (H2O = water) ...
Pre-AP Chemistry Kinetic Theory and Heat Quiz
... predictable pattern of boiling point temperatures? (i.e. ionic higher than polar covalent, which is higher than nonpolar covalent) because of the intermolecular forces that hold them together - the stronger the intermolecular force the more energy it takes to separate the molecules to form a gas How ...
... predictable pattern of boiling point temperatures? (i.e. ionic higher than polar covalent, which is higher than nonpolar covalent) because of the intermolecular forces that hold them together - the stronger the intermolecular force the more energy it takes to separate the molecules to form a gas How ...
Word
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
... b. Water boils above 100 0C at higher pressures c. Water boils below 100 0C at lower pressures C. Condensation 1. The conversion of a gas to a liquid by the removal of energy IV. Freezing and Melting A. Freezing Point 1. The temperature at which the solid and liquid are in equilibrium at 1 atm 2. Fo ...
Honors Chemistry Review Packet KEY
... 35. In a physical change, the chemical composition of the substance does not change. In a chemical change, the chemical composition of the reactant(s) changes to form one or more products. 36. a) physical, b) physical, c) chemical, d) chemical 38. 43.2 grams (4.8 g hydrogen + 38.4 g oxygen = 43.2 g ...
... 35. In a physical change, the chemical composition of the substance does not change. In a chemical change, the chemical composition of the reactant(s) changes to form one or more products. 36. a) physical, b) physical, c) chemical, d) chemical 38. 43.2 grams (4.8 g hydrogen + 38.4 g oxygen = 43.2 g ...
Liquid

A liquid is a nearly incompressible fluid that conforms to the shape of its container but retains a (nearly) constant volume independent of pressure. As such, it is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, gas, and plasma), and is the only state with a definite volume but no fixed shape. A liquid is made up of tiny vibrating particles of matter, such as atoms, held together by intermolecular bonds. Water is, by far, the most common liquid on Earth. Like a gas, a liquid is able to flow and take the shape of a container. Most liquids resist compression, although others can be compressed. Unlike a gas, a liquid does not disperse to fill every space of a container, and maintains a fairly constant density. A distinctive property of the liquid state is surface tension, leading to wetting phenomena.The density of a liquid is usually close to that of a solid, and much higher than in a gas. Therefore, liquid and solid are both termed condensed matter. On the other hand, as liquids and gases share the ability to flow, they are both called fluids. Although liquid water is abundant on Earth, this state of matter is actually the least common in the known universe, because liquids require a relatively narrow temperature/pressure range to exist. Most known matter in the universe is in gaseous form (with traces of detectable solid matter) as interstellar clouds or in plasma form within stars.